Kanker: Konsep Dasar | Ilmu Biomedik Dasar | Brainy Panda
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the cellular processes that lead to cancer, beginning with the normal functioning of cells, including growth, division, and contact inhibition. It highlights how mutations in DNA, often caused by external factors like carcinogens, can disrupt these processes. The video discusses the differences between benign and malignant tumors, with malignant tumors being invasive, poorly differentiated, and capable of metastasis. It also touches on why cancer is so hard to treat, due to the rapid mutation of cancer cells and their spread throughout the body, making it difficult to target with one type of treatment.
Takeaways
- 😀 Cells grow, divide, and undergo mitosis as part of their daily processes, but they stop growing when they reach contact inhibition to prevent overcrowding.
- 😀 Contact inhibition is a mechanism that halts cell division once cells touch each other, helping to prevent cancer or tumor formation.
- 😀 DNA is a vulnerable component within cells, and when damaged or mutated during mitosis or due to external factors (carcinogens), it can lead to cancer.
- 😀 Mutations in DNA can sometimes cause the process of apoptosis (cell death) to be delayed or inhibited, leading to uncontrolled cell growth.
- 😀 Genetic changes may cause cells to lose contact inhibition and divide uncontrollably, resulting in abnormal clusters of cells known as neoplasms or tumors.
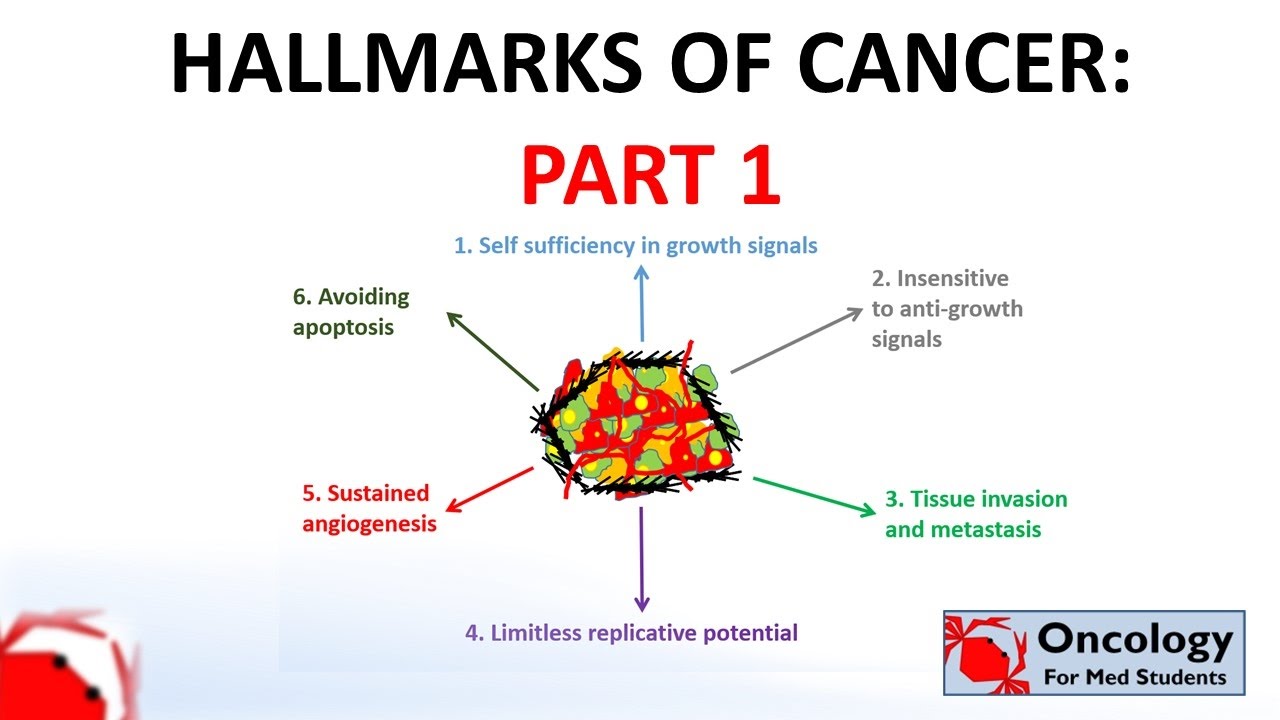
- 😀 Benign tumors (non-cancerous) are defined by slow growth, clear boundaries, and little to no damage to surrounding cells.
- 😀 Malignant tumors (cancerous) grow rapidly, invade nearby tissues, and spread through metastasis, making them dangerous.
- 😀 Malignant tumors are typically poorly differentiated, meaning their structure and function differ significantly from normal cells, unlike benign tumors that resemble normal cells.
- 😀 Cancer cells have the ability to spread through blood vessels and invade other organs, which is called metastasis, making cancer challenging to treat.
- 😀 Cancer is difficult to cure because it consists of cells with varying DNA mutations, making it hard for a single treatment to target all tumor cells effectively.
Q & A
What is contact inhibition, and why is it important in preventing cancer?
-Contact inhibition is a process where cells stop growing and dividing when they come into contact with neighboring cells. It is crucial in preventing cancer because it regulates normal cell growth and prevents cells from proliferating uncontrollably, which can lead to tumor formation.
What happens when a cell's DNA is damaged or mutated?
-When a cell's DNA is damaged, such as through exposure to carcinogens or aging, it may undergo mutations. These mutations can disrupt normal cell function, leading to uncontrolled growth. In some cases, the cell will try to repair itself, but if the mutations persist, it can result in the formation of abnormal cells or tumors.
What is apoptosis, and how does it relate to cancer prevention?
-Apoptosis is a form of programmed cell death where damaged or mutated cells self-destruct. This process helps prevent cancer by eliminating cells that may pose a risk of developing into tumors. However, in some cases, mutations can prevent apoptosis, allowing abnormal cells to survive and proliferate.
What distinguishes a benign tumor from a malignant tumor?
-A benign tumor is a non-cancerous growth that does not spread to other parts of the body. It grows slowly and has clear boundaries. In contrast, a malignant tumor (cancer) is invasive, spreads to other tissues (metastasis), and has an irregular shape. Malignant tumors are more dangerous and harder to treat.
How does metastasis contribute to the spread of cancer?
-Metastasis is the process by which cancer cells spread from the primary tumor to other parts of the body through the bloodstream. This enables the cancer to form secondary tumors in distant organs, complicating treatment and increasing the severity of the disease.
What is the significance of 'well-differentiated' cells in a benign tumor?
-In a benign tumor, the cells are 'well-differentiated,' meaning their structure and function closely resemble normal cells. This is why benign tumors generally do not invade surrounding tissues and are less dangerous compared to malignant tumors, where the cells are poorly differentiated and behave abnormally.
Why are malignant tumors difficult to treat surgically?
-Malignant tumors are challenging to treat surgically because they lack clear boundaries and may invade surrounding tissues. Additionally, they can metastasize to other parts of the body, making it difficult to remove all cancerous cells in one procedure. Unlike benign tumors, malignant tumors cannot always be completely excised.
What role does DNA mutation play in the formation of cancer?
-DNA mutation plays a central role in the development of cancer. Mutations in genes that control cell growth, division, and death can lead to uncontrolled cell proliferation, forming tumors. These mutations can accumulate over time, especially in the presence of carcinogens or aging, leading to the progression of cancer.
Why is cancer so difficult to cure?
-Cancer is difficult to cure because it involves many different mutations across a large number of cells, each potentially requiring different treatments. As cancer cells divide and spread, new mutations can emerge, making it harder to target them with a single treatment. Additionally, cancer cells can spread to multiple locations in the body, complicating treatment efforts.
What is the significance of the lack of a capsule in malignant tumors?
-The lack of a capsule in malignant tumors is significant because it allows the tumor to invade surrounding tissues and spread to other parts of the body. This invasiveness makes malignant tumors more dangerous and harder to treat compared to benign tumors, which are usually encapsulated and confined to one area.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)