5. Hallmarks of cancer (part 2)
Summary
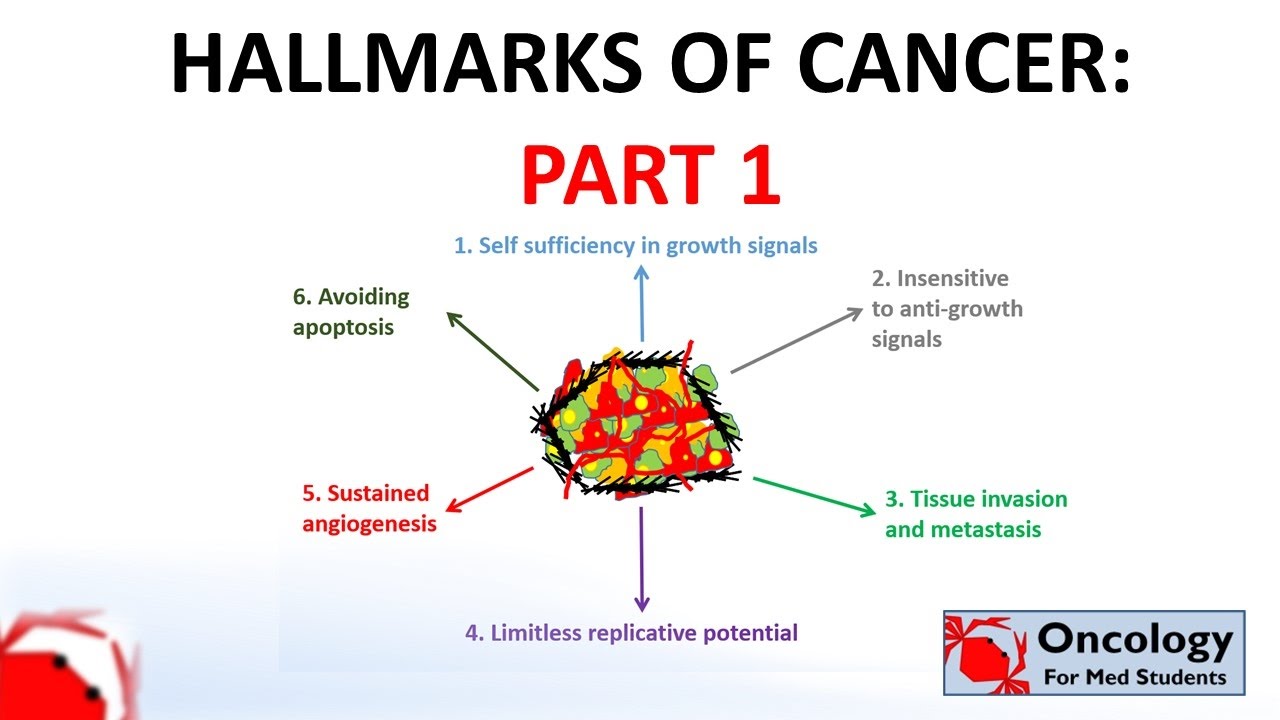
TLDRThis video explores the six hallmarks of cancer, crucial traits that enable cancer cells to thrive. It covers self-sufficiency in growth signals, insensitivity to anti-growth signals, tissue invasion and metastasis, unlimited division potential, angiogenesis (blood vessel growth), and the avoidance of apoptosis (programmed cell death). The script delves into how cancer cells bypass normal processes to grow uncontrollably, spread to other organs, maintain their division, form their own blood supply, and evade self-destruction, ultimately making cancer a challenging disease to treat. The video also highlights the importance of telomerase and the protein p53 in cancer progression.
Takeaways
- 😀 Cancer cells exhibit self-sufficiency in growth signals, meaning they can continuously stimulate their own growth without relying on external factors.
- 😀 Cancer cells are insensitive to anti-growth signals, allowing them to ignore signals that would typically stop their proliferation.
- 😀 Tissue invasion and metastasis are crucial hallmarks, enabling cancer cells to invade surrounding tissues and spread to other organs.
- 😀 The extracellular matrix plays a key role in the cancer cell's ability to break away and travel to distant parts of the body.
- 😀 Metastasis is a complex, non-random process involving the interaction of various proteins and gene mutations.
- 😀 Cancer cells bypass the Hayflick limit (the normal limit on cell divisions) by activating telomerase, which keeps their telomeres intact and allows unlimited division.
- 😀 Telomeres protect the ends of chromosomes from damage, and without telomerase, they would shrink with each cell division, leading to DNA loss and cell death.
- 😀 Angiogenesis is the process by which tumors stimulate the formation of new blood vessels to supply nutrients to growing cancerous tissues.
- 😀 In adults, angiogenesis mainly occurs during wound healing, but cancerous tumors exploit this process to maintain their growth beyond 1 millimeter in size.
- 😀 Apoptosis is the programmed cell death mechanism that protects the body from damaged cells, but cancer cells avoid this process by mutating genes like p53, which is essential for initiating cell death in the presence of DNA damage.
Q & A
What are the hallmarks of cancer?
-The hallmarks of cancer are a set of traits that cancer cells need to acquire to become cancerous. These include self-sufficiency in growth signals, insensitivity to anti-growth signals, tissue invasion and metastasis, unlimited potential to divide, angiogenesis, and avoiding apoptosis.
What is tissue invasion and metastasis in cancer?
-Tissue invasion and metastasis refer to the ability of cancer cells to invade surrounding tissues and spread to other parts of the body through the bloodstream or lymphatic system. This process helps the tumor find areas with more nutrients to sustain its growth.
How does the extracellular matrix relate to cancer metastasis?
-The extracellular matrix is a structure surrounding cells that provides support for tissues. Cancer cells need to break away from the extracellular matrix to invade other tissues and spread to distant organs. Mutations in genes that code for proteins in the extracellular matrix facilitate this process.
What is the Hayflick limit?
-The Hayflick limit refers to the maximum number of times a normal cell can divide, typically between 40 to 60 divisions. This limitation occurs due to the gradual loss of DNA sequences during cell division.
How do cancer cells bypass the Hayflick limit?
-Cancer cells bypass the Hayflick limit by activating an enzyme called telomerase, which adds DNA bases to the telomeres, thus preventing the loss of crucial genetic information and allowing the cell to keep dividing.
What is the role of telomeres in cell division?
-Telomeres are protective caps at the ends of chromosomes that prevent the loss of important DNA sequences during cell division. Over time, telomeres shorten, which limits the number of times a cell can divide. In cancer cells, telomerase extends the telomeres to enable continued division.
What is angiogenesis and why is it important in cancer?
-Angiogenesis is the process of forming new blood vessels to supply growing tissues with nutrients. Cancer cells stimulate angiogenesis to create a blood supply for themselves, which is necessary for their growth beyond a size of 1 millimeter.
How do cancer cells avoid apoptosis?
-Cancer cells avoid apoptosis (programmed cell death) by evading signals that would normally trigger cell death, such as DNA damage or nutrient deprivation. This allows the cancer cells to continue dividing despite having damaged or unstable DNA.
What is the role of the p53 protein in apoptosis?
-The p53 protein, known as the 'guardian of the genome,' plays a critical role in activating apoptosis in cells with damaged DNA. It helps prevent the replication of defective cells, but cancer cells often mutate the p53 gene to avoid this safeguard.
Why is metastasis considered the most important factor in cancer prognosis?
-Metastasis is the process by which cancer spreads to other parts of the body. Whether or not a tumor has metastasized is the most significant factor in determining if cancer is treatable or curable, as metastasized cancers are much harder to manage.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)