🔴 Carbs Are Killing You! | Dr. Rob Cywes
Summary
TLDRIn this insightful discussion, the complexities of lipid metabolism, especially LDL and VLDL, are explored in depth. The conversation touches on how these lipoproteins impact fat storage and energy use, as well as the challenges posed by high-protein, low-fat carnivore diets. The speaker emphasizes the importance of understanding fat metabolism, the role of insulin in fat storage, and the evolutionary context of human diets. Practical advice is shared, including a fat-dominant diet and the need for critical thinking in nutrition and health. Ultimately, the video highlights the need to rethink conventional dietary wisdom and consider alternative approaches.
Takeaways
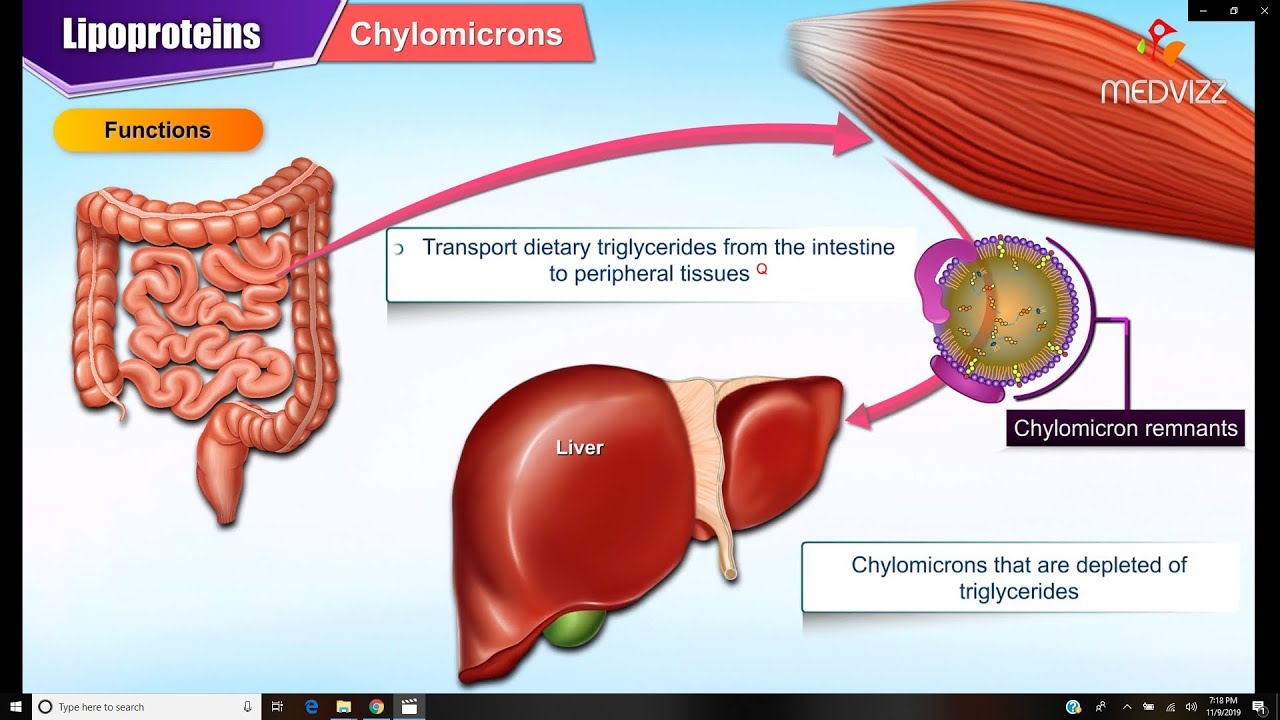
- 😀 VLDL (Very Low-Density Lipoprotein) is crucial for transporting triglycerides from the liver to fat cells, and LDL is a byproduct of VLDL metabolism.
- 😀 The size and density of LDL can vary depending on whether VLDL is dominant or not, which affects lipid metabolism and cholesterol profiles.
- 😀 Excess protein consumption in carnivore diets may cause the body to convert protein to sugar or fat for storage, leading to metabolic challenges.
- 😀 Fat has been wrongly vilified in modern dietary discussions, but it is essential for bodily functions, and without it, we cannot survive.
- 😀 The body has a limited capacity to absorb fat, relying on bile to help with the digestion and absorption process.
- 😀 Insulin resistance can cause paradoxical hypoglycemia, where high blood sugar coexists with low cellular energy due to impaired glucose uptake.
- 😀 In individuals with high protein intake, such as those on a carnivore diet, there is a risk of inadequate fat consumption, which may affect metabolism.
- 😀 Fat is necessary for the body’s energy balance, and a fat-dominant diet may be more evolutionarily aligned with our natural nutrition needs.
- 😀 Historical diets, such as those of hunter-gatherers, may have included lean meat, but fat from the gut was often consumed for its nutrients.
- 😀 The importance of thinking critically about diet and metabolic processes is emphasized, encouraging open-mindedness and scientific inquiry in health discussions.
Q & A
What is the role of VLDL in lipid metabolism?
-VLDL (Very Low-Density Lipoprotein) is produced by the liver to transport triglycerides and cholesterol to fat cells. Once VLDL delivers its triglycerides to fat cells, it becomes LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein), which can either be large and fluffy or small and dense depending on lipid traffic.
How does LDL relate to VLDL?
-LDL is a byproduct of VLDL. When VLDL delivers triglycerides to fat cells, it breaks off and forms LDL. The characteristics of LDL (whether it’s large and fluffy or small and dense) depend on the amount and type of VLDL in circulation.
What is the relationship between insulin and fat storage?
-When insulin levels are elevated, fat utilization is blocked, leading to fat storage. However, when insulin levels are very low, fat is released from fat cells for energy use. This paradox occurs when trying to handle a large meal while releasing fat from fat cells.
What is insulin resistance, and how does it affect metabolism?
-Insulin resistance occurs when the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin, making it difficult for sugar to enter cells. This results in high blood sugar levels, prompting the liver to release more sugar into the bloodstream, even in the absence of hypoglycemia.
What is paradoxical hypoglycemia?
-Paradoxical hypoglycemia occurs in insulin-resistant patients when both glucagon and insulin are elevated, leading to high blood sugar levels while the cells are energy-deprived. This condition is characterized by an apparent hypoglycemic state despite elevated glucose levels.
How does the carnivore diet impact lipid metabolism?
-On a carnivore diet, the excess protein consumed can be converted into sugar and fat for storage, as there is no dedicated storage system for protein. This can potentially affect lipid metabolism by increasing fat storage, though the long-term effects remain uncertain.
What is the significance of fat in human nutrition?
-Fat is essential for survival as it provides energy and is necessary for various bodily functions, including hormone production and cell membrane integrity. Despite being vilified, fat is critical to health, while protein and carbohydrates are less essential for survival.
Why might some people on the carnivore diet struggle with fat metabolism?
-People on the carnivore diet may struggle with fat metabolism due to an imbalance in their fat-to-protein ratio. Excess protein can be converted into sugar or fat, potentially leading to higher fat storage. A higher fat-to-protein ratio might be more beneficial for fat utilization.
What is the difference between farm-raised and wild game meat in terms of fat content?
-Wild game meat, such as deer, tends to be lean, with most of the fat stored viscerally. In contrast, farm-raised meat, including grass-fed beef, often has higher fat content, making it richer in fat compared to wild game.
How does the intake of carbohydrates affect fat storage and utilization?
-Carbohydrates influence fat storage through insulin. When insulin levels are slightly elevated, fat utilization is blocked, leading to fat storage. By consuming fewer carbohydrates, insulin levels can remain low, promoting fat release from fat cells and energy utilization.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

22: VLDL, LDL Metabolism | Lipid metabolism | Biochemistry | N'JOY Biochemistry

LIPOPROTEÍNAS - QUILOMÍCRONS, VLDL, LDL E HDL

Kimia Klinik: Analisis Lipid dan Lipoprotein

Konsep Dasar Lipid(Lemak) : Kolesterol, Trigliserida, Fosfolipid
Lipoproteins and Apolipoproteins - Structure , function and metabolism : Medical Biochemistry

Lipids and Lipoproteins - Part 3 (Endogenous Pathway)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)