22: VLDL, LDL Metabolism | Lipid metabolism | Biochemistry | N'JOY Biochemistry
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the intricate metabolism of Very Low-Density Lipoproteins (VLDL) and its vital role in cholesterol transport and health. It explores how VLDL, produced in the liver, carries cholesterol and fatty acids to various tissues, and its eventual transformation into LDL, the 'bad cholesterol'. The script also covers the importance of cholesterol in bodily functions, the impact of imbalanced cholesterol levels on cardiovascular health, and the genetic factors influencing lipid metabolism. Additionally, it discusses potential therapeutic approaches for managing cholesterol-related diseases, underscoring the need for balance between HDL and LDL for optimal health.
Takeaways
- 😀 VLDL (Very Low-Density Lipoprotein) is synthesized in the liver and plays a critical role in lipid metabolism, transporting cholesterol and triglycerides to various tissues.
- 😀 The metabolism of VLDL is crucial for managing cholesterol levels in the body and involves its transformation into IDL (Intermediate-Density Lipoprotein) and LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein).
- 😀 Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is rich in cholesterol esters and is involved in transporting cholesterol from the liver to peripheral tissues, a process that can contribute to atherosclerosis if not properly regulated.
- 😀 VLDL is initially formed in the liver and, as it circulates, it gets modified to become IDL and eventually LDL, which plays a role in fat deposition and energy usage in tissues.
- 😀 The role of LDL in the body includes carrying cholesterol for cellular functions, but an excess of LDL can lead to plaque buildup in arteries, causing cardiovascular diseases.
- 😀 Research suggests that the interaction of lipoproteins with cell receptors plays a significant role in regulating cholesterol levels and maintaining homeostasis.
- 😀 The process of converting VLDL into IDL and LDL is essential for providing energy to muscles and tissues by transferring fatty acids and glycerol for oxidation.
- 😀 Cholesterol is required for various bodily functions, including the synthesis of vitamin D and hormones like those produced by the adrenal glands.
- 😀 Familial hypercholesterolemia is a genetic condition resulting in high cholesterol levels due to defective LDL receptors, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- 😀 Proper regulation of lipoproteins in the blood is critical to avoid disorders such as coronary heart disease, which is linked to excessive cholesterol deposition in arteries.
Q & A
What is the role of VLDL (Very Low-Density Lipoprotein) in metabolism?
-VLDL is synthesized in the liver and carries cholesterol and triglycerides from the liver to various tissues in the body. It plays a crucial role in lipid metabolism by transporting these fats for energy production and storage.
How does VLDL contribute to cholesterol storage in the liver?
-VLDL is rich in cholesterol esters and is involved in the transport of cholesterol from the liver to peripheral tissues. When it undergoes metabolism, it forms LDL, which further helps in the distribution and storage of cholesterol in the body.
What is the connection between VLDL and stress relief in the liver?
-VLDL is associated with transporting lipids that help reduce oxidative stress in the liver. By carrying fats like cholesterol and fatty acids, it supports liver function and protects it from stress-related damage.
What happens when VLDL levels are reduced in the circulation?
-When VLDL levels are reduced, it decreases the transport of cholesterol and triglycerides to tissues, which can affect lipid metabolism and potentially lead to metabolic disorders or other cardiovascular issues.
How does the body utilize fatty acids from VLDL for energy?
-Fatty acids from VLDL are taken up by muscle tissues and oxidized to produce energy. This process is essential during periods of high energy demand, such as exercise or fasting.
What is the role of HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein) in cholesterol metabolism?
-HDL is responsible for reverse cholesterol transport, where it collects excess cholesterol from tissues and returns it to the liver for processing or excretion. This process helps maintain healthy cholesterol levels and prevents atherosclerosis.
How do LDL receptors contribute to lipid metabolism?
-LDL receptors on cell surfaces bind to LDL particles, allowing them to be taken up into cells for the delivery of cholesterol. This process is essential for maintaining proper cholesterol levels and cell function.
What is familial hypercholesterolemia, and how is it related to lipoprotein metabolism?
-Familial hypercholesterolemia is a genetic disorder where mutations in LDL receptors result in high cholesterol levels. This leads to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, as LDL cholesterol cannot be effectively cleared from the bloodstream.
What is the significance of intermediate-density lipoproteins (IDL) in metabolism?
-Intermediate-density lipoproteins (IDL) are formed when VLDL loses its triglycerides. They are precursors to LDL and play an intermediate role in the transport and redistribution of lipids, contributing to the balance of cholesterol and fatty acids in circulation.
How does insulin affect the activity of lipoproteins in the body?
-Insulin activates lipoprotein lipase, which helps break down triglycerides in lipoproteins like VLDL. This activity facilitates the delivery of fatty acids to tissues and influences overall lipid metabolism, particularly in the context of energy storage and usage.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

LIPOPROTEÍNAS - QUILOMÍCRONS, VLDL, LDL E HDL
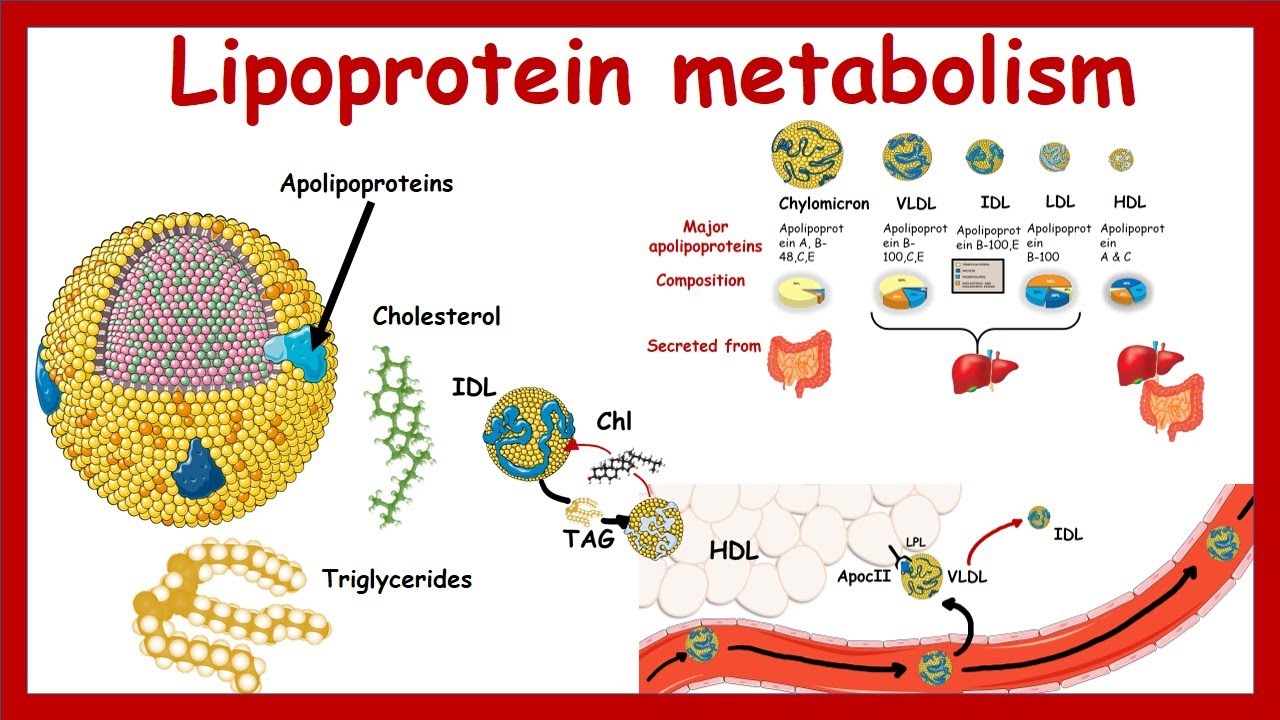
Lipoprotein metabolism and transport | Chylomicron, VLDL,IDL, LDL,HDL | Metabolism | Biochemistry
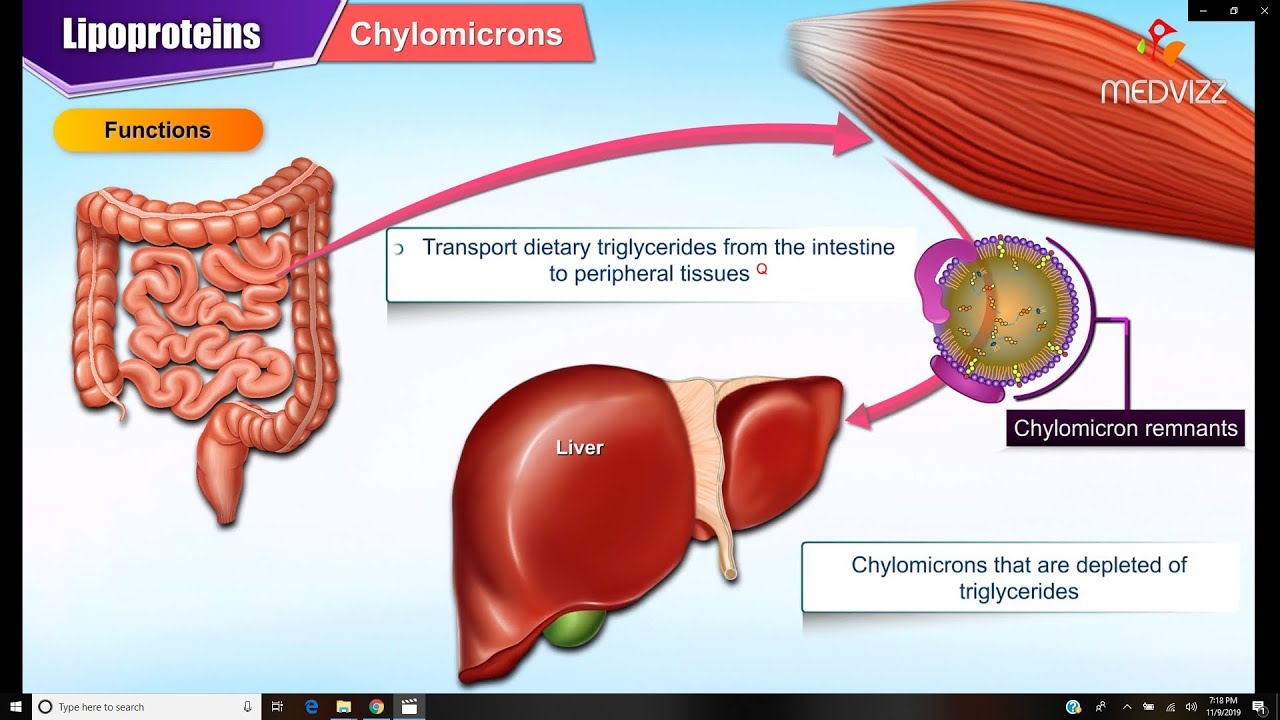
Lipoproteins and Apolipoproteins - Structure , function and metabolism : Medical Biochemistry

Lipids Part 1

Tiga Jalur Metabolisme Lipid dalam Tubuh

Konsep Dasar Lipid(Lemak) : Kolesterol, Trigliserida, Fosfolipid
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)