Apa Itu Data, Basis Data dan DBMS
Summary
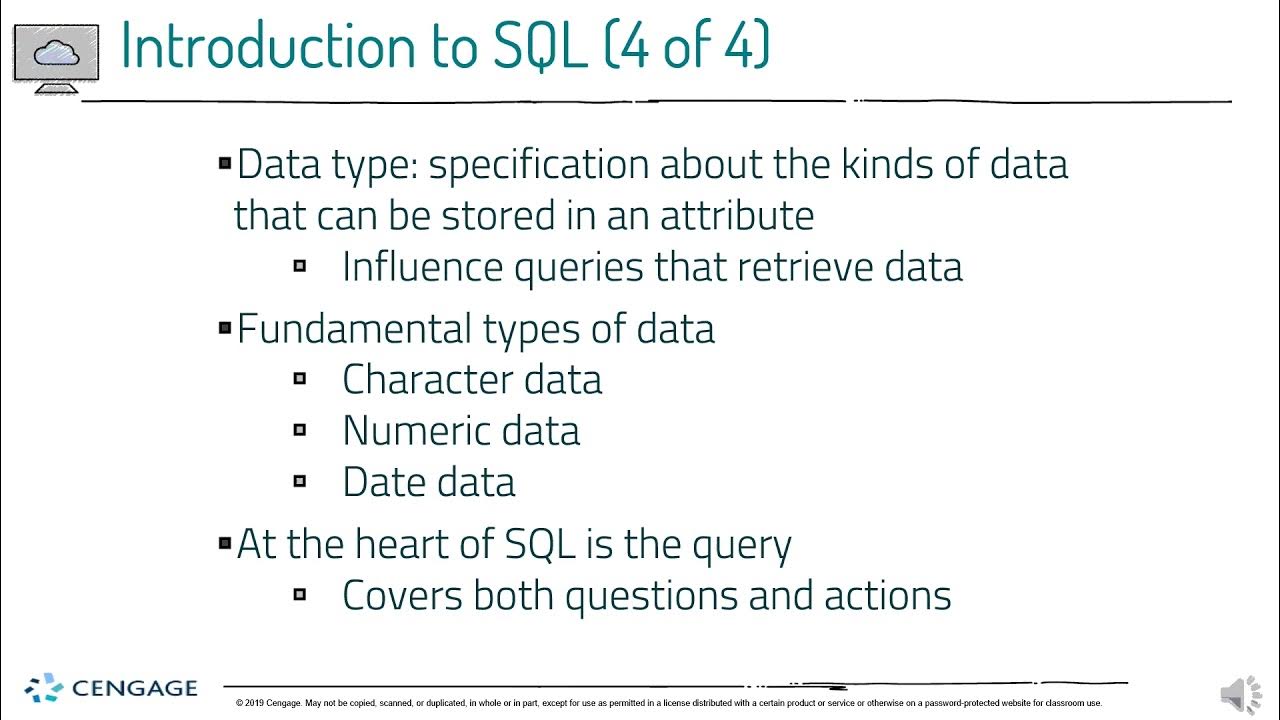
TLDRThis video introduces the concept of data and databases, explaining how raw information becomes useful through processing. It emphasizes the importance of organizing data in databases, comparing them to filing cabinets that categorize information into tables. Each table contains fields and records that store specific data attributes, like student details or course information. The video further explains the role of Database Management Systems (DBMS) in managing databases and retrieving data efficiently. Examples such as MySQL and SQL Server are mentioned, showcasing how DBMS help in organizing and handling data. This is an essential primer on how data is structured and managed.
Takeaways
- 😀 Data refers to raw information that needs to be processed and organized to become useful.
- 😀 Data can be found everywhere in our daily lives, such as details about buildings, people, vehicles, and personal attributes.
- 😀 A student's personal information like name, NIM, faculty, and semester are all examples of data.
- 😀 Large datasets, such as those found at a university, require proper management and organization for efficient access.
- 😀 A database (DB) is like a filing cabinet used to store and organize related data in categories.
- 😀 Within a database, data is organized into tables, with each table containing specific data points or attributes.
- 😀 Database management systems (DBMS), such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server, are used to manage and handle databases effectively.
- 😀 A DBMS can manage multiple databases, allowing for efficient access to data stored in these databases.
- 😀 The structure of a database follows a hierarchy: database → tables → records → fields → characters.
- 😀 Records within tables represent individual entries (such as a student's data) with fields containing specific data types like names or faculties.
Q & A
What is data, and how is it different from information?
-Data refers to raw, unprocessed facts or details, which on their own may not be useful. Information, on the other hand, is data that has been processed and organized to make it useful and meaningful.
Can you give examples of data encountered in daily life?
-Examples of data in daily life include the dimensions of a building (like height and width), personal details like name and age, and technical specifications of objects like a laptop or car.
What is the role of a database?
-A database is used to store, organize, and manage large amounts of data efficiently, making it easy to retrieve specific pieces of information when needed.
How can data be managed effectively in an organization?
-Data can be managed effectively by organizing it into a database where it is categorized into tables. Each table can store data related to specific entities, such as students, courses, or employees.
What are tables in a database?
-Tables in a database are structures that organize data into rows and columns. Each table stores information about a specific category, such as student data, faculty data, or course information.
What is a Database Management System (DBMS)?
-A DBMS is a software application used to manage databases. It helps users create, maintain, and interact with databases by facilitating data storage, retrieval, and manipulation.
What is the relationship between a database and a DBMS?
-A database is a collection of data, while a DBMS is the software that manages and manipulates the database. The DBMS handles all operations like data entry, retrieval, and updates.
What is meant by a 'field' in a database?
-A field in a database refers to a single piece of data within a table, such as a student's name, age, or email address. Fields are organized in columns within the table.
What is a 'record' in a database?
-A record in a database refers to a complete set of data fields for a specific entity. For example, a record could be all the information related to a single student, including their name, age, and faculty.
How is a database structured hierarchically?
-A database is structured hierarchically with the database at the top, followed by tables, fields (columns), and records (rows). This hierarchy helps organize and manage data efficiently.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)