Tektonik dan Struktur Geologi
Summary
TLDRThis video discusses the relationship between tectonics and structural geology, emphasizing the difference between the two concepts. Structural geology focuses on results like folding and faulting, while tectonics deals with large-scale processes. Key concepts such as stress, strain, and their effects on rocks are explored, including how stress can lead to fractures or deformations in brittle or ductile materials. The video also explains how temperature influences rock behavior, with the outer crust being brittle and the inner crust being ductile. It highlights how different stress conditions shape geological structures and how deformation varies with depth.
Q & A
What is the primary difference between tektonik and geologi struktur?
-Tektonik focuses on large-scale processes, while geologi struktur is more concerned with the results caused by forces such as folds and faults.
What is the role of geologi struktur in understanding tektonik?
-Geologi struktur is used to investigate the causes of tectonic activities, helping to understand how these large-scale processes occur.
What are the two fundamental concepts when studying geologi struktur?
-The two fundamental concepts are stress and strain.
How is strain defined in the context of geologi struktur?
-Strain is the deformation or change in shape and size of rocks due to stress, reflecting the original structure after stress is applied.
What is the concept of extension in relation to strain?
-Extension refers to the change in shape when an elastic object is stretched, causing it to become longer and change shape.
What happens when extension occurs on one side of a rock or structure?
-When extension occurs on one side, contraction happens on the opposite side due to stress.
What is stress in geologi struktur?
-Stress is the force applied per unit area on a rock or structure. It can vary depending on the conditions, such as the position of the object (e.g., lying flat or standing).
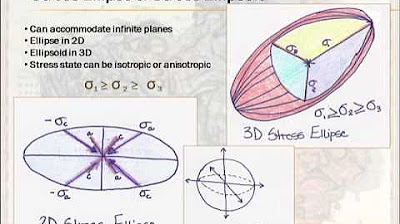
What are the 'three orthogonal principle stress axes' in relation to the Earth's crust?
-The 'three orthogonal principle stress axes' describe stress in the Earth's crust, with σ1 being the largest stress and σ3 being the smallest. The difference between these stresses is crucial in determining the type of structure that forms.
How does the temperature affect the behavior of rocks under stress?
-Temperature influences whether rocks respond in a brittle or ductile manner. At higher temperatures, rocks become more ductile (plastic), while at lower temperatures, they become more brittle and prone to fracture.
What are the dominant characteristics of the upper and lower crust?
-The upper crust is primarily brittle due to the cold conditions, while the lower crust is more ductile or plastic because of the higher temperatures. There is a transition zone between the upper and lower crust where rocks exhibit plastic behavior before fracturing.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)