Understand GST in 10 minutes
Summary
TLDRThis video explains Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India, comparing it to the previous taxation system. It highlights the differences between direct and indirect taxes, and how GST, by replacing multiple indirect taxes, benefits the economy. Through a simple example, the video shows how GST reduces the final cost of products. It also introduces the three types of GST—CGST, SGST, and IGST—and explains various tax rates (0%, 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%) for different products. Additionally, it outlines GST exemptions and its impact on prices, making it a valuable introduction to understanding GST for the general audience.
Takeaways
- 😀 Taxes are payments made to the government to fund public services and reduce national debt, impacting income, business profits, goods, and services.
- 😀 There are two types of taxes: Direct taxes, which cannot be shifted (e.g., Income Tax), and Indirect taxes, which can be transferred (e.g., Sales Tax, Service Tax).
- 😀 GST (Goods and Services Tax) replaces various indirect taxes such as excise duty, service tax, and VAT in India.
- 😀 GST simplifies the taxation process by consolidating multiple taxes into one unified tax structure.
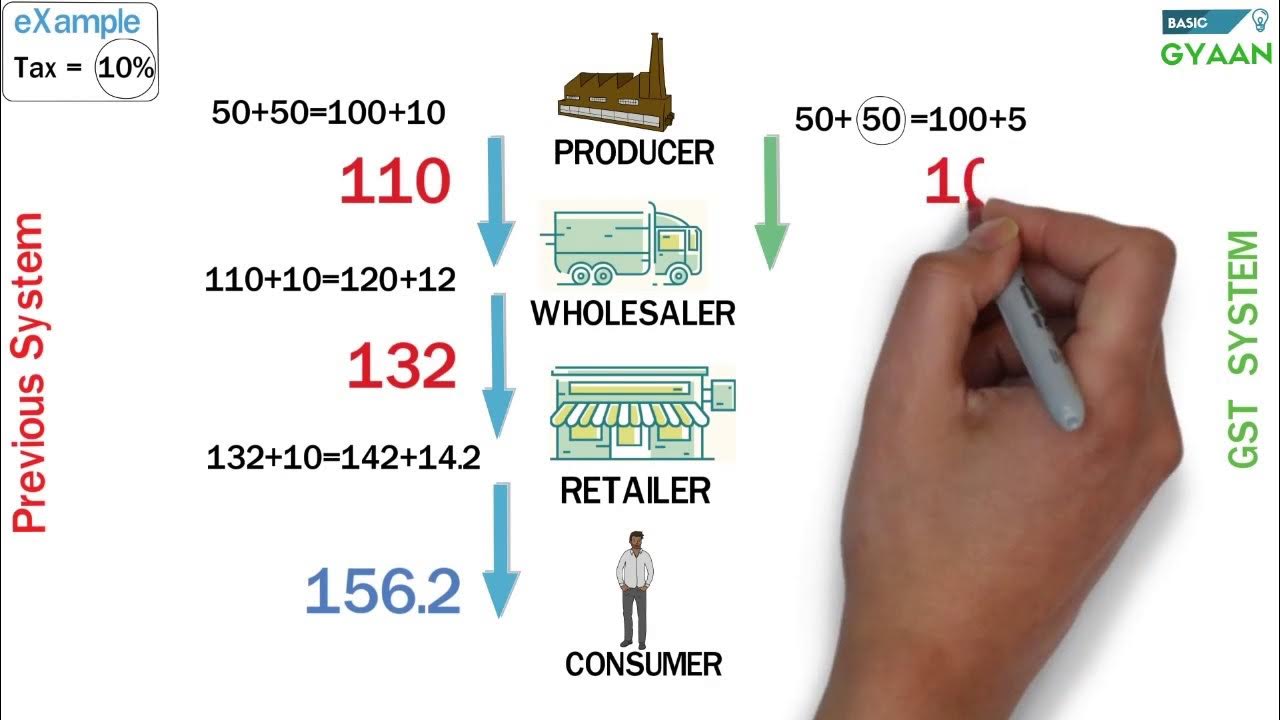
- 😀 The existing tax system adds layers of taxes at different stages (e.g., manufacturer, distributor, wholesaler, retailer), increasing the product price progressively.
- 😀 In the GST system, the product's price is simplified and tax is only levied on the value added at each stage, reducing overall costs.
- 😀 Under GST, the final price of a product can be significantly cheaper than in the previous tax system. For example, the product price could be ₹59.23 cheaper in GST than under the old system.
- 😀 GST is divided into three types: CGST (Central GST), SGST (State GST), and IGST (Integrated GST), with IGST applied in interstate transactions.
- 😀 The GST system in India has five main tax slabs: 0%, 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%, depending on the nature of the goods or services.
- 😀 Certain items are exempt from GST, such as alcohol, petroleum products, and other taxes like stamp duty, property tax, toll tax, and electricity duty.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of taxes?
-Taxes are collected by the government to fund public interests, such as national debt repayment and providing public services.
What are the two types of taxes mentioned?
-The two types of taxes are Direct Taxes, where liability cannot be shifted (e.g., corporate tax, income tax), and Indirect Taxes, where liability can be shifted (e.g., excise duty, service tax).
What indirect taxes are being replaced by GST?
-GST replaces several indirect taxes including excise duty, service tax, additional duty of customs, VAT, central sales tax, entertainment tax, and luxury tax.
How does the current taxation system work in India?
-In the current system, taxes are applied at each stage of the supply chain: from manufacturer to distributor, wholesaler, retailer, and finally to the consumer, with taxes added at each stage.
How is the GST system different from the current taxation system?
-Under GST, taxes are levied only on the value added at each stage of production or distribution, and the price for consumers is lower because tax is only paid on the value added at each stage, not on the full price.
What is the simplified example used to explain the difference between the current system and GST?
-In the example, a product costs Rs. 50 in the current system, and taxes are applied at each stage. In the GST system, the product cost is Rs. 100, but taxes are applied only to the value added at each step, leading to a cheaper final price for consumers.
What are the components of GST in India?
-GST in India consists of three components: CGST (Central GST), SGST (State GST), and IGST (Integrated GST), with IGST applicable for interstate transactions.
What are the different tax rate categories under GST?
-GST in India has five tax categories: 0%, 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%, with different goods and services falling under each rate depending on their usage and necessity.
Which goods and services are exempt from GST?
-Some goods and services exempt from GST include alcohol for human consumption, petroleum products (like petrol and diesel), and certain items like stamp duty, property tax, and toll taxes.
How will GST impact the prices of goods and services?
-After the implementation of GST, some items will see a price increase (e.g., packaged food, jewellery, mobile services), while others will become cheaper (e.g., home appliances, small cars, restaurant bills).
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

1. Concept of Indirect Taxes - Introduction | GST Lecture 1 | CA Raj K Agrawal

Why are Cars so expensive? | Truth about Indian Car Prices
GST Easy Explanation (Hindi)

Goods and Services Tax (GST) (Part-1) - Simplified | Drishti IAS English

The only TAX SYSTEM VIDEO you will ever need. | INDIAN TAX SYSTEM EXPLAINED | Aaditya Iyengar

Nirmala Seetharaman Point By Potluri నిర్మలమ్మ నిజంగా వేధిస్తోందా
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)