MANIFESTASI KLINIK SECARA UMUM
Summary
TLDRThis video lecture focuses on the clinical manifestations of infectious diseases, explaining how they progress from early, asymptomatic stages to severe, life-threatening conditions. It covers key concepts such as the spectrum of diseases, hidden infections, and the stages from prepatogenesis to clinical manifestation. The importance of epidemiological surveys, proper testing, and accurate reporting is emphasized to control and manage outbreaks effectively. The lecture also highlights diseases that are clinically silent versus those that are clearly visible, stressing the need for intervention and prevention in the face of asymptomatic carriers and severe cases.
Takeaways
- 😀 Understanding the spectrum of infectious diseases is essential for identifying their manifestations.
- 😀 The process of disease progression involves multiple stages, from prepatogenesis to severe clinical stages.
- 😀 Prepatogenesis is the initial stage where the disease is still outside the host's body, influenced by environmental factors.
- 😀 Patogenesis occurs when the disease enters the body, but symptoms may not yet appear, often represented by an incubation period.
- 😀 The incubation period varies for different diseases, such as a few days for some, or several years for others like HIV/AIDS.
- 😀 Subclinical stages involve mild symptoms where the individual can still perform normal activities, potentially leading to either recovery or progression to clinical illness.
- 😀 Clinical stages can be 'unclear,' where symptoms are present but not yet severe enough to indicate major organ dysfunction.
- 😀 Severe clinical stages include organ damage, complications, and symptoms that are much more apparent, potentially leading to fatal outcomes.
- 😀 There are three primary groups of clinical manifestations in infectious diseases: asymptomatic, clinically evident, and fatal diseases.
- 😀 Hidden or asymptomatic infections (like tuberculosis) can spread unnoticed, and detecting these infections requires specific diagnostic tests or epidemiological surveys.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video?
-The main topic of the video is the general clinical manifestations of infectious diseases and how they progress through various stages in individuals.
What are the learning objectives of this session?
-The learning objectives include understanding the spectrum of infectious diseases, explaining the process of disease occurrence, understanding latent infections, and providing examples of clinical manifestations of three types of infectious diseases.
What is 'prepatogenesis' in the context of epidemiology?
-Prepatogenesis refers to the stage where the disease-causing agent is still outside the host body and not yet interacting with it, representing the initial phase of the epidemiological triangle.
How does the disease progress from prepatogenesis to pathogenesis?
-After prepatogenesis, the disease agent enters the host body, and during the pathogenesis stage, symptoms are not yet visible. This phase includes the incubation period, which varies by disease.
What is the significance of the 'incubation period'?
-The incubation period is the time between exposure to the pathogen and the appearance of symptoms. It differs for each disease, and it can range from a few days to years, depending on the illness.
What happens in the 'subclinical' phase of a disease?
-In the subclinical phase, the host may experience mild symptoms but is still able to carry out normal activities. Some individuals may recover, while others may progress to more severe stages.
What are the three types of clinical manifestations of infectious diseases?
-The three types of clinical manifestations are: 1) diseases without clinical symptoms (latent infections), 2) diseases with clear clinical symptoms, and 3) diseases that often result in death.
What is meant by the term 'iceberg' phenomenon in infectious diseases?
-The 'iceberg' phenomenon refers to diseases where only a small portion of infected individuals show symptoms, while the majority remain undiagnosed or asymptomatic. Tuberculosis is a classic example.
What is the difference between 'clear clinical' and 'unclear clinical' stages of a disease?
-In the 'clear clinical' stage, symptoms are evident, and diagnosis is easier, while in the 'unclear clinical' stage, symptoms are either mild or not yet developed, making the disease harder to diagnose without laboratory tests.
How does latent infection affect the control of infectious diseases?
-Latent infections, where individuals do not exhibit symptoms, can be a significant source of disease transmission. Identifying and controlling latent infections is crucial in preventing widespread outbreaks, as seen with diseases like COVID-19.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Demographic & Epidemiological Transition Model [AP Human Geography Unit 2 Topic 5] (2.5)

Avaliação Semiológica e Diagnóstico em Pequenos Animais - Aula 4 a 4.1

KONSEP DASAR PATOLOGI & PATOFISIOLOGI | Yudi Adnan, S. Kep., M.Kes
Alert: "For this dangerous reason, you will have glaucoma
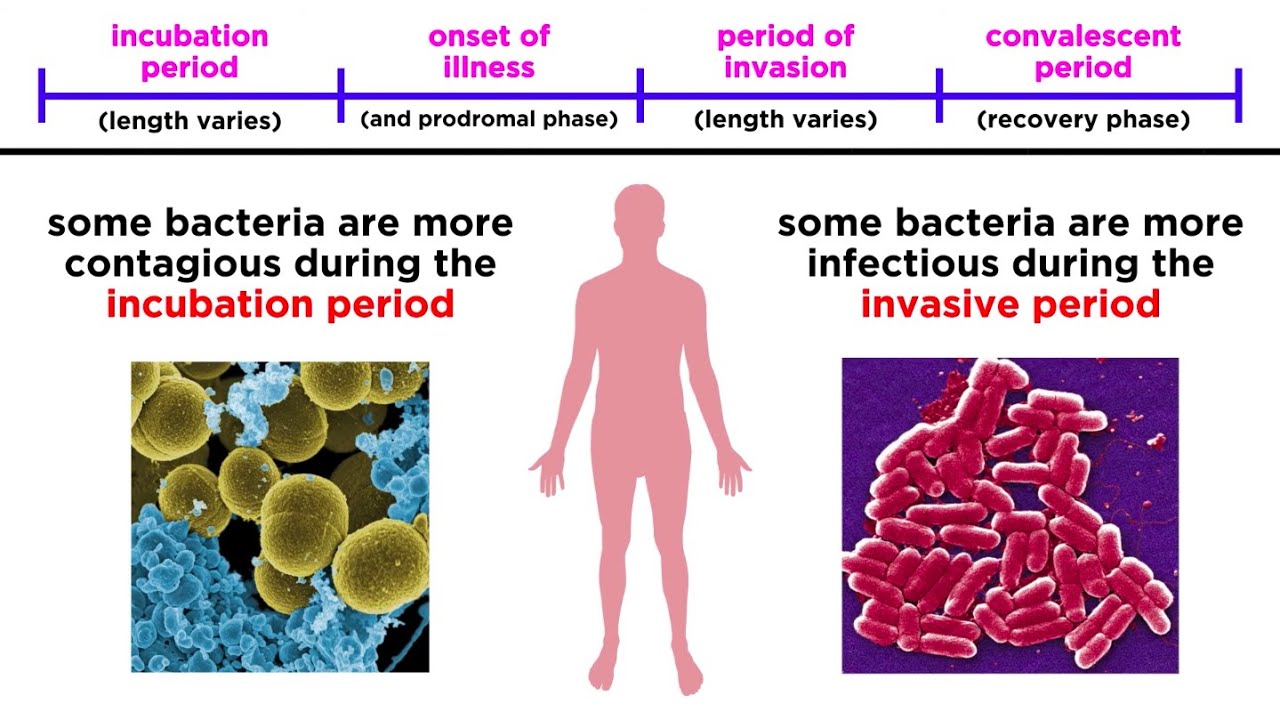
Bacterial Infections in Humans

Oral Pathology | Mucosal Infections | INBDE, ADAT
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)