Lec-4: Physical layer in computer networks in hindi | Functions of Physical layer | OSI
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the presenter explains the key functionalities of the physical layer in the OSI model. The physical layer is crucial for converting data into signals and transmitting them across various media, such as cables (twisted pair, coaxial, optical fiber) or wireless methods. The video highlights key topics like cables, connectors, topologies (star, mesh, bus), transmission modes (simplex, half-duplex, full-duplex), multiplexing, encoding, and the role of hardware like repeaters and hubs. The video emphasizes the importance of understanding these concepts in networking and provides additional resources for deeper learning.
Takeaways
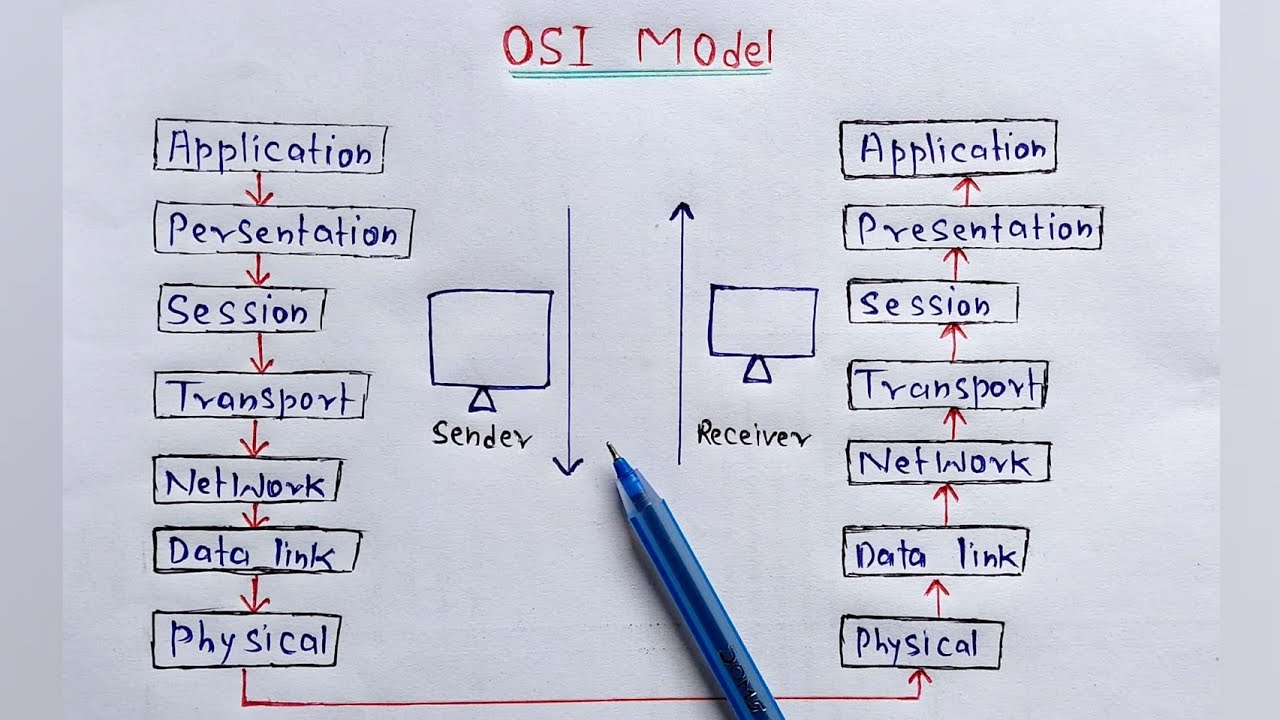
- 😀 The physical layer is the first layer on the receiver side and the last on the sender side, responsible for converting signals into bits and vice versa.
- 😀 The physical layer deals with tangible hardware like cables, connectors, and transmission media, distinguishing it from upper layers that combine hardware and software.
- 😀 Different types of cables used in the physical layer include twisted cables, co-axial cables, and optical fibers, each with unique functionalities like carrying electrical or light signals.
- 😀 Connectors such as UTP, BNC, and MGRT are physical devices used to join cables in the physical layer.
- 😀 The physical layer defines the physical topology of the network, including star, mesh, and bus topologies, and handles point-to-point or multipoint communication.
- 😀 Hardware devices like repeaters and hubs are essential in the physical layer, with repeaters boosting signal strength and hubs facilitating multipoint connections.
- 😀 Transmission modes in the physical layer include simplex (one-way communication), half-duplex (two-way communication, but not simultaneously), and full-duplex (two-way communication simultaneously).
- 😀 Multiplexing in the physical layer allows multiple signals to share the same transmission channel by dividing the frequency, with demultiplexing used on the receiver side.
- 😀 Encoding in the physical layer is used to convert data from digital to analog or vice versa, depending on the signal type (e.g., FM is analog).
- 😀 The main function of the physical layer is to convert a continuous stream of bits into signals for transmission and then reconvert signals into bits at the receiver end, using various transmission media such as wired or wireless.
Q & A
What is the role of the physical layer in the OSI model?
-The physical layer is the last layer on the sender's side and the first layer on the receiver's side in the OSI model. It deals with the transmission and reception of raw bits over a transmission medium, such as cables or wireless signals.
What types of data does the physical layer work with?
-The physical layer works with physical data, which means it deals with actual bits in the form of signals that can be transmitted over media, unlike upper layers that work with logical data like frames and packets.
How does the physical layer transmit data?
-The physical layer transmits data by converting the bits it receives from the data link layer into signals and sending them through transmission media, which can either be guided (wired) or unguided (wireless).
What are the main types of transmission media discussed in the physical layer?
-The main types of transmission media discussed include guided media, such as twisted pair cables, coaxial cables, and optical fibers, as well as unguided media like wireless communication signals.
What are connectors, and how are they related to the physical layer?
-Connectors, such as UTP, BNC, and MGRT connectors, are used to join different types of cables in the physical layer. They are tangible hardware components that enable the physical connection and transmission of data.
What is the significance of physical topology in the physical layer?
-Physical topology refers to the physical arrangement of devices and their connections in a network. It defines how devices are connected and how communication occurs between them, with examples including star, mesh, and bus topologies.
What types of hardware are typically used in the physical layer?
-Common hardware in the physical layer includes repeaters and hubs. Repeaters amplify weak signals, and hubs facilitate multipoint connections between devices.
What is multiplexing, and how does it function in the physical layer?
-Multiplexing is the technique used to combine multiple signals into one channel for transmission. It allows multiple signals to share the same channel without interference by dividing the channel's frequency into smaller segments. The opposite process, demultiplexing, is used at the receiver's end to separate the combined signals.
What are the different transmission modes discussed in the physical layer?
-The transmission modes in the physical layer include simplex (one-way communication), half-duplex (two-way communication but not simultaneously), and full-duplex (two-way communication simultaneously).
How does encoding work in the physical layer?
-Encoding in the physical layer involves converting data into a form suitable for transmission over a channel. This could involve converting digital data into analog signals, or encoding digital data into discrete digital forms based on the medium used.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)