TCP/IP Protocol Explained | What Is TCP/IP Address? | TCP/IP Configuration Tutorial | Simplilearn
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an insightful overview of the TCP/IP model, explaining its role in data transmission across networks. It delves into the four-layer structure of the model—application, transport, internet, and network access—highlighting the specific protocols like HTTP, TCP, and IP that operate at each layer. The video also contrasts the TCP/IP model with the OSI model, noting key differences such as the number of layers and their functionalities. By the end, viewers gain a clear understanding of how the TCP/IP model facilitates effective communication between devices in a network.
Takeaways
- 😀 The TCP/IP model is essential for sharing data across communication channels, utilizing a four-layer structure.
- 📦 Each layer of the TCP/IP model has specific tasks, including data transmission, remodeling, and error handling.
- 🌐 The application layer of TCP/IP combines the top three layers of the OSI model, handling protocols like FTP, HTTP, Telnet, and SMTP.
- 🚦 The transport layer in the TCP/IP model establishes connections and manages data flow, using TCP and UDP protocols.
- 🗺️ The internet layer routes packets across networks, utilizing protocols like IP, ICMP, and ARP for addressing and control.
- 🔌 The network access layer, derived from the OSI model's data link and physical layers, handles the physical transfer of data.
- ✅ The TCP/IP model assigns unique IP addresses to devices for identification on the internet.
- 💡 The model supports various data formats for efficient communication across networks.
- 🔍 The OSI model consists of seven layers, while the TCP/IP model is more streamlined with four layers.
- ⚖️ The TCP/IP model is used as a reference framework for network communication, unlike the OSI model, which is actively implemented.
Q & A
What is the TCP/IP model?
-The TCP/IP model is a framework used for sharing data and information over communication channels. It consists of a layered structure through which data must pass, performing tasks such as data remodeling, efficient transmission, and addressing error-related issues.
How many layers are there in the TCP/IP model, and what are they?
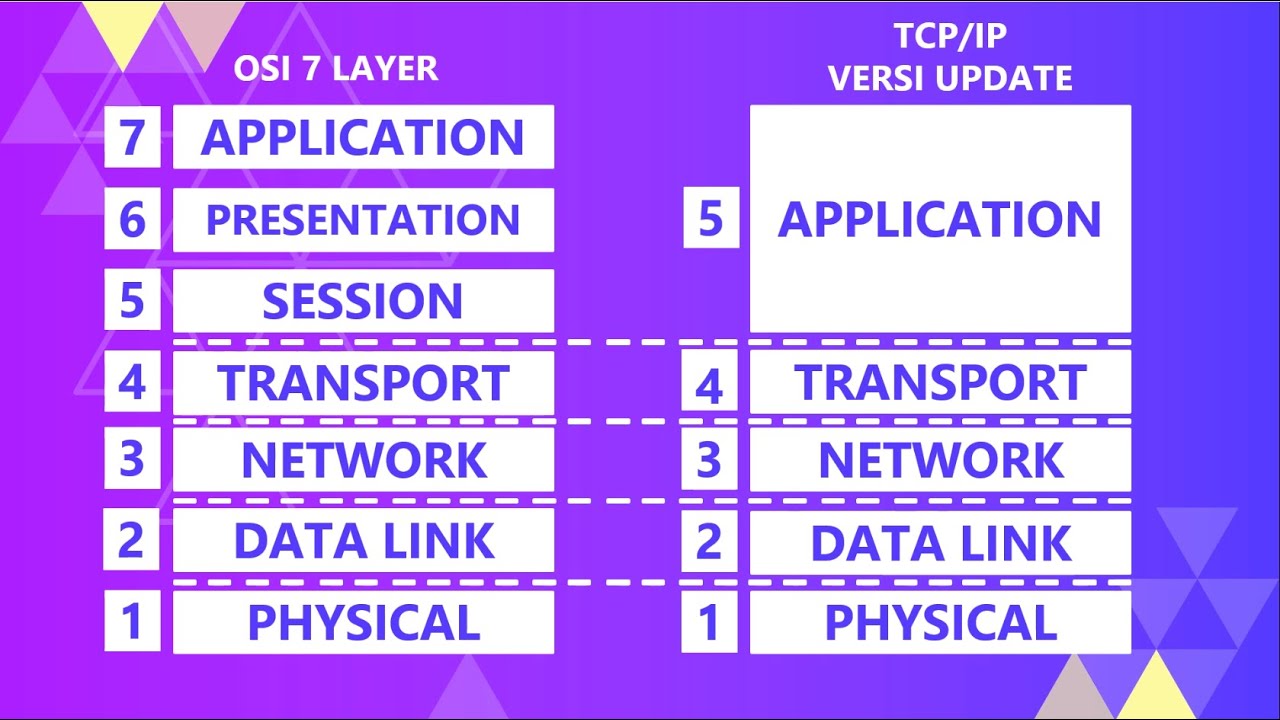
-The TCP/IP model originally consists of four layers: Application Layer, Transport Layer, Internet Layer, and Network Access Layer. An updated version includes Data Link Layer and Physical Layer.
What are the key protocols used in the Application Layer of the TCP/IP model?
-Key protocols in the Application Layer include FTP (File Transfer Protocol), HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol), SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol), and Telnet.
What role does the Transport Layer play in the TCP/IP model?
-The Transport Layer is responsible for establishing connections between sender and receiver devices, dividing data into packets, ensuring error-free transmission, and controlling data flow rate.
Which protocols are associated with the Transport Layer in the TCP/IP model?
-The Transport Layer uses TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) for reliable transmission and UDP (User Datagram Protocol) for error detection in data transmission.
What is the purpose of the Internet Layer in the TCP/IP model?
-The Internet Layer is responsible for routing data packets over the network, ensuring they are transmitted correctly to their destination. It includes protocols like IP (Internet Protocol) and ARP (Address Resolution Protocol).
What are the advantages of using the TCP/IP model?
-Advantages include the assignment of unique IP addresses for network devices, support for various data formats, and the implementation of multiple protocols to enhance data transmission efficiency.
How does the TCP/IP model differ from the OSI model?
-The TCP/IP model consists of four layers compared to the OSI model's seven layers. The OSI model has separate Session and Presentation layers, while TCP/IP combines them into a single Application layer. Additionally, the OSI model provides packet delivery protocols, while TCP/IP focuses on connection-oriented and connectionless communication.
What does the Network Access Layer do in the TCP/IP model?
-The Network Access Layer combines the Data Link Layer and Physical Layer from the OSI model. It is responsible for sending and receiving raw bits over the physical medium, such as Ethernet and Wi-Fi.
Why is the TCP/IP model considered a foundational reference model?
-The TCP/IP model is foundational because it provides a standard framework for network communications, guiding the development and implementation of various networking protocols and technologies.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)