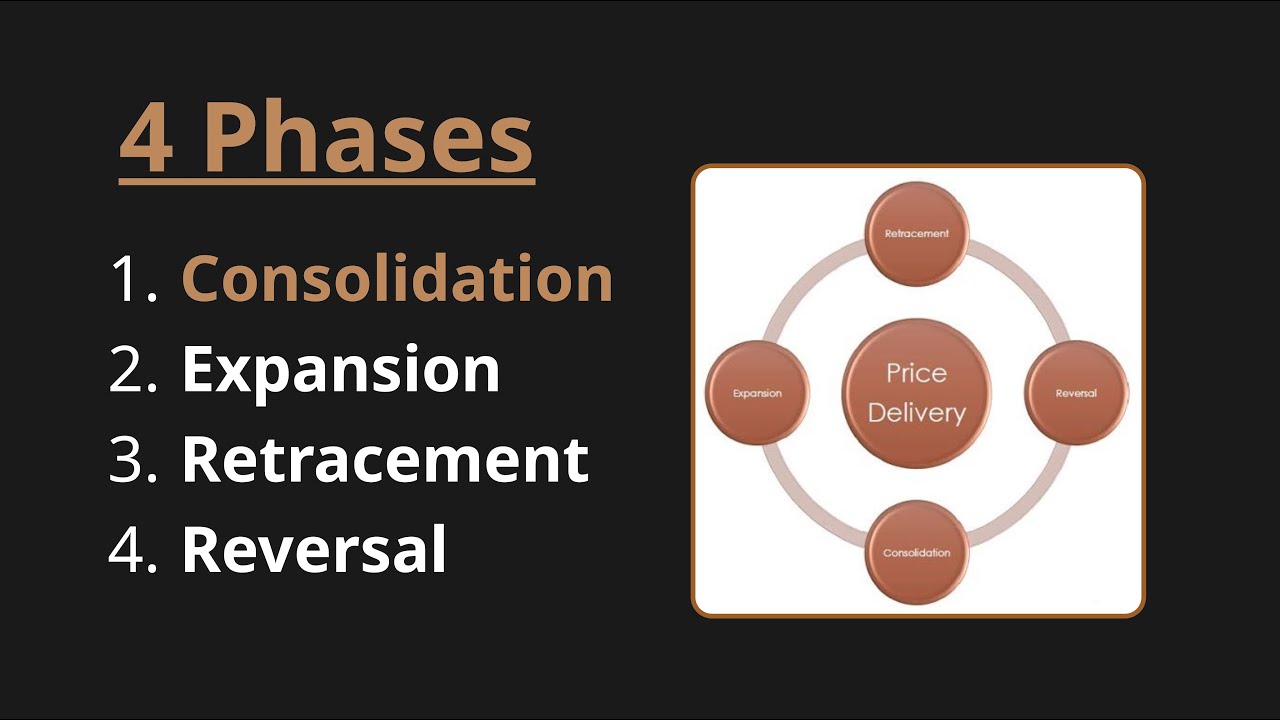
4 Stages of Price Delivery (ICT Concepts)
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the presenter explains the four stages of price delivery in trading: consolidation, expansion, retracement, and reversal. He discusses how smart money manipulates market movements by accumulating and distributing positions. The fractal nature of these stages is emphasized, where they occur on different timeframes. Smart money buys at lower prices during dips and sells at higher prices, often using sentiment manipulation and media influence. The video also critiques retail trading strategies, focusing on price action and market structure over traditional chart patterns like head and shoulders.
Takeaways
- 😀 Price delivery in the market involves four main stages: consolidation, expansion, retracement, and reversal.
- 😀 Consolidation occurs when smart money accumulates or distributes positions, keeping price within a range.
- 😀 Expansion happens after consolidation, where price moves rapidly in one direction as smart money facilitates positions.
- 😀 Retracement occurs when price temporarily reverses after an expansion before continuing in the original direction.
- 😀 Reversal indicates a complete trend change, shifting the market from bullish to bearish or vice versa.
- 😀 Market movements are fractal, meaning these stages happen on various timeframes (minutes, hours, days, months).
- 😀 Smart money typically buys at low prices during consolidations and sells at high prices during expansions.
- 😀 Manipulation of sentiment, often through news and chart patterns, is a key strategy for smart money to influence retail traders.
- 😀 Retail traders often make the mistake of buying during expansions (when prices are high) and selling during retracements (when prices are low).
- 😀 The speaker advises against using common retail trading patterns like head and shoulders or cup and handle, focusing instead on market structure and candlestick analysis.
- 😀 Understanding price delivery and smart money's behavior can significantly improve trading decisions by identifying opportune entry and exit points.
Q & A
What are the four stages of price delivery according to ICT concepts?
-The four stages are Consolidation, Expansion, Retracement, and Reversal. These stages describe how price moves in a market and how smart money operates during these phases.
What happens during the Consolidation phase?
-During the Consolidation phase, price stays within a certain range for an extended period of time. Smart money is either accumulating or distributing positions, taking time to enter and exit due to the size of their trades.
Why is the Consolidation phase important for smart money?
-The Consolidation phase is crucial for smart money because it allows them to accumulate positions at favorable prices. They want to buy at a low price (if going long) and accumulate enough liquidity before expanding the price in their desired direction.
What happens after the Consolidation phase?
-After Consolidation, the market typically enters an Expansion phase, where price moves quickly in a particular direction, usually in line with smart money's positions, allowing them to sell at higher prices after accumulating during the consolidation.
How does Expansion differ from Retracement?
-Expansion is a rapid movement in price in one direction, typically after accumulation. A Retracement, on the other hand, is a temporary pullback or correction, allowing smart money to accumulate more positions before the price resumes its upward or downward trend.
What role does fear and greed play in smart money's strategy?
-Fear and greed are manipulated by smart money to create favorable market conditions. For instance, during an expansion, retail traders may buy at high prices due to greed, while smart money sells to them. Similarly, during retracements, fear may cause traders to panic-sell, allowing smart money to buy at lower prices.
What does 'fractal' mean in relation to price movement?
-Fractal means that price movements follow similar patterns at different time frames. For example, consolidations, expansions, retracements, and reversals can occur on small time frames (like 5-minute charts) and larger time frames (like daily or monthly charts).
How does smart money manipulate price during expansions?
-During expansions, smart money exploits the greed of retail traders by driving the price higher. Retail traders tend to buy as the price increases, and smart money takes advantage of this by selling to them at inflated prices.
What is the relationship between price and liquidity in the market?
-Liquidity is essential for smart money to fill large positions. They manipulate price to create liquidity, encouraging retail traders to buy or sell at certain levels. Smart money can then buy or sell at the prices they desire by taking advantage of these retail movements.
Why is it important for traders to understand the stages of price delivery?
-Understanding these stages allows traders to align their strategies with the behavior of smart money. By recognizing the stages of consolidation, expansion, retracement, and reversal, traders can enter trades at opportune moments, improving their chances of success.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

ICT 4 Phases of Price Delivery, Find Daily Bias with Phases of Price Delivery,
Anticipating Expansions From Consolidations - Episode 1

IPDA Market Cycles - Phases of Price Delivery | ICT Concept in Trading

Using Weekly Profiles for Daily Bias (Simplified)
The Secret To ICT Daily Bias: A Mechanical Approach

You Are Using Discount and Premium Wrong! - EQ For Expansions
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)