LAPISAN BUMI PART 2. LITOSFER & HIDROSFER : IPA SMP KELAS 7
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the presenter explains the Earth's layers, focusing on the lithosphere and hydrosphere. The lithosphere consists of the Earth's outer layers, including the crust, mantle, and core, with tectonic plates that move and cause geological events like earthquakes and volcanoes. The hydrosphere, covering 70% of the Earth, encompasses all water bodies and emphasizes the water cycle. The video also explores the causes of earthquakes, types of faults, and how tsunamis occur. With engaging visuals and simplified explanations, this video encourages students to learn and revisit the concepts for better understanding.
Takeaways
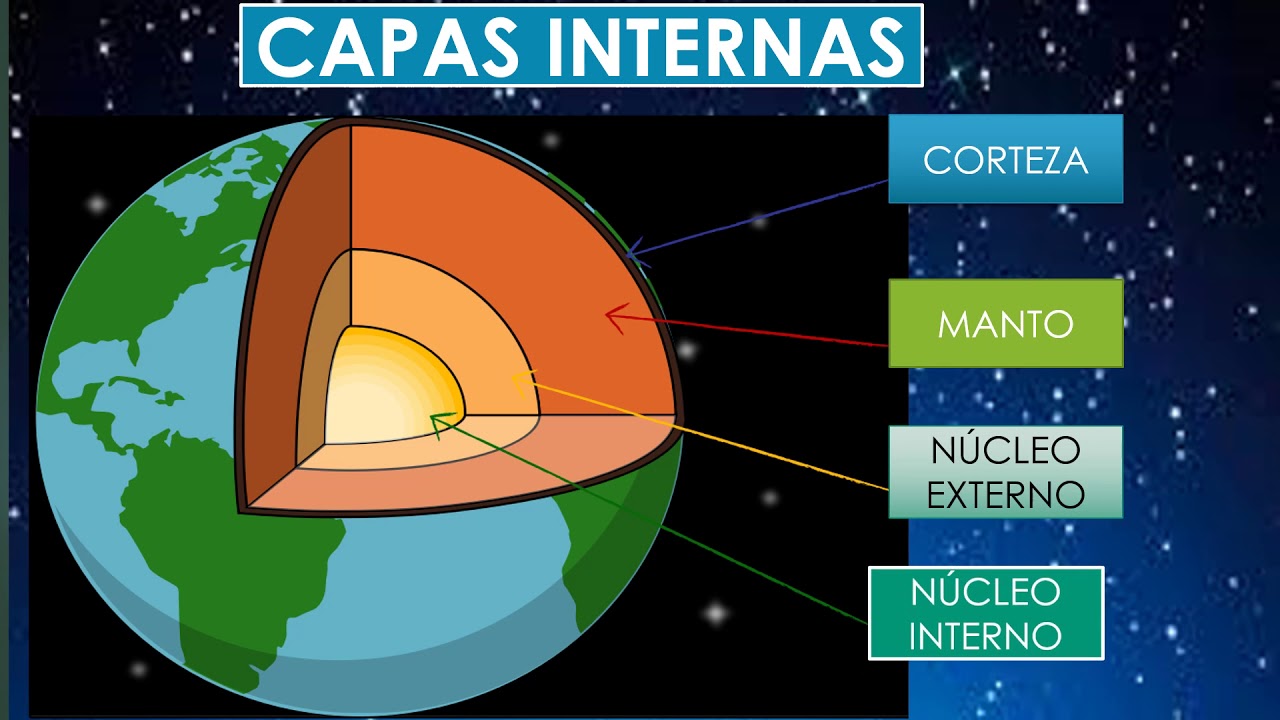
- 😀 The Earth's lithosphere is made up of four layers: the crust, the mantle, the outer core, and the inner core.
- 😀 The lithosphere consists of tectonic plates, which are large pieces of the Earth's surface that move slowly over time.
- 😀 Alfred Wegener's theory of continental drift suggests that all continents were once part of a supercontinent called Pangea.
- 😀 The movement of tectonic plates is driven by convection currents in the Earth's mantle, causing them to either converge or diverge.
- 😀 Plate movement can lead to geological events such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and the formation of mountain ranges.
- 😀 Earthquakes are caused by the movement of tectonic plates and can result in various types of fault lines: strike-slip faults, reverse faults, and normal faults.
- 😀 Tsunamis are large ocean waves generated by underwater earthquakes, often followed by the retreat of seawater from the shore.
- 😀 Seismographs are used to measure and record seismic waves from earthquakes, producing a seismogram that shows the intensity and duration of the event.
- 😀 The Earth's hydrosphere consists of all water on the planet, including oceans, rivers, lakes, groundwater, and water vapor.
- 😀 The water cycle (hydrological cycle) is a continuous process where water evaporates, condenses into clouds, precipitates as rain, and returns to bodies of water, maintaining the Earth's water supply.
Q & A
What is the lithosphere?
-The lithosphere is the outermost layer of the Earth, made up of rocks that cover both the land and the oceans. It is divided into four layers: the crust, the mantle, the outer core, and the inner core.
What is the role of tectonic plates in shaping the Earth's surface?
-Tectonic plates are parts of the lithosphere that move slowly over the Earth's surface. Their movement, driven by convection currents in the mantle, leads to the formation of mountains, earthquakes, and volcanoes.
What is the theory of continental drift?
-The theory of continental drift, proposed by Alfred Wegener, suggests that all continents were once part of a single supercontinent called Pangea. Over time, the continents drifted apart, forming the present-day configuration of continents.
What causes earthquakes?
-Earthquakes are caused by the movement of tectonic plates. The plates can either slide past each other, collide, or move away from each other, creating stress that is released as seismic waves, resulting in an earthquake.
What are the three types of plate movements that cause earthquakes?
-The three main types of plate movements that cause earthquakes are: strike-slip faults (plates sliding past each other), reverse faults (plates colliding), and normal faults (plates moving apart).
What is the difference between the hypocenter and the epicenter of an earthquake?
-The hypocenter is the point within the Earth where an earthquake originates, while the epicenter is the point on the Earth's surface directly above the hypocenter.
What is a tsunami, and how is it related to earthquakes?
-A tsunami is a large ocean wave typically caused by an underwater earthquake. It results from a sudden shift in the ocean floor, displacing a large volume of water and creating a wave that travels across the ocean.
What is the hydrosphere?
-The hydrosphere is the layer of Earth that consists of all its water, including oceans, rivers, lakes, groundwater, and water vapor in the atmosphere.
What is the water cycle?
-The water cycle is the continuous process through which water moves around the Earth. It involves evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and transpiration, ensuring the recycling of water in the environment.
What is the significance of the process of evaporation in the water cycle?
-Evaporation is the process where water from oceans, rivers, and lakes changes into water vapor. This is the first step in the water cycle and plays a key role in redistributing water across the Earth's surface.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

IPA kelas 7 : Struktur/Lapisan Bumi (Atmosfer)
VIDEO DE LAS CAPAS EXTERNAS E INTERNAS DE LA TIERRA. AUTORA VICTORIA GUAMÁN.

Lapisan Bumi (Litosfer, Hidrosfer, dan Atmosfer) - Materi IPAS Kelas 5 Kurikulum Merdeka

SOAL LATIHAN BAB 6 STRUKTUR BUMI DAN PERKEMBANGANNYA - IPA Kelas 8 Kurikulum Merdeka

Struktur Bumi dan Perkembangannya

BAB 6 STRUKTUR BUMI DAN PERKEMBANGANNYA BAGIAN 1 - IPA Kelas 8 Kurikulum Merdeka
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)