Sistema Respiratório 2/6: Vias Aéreas Superiores
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explains the divisions of the respiratory system, focusing on the upper airways. It details the two main functional zones: the conducting zone, which includes structures like the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles; and the respiratory zone, where gas exchange occurs. The video emphasizes the role of the nose in filtering, warming, and humidifying air, as well as the structure and function of the pharynx and larynx, including the vocal cords. The information is presented clearly and is ideal for understanding the anatomy and functions of the upper respiratory system.
Takeaways
- 😀 The respiratory system is divided into two functional zones: the conducting zone and the respiratory zone.
- 😀 The conducting zone includes the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles, which are responsible for directing air to the respiratory zone.
- 😀 The respiratory zone, where gas exchange occurs, consists of respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs, and alveoli.
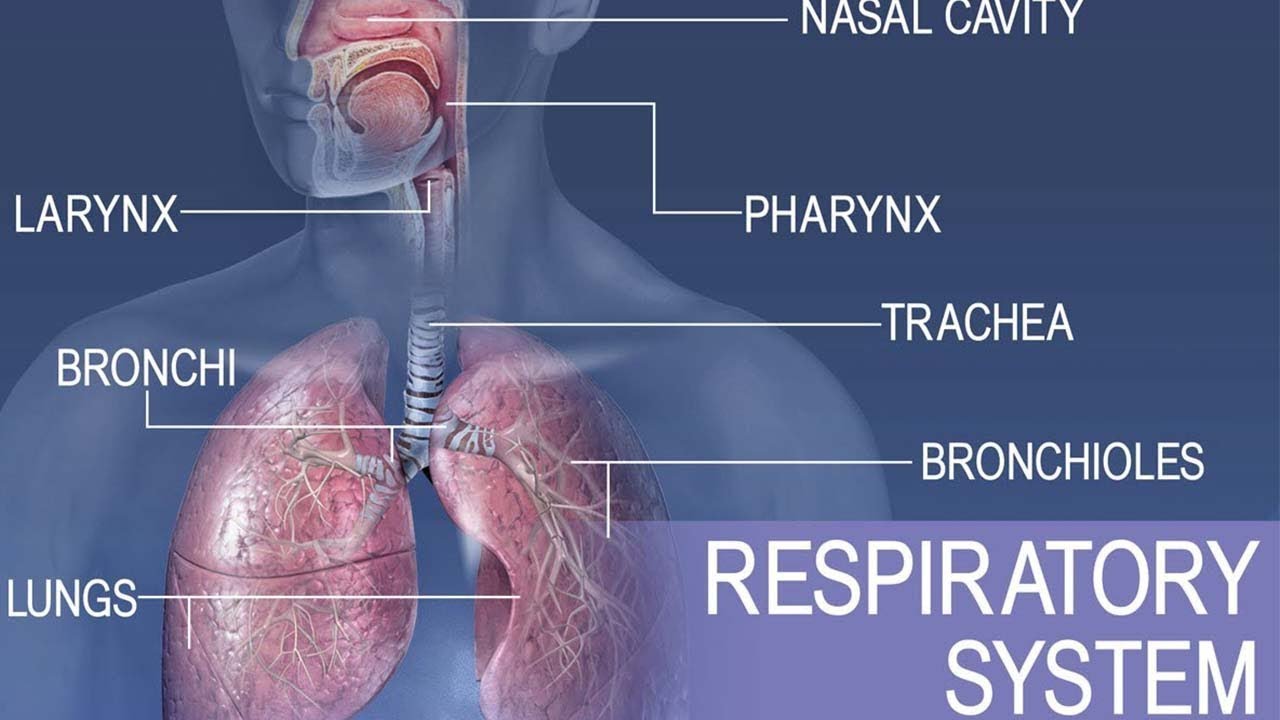
- 😀 The upper respiratory airways are located above the chest and include the nose, pharynx, and larynx.
- 😀 The lower respiratory airways are located within the chest and consist of the trachea, bronchi, and lungs.
- 😀 The nose has both external and internal parts, with the external part visible and the internal part located within the skull, separated by the nasal septum.
- 😀 Nasal hairs help filter larger particles from the air, and the nasal cavity's mucous membranes help filter smaller particles and humidify the air.
- 😀 The nasal cavity also contains ciliated cells that aid in cleaning the air and produce mucus to trap particles.
- 😀 The nasal conchae (or turbinates) increase the surface area for air contact, helping to heat, filter, and humidify the air before it reaches the lungs.
- 😀 The pharynx is divided into three regions: nasopharynx (connected to the nasal cavity), oropharynx (connected to the oral cavity), and laryngopharynx (connected to the larynx and esophagus).
Q & A
What are the two functional zones of the respiratory system?
-The respiratory system is divided into two functional zones: the conducting zone (or conducting portion) and the respiratory zone (or respiratory portion).
What structures are part of the conducting zone?
-The conducting zone includes the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles. These structures conduct air from the external environment to the respiratory zone.
What is the function of the respiratory zone?
-The respiratory zone is where gas exchange occurs, and it consists of structures such as respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs, and the alveoli themselves.
What are the main functions of the nasal hairs?
-The nasal hairs help filter larger particles from the air, acting as a coarse filter to prevent larger debris from entering the respiratory system.
How do the nasal conchae contribute to respiratory function?
-The nasal conchae, also known as turbinates, increase the surface area inside the nasal cavity, helping to heat, filter, and humidify the air before it reaches the lungs.
What role do the ciliated cells in the nasal cavity play?
-Ciliated cells in the nasal cavity help to clean the inhaled air by moving mucus that traps smaller particles, thus aiding in the filtration process.
What is the function of the mucus in the respiratory system?
-Mucus serves as an adhesive filter, trapping smaller particles that may have bypassed the nasal hairs and cilia, and also helps to humidify the air entering the respiratory system.
What are the paranasal sinuses, and what is their role?
-The paranasal sinuses are air-filled cavities within the bones of the skull. They help to increase voice resonance, produce mucus, and assist in the overall function of the nasal cavity.
What structures are found in the pharynx?
-The pharynx is divided into three parts: the nasopharynx (connected to the nasal cavity), the oropharynx (connected to the oral cavity), and the laryngopharynx (connected to the larynx and esophagus).
What is the function of the larynx in the respiratory system?
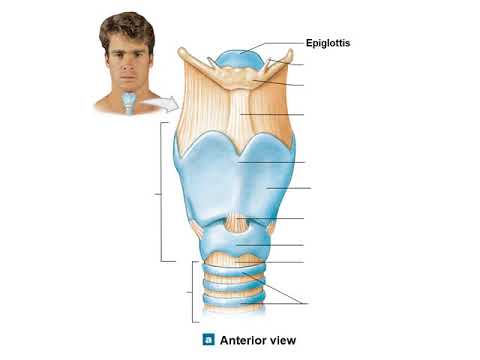
-The larynx connects the pharynx to the trachea and contains important structures like the thyroid cartilage, epiglottis, cricoid cartilage, and vocal cords, which are essential for voice production and for protecting the trachea during swallowing.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Respiratory System of the Human Body - How the Lungs Work! (Animation)
Anatomi Sistem Respirasi | Materi Kedokteran Dasar

Anatomi Systema Respiratorium : Nasus

Airway Anatomy - 3D Tutorial
FISIOLOGI PERNAFASAN 1 | Yuk review kembali fisiologi pernafasan pada manusia
Anatomy and physiology of Respiratory system
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)