SISTEM REPRODUKSI MANUSIA 2
Summary
TLDRThis video script provides an in-depth explanation of the menstrual cycle, breaking it down into key phases such as menstruation, pre-ovulation, ovulation, and post-ovulation. It highlights the role of hormones like FSH, estrogen, LH, and progesterone in regulating these phases. The script also touches on the process of pregnancy, explaining the development of the embryo, the placenta, and the umbilical cord. Visuals are used to support the explanations, showing the anatomy of the female reproductive system and the physiological processes involved in menstruation and conception. The script aims to provide a clear understanding of these biological processes.
Takeaways
- 😀 Menstrual cycles typically last around 28 days, but it can vary by up to 7 days, either earlier or later.
- 😀 The menstrual cycle begins on the first day of menstruation, lasting about 6-7 days, which is when the uterine lining sheds.
- 😀 The cycle can be divided into phases: pre-ovulation, ovulation, and post-ovulation.
- 😀 The hormone FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) increases early in the cycle to mature the follicles in the ovaries.
- 😀 Estrogen rises after FSH stimulates the follicles, leading to ovulation.
- 😀 LH (Luteinizing Hormone) peaks around day 14, triggering ovulation and the release of the egg from the follicle.
- 😀 After ovulation, progesterone levels rise, which is important for thickening the uterine lining in preparation for pregnancy.
- 😀 If pregnancy does not occur, hormone levels (LH and FSH) decrease, and menstruation will follow.
- 😀 The corpus luteum, formed from the ruptured follicle after ovulation, produces progesterone to maintain the uterine lining.
- 😀 The presence of the placenta and umbilical cord is crucial in pregnancy, as the placenta delivers nutrients and oxygen from the mother to the embryo.
Q & A
What is the average length of the menstrual cycle?
-The average menstrual cycle is about 28 days, but it can vary by up to 7 days, either longer or shorter.
What happens during the menstruation phase?
-During the menstruation phase, the uterine lining sheds, which lasts about 6 to 7 days, marking the beginning of the menstrual cycle.
What is the pre-ovulatory phase in the menstrual cycle?
-The pre-ovulatory phase is the time between menstruation and ovulation, where the body prepares for ovulation, and hormone levels, like estrogen, start to rise.
When does ovulation occur in the typical menstrual cycle?
-Ovulation typically occurs on day 14 of the cycle when a mature egg is released from the ovary.
What role do hormones like FSH and LH play in the menstrual cycle?
-FSH (Follicle-Stimulating Hormone) stimulates the maturation of ovarian follicles, while LH (Luteinizing Hormone) triggers ovulation and the formation of the corpus luteum.
How does estrogen affect the menstrual cycle?
-Estrogen helps to mature the ovarian follicles and eventually inhibits the production of FSH when it reaches a certain level. It also contributes to the thickening of the uterine lining.
What is the role of progesterone in the menstrual cycle?
-Progesterone is produced by the corpus luteum after ovulation and helps to maintain the uterine lining, preparing it for a potential pregnancy.
What happens if pregnancy does not occur after ovulation?
-If pregnancy does not occur, hormone levels drop, which causes the uterine lining to shed and menstruation to begin.
How does the body prepare for pregnancy during the menstrual cycle?
-The body prepares for pregnancy by thickening the uterine lining under the influence of estrogen and progesterone, which would support the implantation of a fertilized egg.
What is the function of the placenta during pregnancy?
-The placenta facilitates the exchange of nutrients, oxygen, and waste between the mother and the fetus, supporting fetal growth and development.
What is the role of the amniotic sac and fluid during pregnancy?
-The amniotic sac, filled with amniotic fluid, protects the developing fetus by cushioning it from external impacts and maintaining a stable environment.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Siklus Menstruasi : Memahami Gambar (Mudah dipahami)
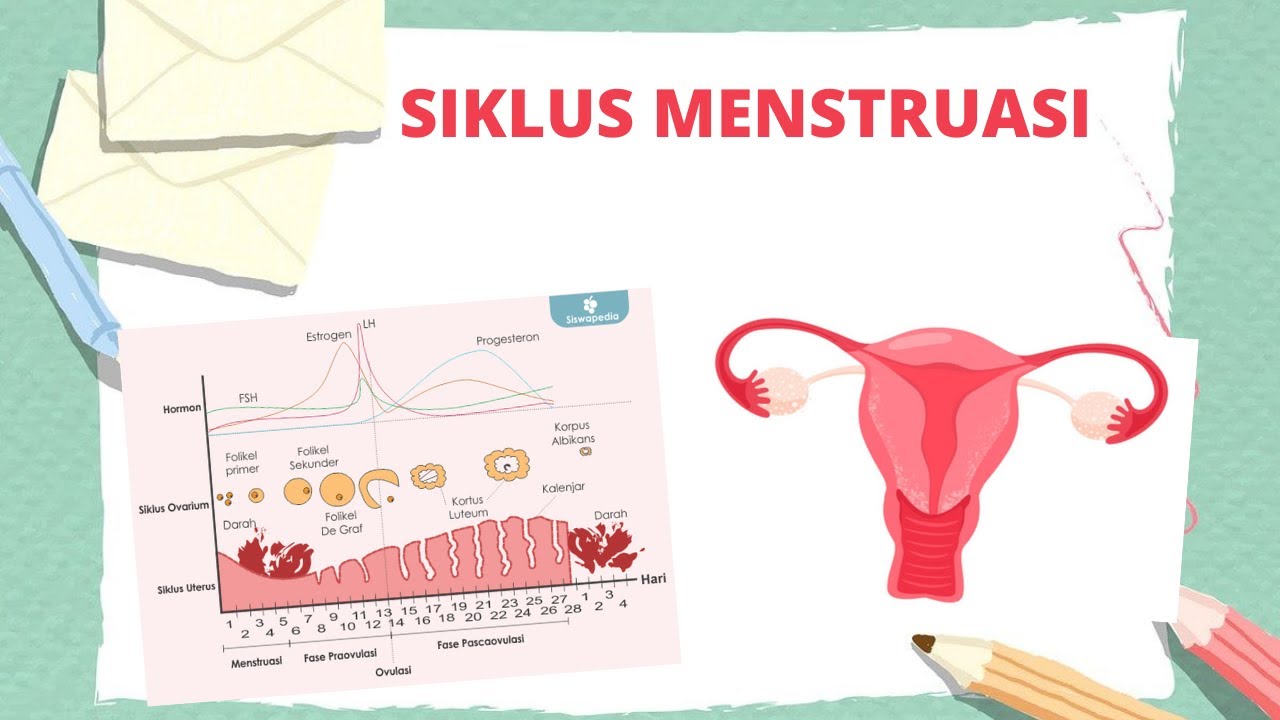
Siklus menstruasi - Grafik siklus menstruasi dan penjelasannya

Siklus menstruasi - Biologi kelas 11 SMA
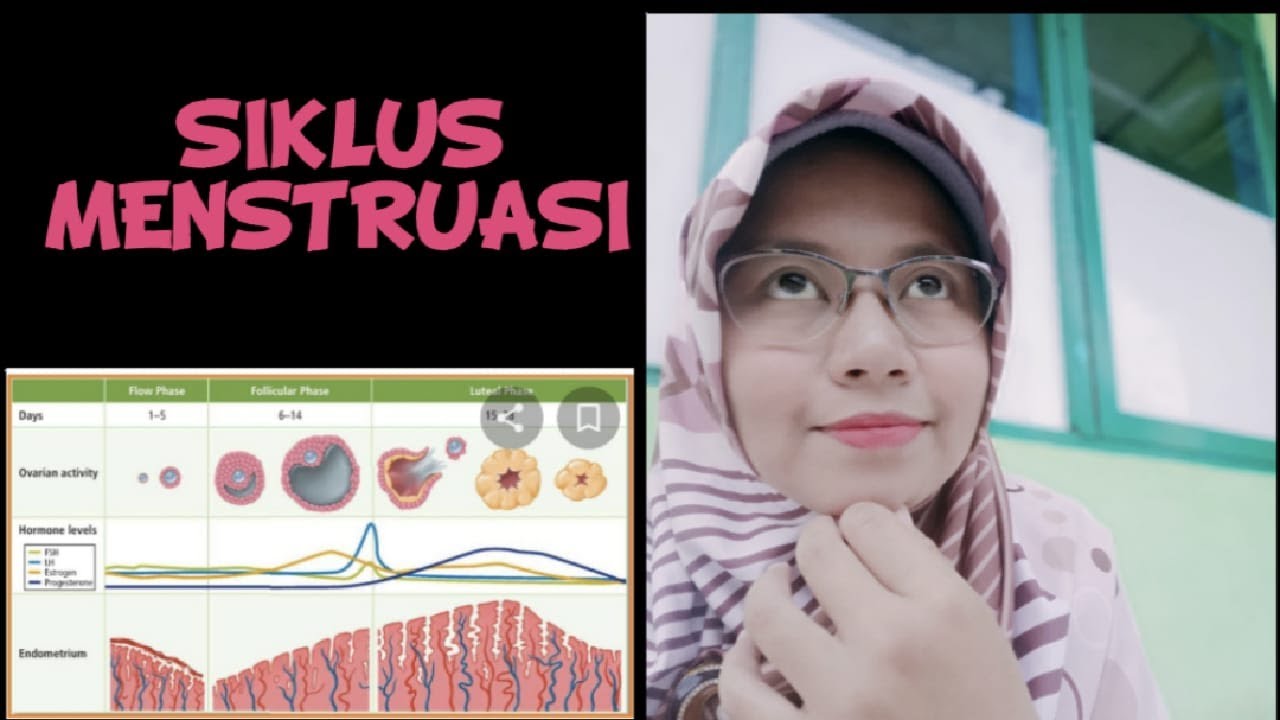
Siklus Menstruasi (Reproduksi Manusia)

Ciclo Menstrual - Aula 35 - Módulo VII: Fisiologia Humana | Prof. Gui
CICLO MENSTRUAL (FISIOLOGIA DE GUYTON) - MENSTRUAÇÃO - FISIOLOGIA HUMANA - OVULAÇÃO
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)