Siklus menstruasi - Biologi kelas 11 SMA
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the presenter explains the menstrual cycle in detail, specifically for high school students studying biology. The cycle is divided into four phases: menstruation, pre-ovulation, ovulation, and post-ovulation. The video outlines how hormonal interactions between estrogen, progesterone, and LH regulate the cycle. It also describes the changes in the ovaries and uterine lining, such as the shedding of the endometrium during menstruation, the development of egg follicles, and the hormonal shifts leading to ovulation. Finally, it covers the changes during the post-ovulatory phase, including what happens when no fertilization occurs.
Takeaways
- 😀 The menstrual cycle is a complex process involving the interaction between the endocrine system (hormones) and the reproductive system.
- 😀 Hormones such as estrogen, LH, and progesterone play key roles in regulating the menstrual cycle.
- 😀 The menstrual cycle is divided into two main cycles: the uterine cycle and the ovarian cycle.
- 😀 The menstrual cycle has four main phases: menstruation, pre-ovulation, ovulation, and post-ovulation.
- 😀 Menstruation occurs from day 1 to day 5, marking the shedding of the uterine lining and unfertilized egg.
- 😀 The pre-ovulation phase (days 6-13) involves the growth of ovarian follicles and the thickening of the uterine lining.
- 😀 Ovulation typically occurs on day 14, when the mature follicle releases the secondary oocyte.
- 😀 Post-ovulation (days 15-28) is marked by the formation of the corpus luteum, which secretes hormones to prepare the uterus for potential implantation.
- 😀 If fertilization does not occur, the corpus luteum degenerates, leading to a drop in hormone levels and the shedding of the uterine lining.
- 😀 Menstruation is the body's natural process of shedding the endometrial lining and is triggered when an egg is not fertilized by sperm.
- 😀 If fertilization and implantation do not occur by day 26, the corpus luteum turns into corpus albicans, causing the cycle to reset with menstruation.
Q & A
What is the menstrual cycle, and how is it defined?
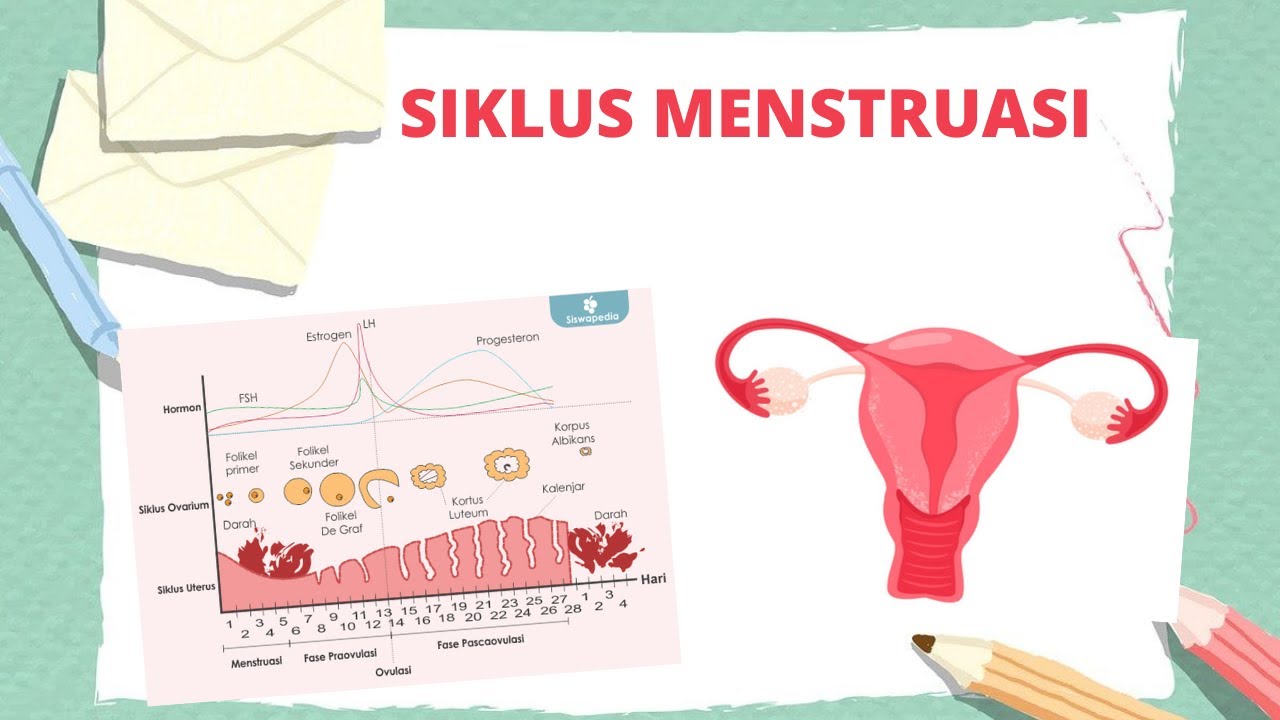
-The menstrual cycle is a complex process that results from the interaction between the endocrine (hormonal) system and the reproductive system. It involves hormones like estrogen, LH, and progesterone and includes changes in the uterus and ovaries.
What hormones are involved in the menstrual cycle?
-The main hormones involved in the menstrual cycle are estrogen, luteinizing hormone (LH), and progesterone. These hormones regulate the development of the egg and the changes in the uterine lining.
How is the menstrual cycle divided?
-The menstrual cycle is divided into four main phases: menstruation, pre-ovulation, ovulation, and post-ovulation (luteal phase). These phases reflect different hormonal and physiological changes in the body.
What happens during the menstruation phase of the cycle?
-During menstruation, the endometrial lining of the uterus is shed along with the unfertilized egg. This phase occurs when fertilization does not take place, leading to a decrease in estrogen and progesterone production.
What is the pre-ovulation phase and what happens during it?
-The pre-ovulation phase, occurring between days 6-13 of the cycle, involves the secretion of gonadotropin hormones like FSH, which stimulate the growth of the egg follicle in the ovaries. Estrogen is released, causing the endometrial lining to thicken.
What is the role of FSH in the menstrual cycle?
-FSH, or Follicle-Stimulating Hormone, stimulates the growth of the ovarian follicle, which contains the egg. It plays a key role in preparing the egg for ovulation.
What triggers ovulation, and when does it occur?
-Ovulation is triggered by a surge in LH (Luteinizing Hormone), which causes the mature follicle to release the secondary oocyte (egg). This typically occurs on day 14 of the menstrual cycle.
What happens after ovulation during the post-ovulation phase?
-After ovulation, the ruptured follicle transforms into the corpus luteum, which secretes progesterone. This hormone helps maintain the thickened endometrium, preparing it for potential embryo implantation.
What happens if no fertilization occurs after ovulation?
-If fertilization does not occur, the corpus luteum breaks down into a structure called the corpus albicans, which no longer produces hormones. As a result, the endometrial lining sheds, leading to the next menstruation phase.
How long is the average menstrual cycle?
-The average menstrual cycle lasts about 28 days, though it can vary from person to person. The phases of the cycle include menstruation (days 1-5), pre-ovulation (days 6-13), ovulation (day 14), and post-ovulation (days 15-28).
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Siklus Menstruasi : Memahami Gambar (Mudah dipahami)

SISTEM SIRKULASI| B. SISTEM LIMFA DAN C. GANGGUAN SISTEM PEREDARAN DARAH| X SMA/MA|KURIKULUM MERDEKA

THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE
Siklus menstruasi - Grafik siklus menstruasi dan penjelasannya

COURS DE TERMINALE SPÉCIALITÉ SVT : CHAP.1: STABILITÉ GÉNÉTIQUE ET ÉVOLUTION CLONALE - Bio Logique

Reproduksi Fungi (Jamur)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)