CORRELATION - Cross Correlation, Auto Correlation and Circular Correlation
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a comprehensive explanation of the three main types of correlation: cross-correlation, autocorrelation, and circular correlation. It breaks down each type with examples, demonstrating how to calculate and interpret them. Cross-correlation involves comparing two different variables, while autocorrelation analyzes a single variable. Circular correlation uses a matrix approach to account for cyclic patterns in data. Through detailed step-by-step instructions, the video explains how to mirror sequences, perform dot products, and compute sums to find correlation values. The video aims to help viewers understand these concepts with clarity and practical examples.
Please replace the link and try again.
Q & A
What are the three types of correlation discussed in the video?
-The three types of correlation discussed in the video are cross-correlation, autocorrelation, and circular correlation.
What is cross-correlation, and how is it represented?
-Cross-correlation involves two different variables, X and Y. It is represented as RXY, where X and Y are the variables being compared.
How do you calculate cross-correlation between two sequences X(n) and Y(n)?
-To calculate cross-correlation, the values of X(n) and Y(n) are combined by multiplying corresponding values. The process involves reversing the Y values (Y(-n)) and shifting them relative to X(n), followed by summing the products at each shift position.
What is the significance of reversing the Y values in cross-correlation?
-Reversing the Y values (Y(-n)) is crucial in the cross-correlation process because it aligns the sequences correctly for multiplication and summation. This helps to compare how similar the two sequences are at different shifts.
In cross-correlation, what does the output matrix represent?
-The output matrix in cross-correlation shows the sum of products at different shifts between the two sequences, representing the degree of correlation at each shift.
What is autocorrelation and how does it differ from cross-correlation?
-Autocorrelation refers to the correlation of a sequence with itself. Unlike cross-correlation, which compares two different sequences, autocorrelation involves only one sequence (X or Y) and measures how it relates to itself over time.
How do you calculate autocorrelation for a sequence X(n)?
-To calculate autocorrelation, the sequence X(n) is multiplied by a shifted version of itself, X(-n), and the products are summed. This is done for different shifts, similar to cross-correlation, but only for the same sequence.
What is circular correlation and how is it calculated?
-Circular correlation involves the correlation of two sequences, X(n) and Y(n), using a circular shift. This type of correlation uses a matrix format, where one sequence is shifted in a circular manner and then multiplied with the other sequence at each shift position.
What makes circular correlation different from other types of correlation?
-Circular correlation differs from cross-correlation and autocorrelation because it applies circular shifts to the sequences rather than linear shifts. The sequences wrap around, which changes how their correlation is calculated.
Why is it important to maintain the correct order of X(n) and Y(n) in circular correlation?
-Maintaining the correct order of X(n) and Y(n) in circular correlation is essential because switching them will result in an incorrect answer. The sequence in the rows of the matrix must correspond to Y(n), and the sequence in the columns must correspond to X(n).
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
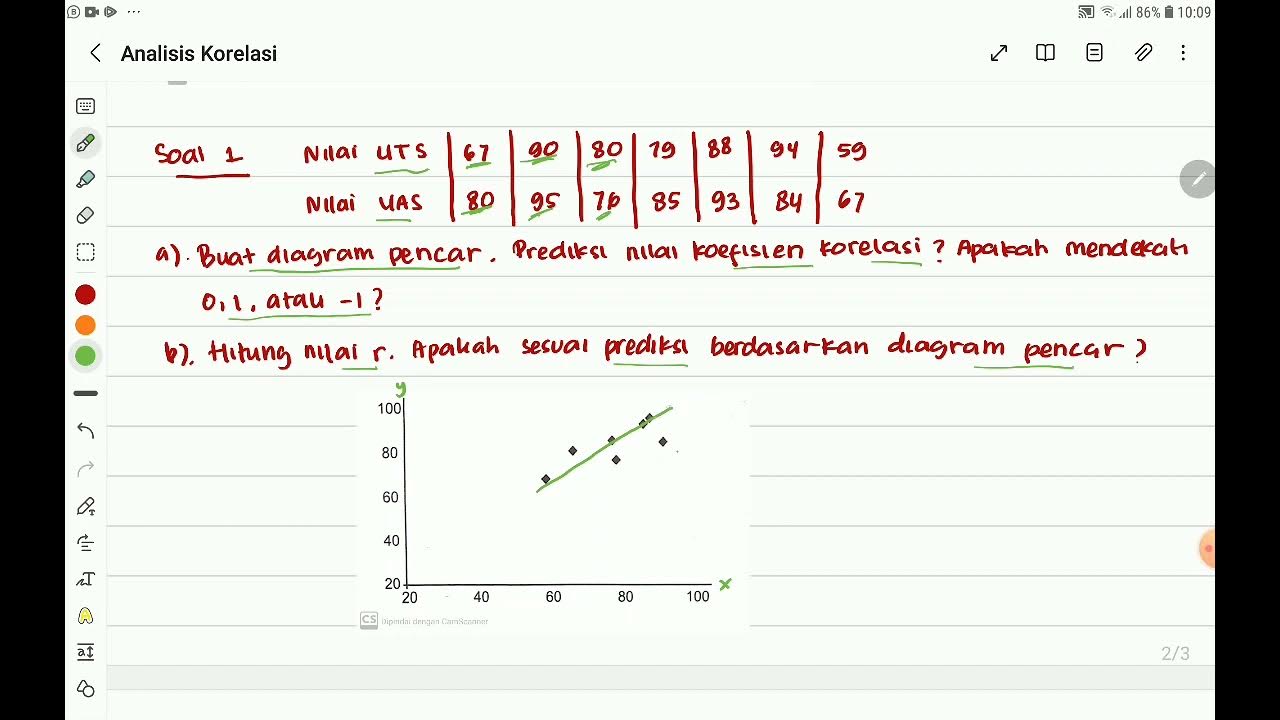
Analisis Korelasi "Nilai Koefisien Korelasi dan Tingkat Korelasi" Part 1 Mtk 11 SMA Kmerdeka

KULIAH STATISTIK - ANALISIS KORELASI
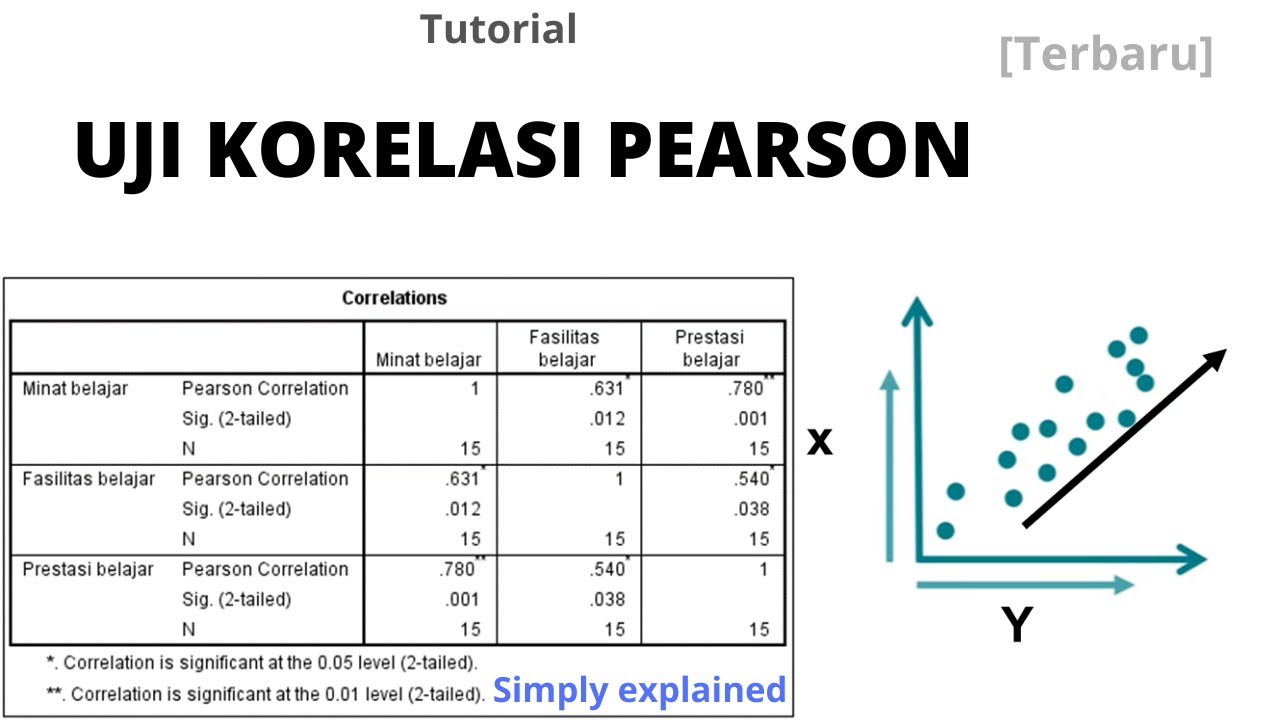
Memahami Uji Korelasi Pearson dan Cara Analisis dengan SPSS

Correlation Analysis - Full Course in 30 min

Acara 4 Korelasi Genetik Pemuliaan Ternak 2023
Correlation vs Regression | Difference Between Correlation and Regression | Statistics | Simplilearn
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)