KULIAH STATISTIK - ANALISIS KORELASI
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a comprehensive overview of correlation analysis in statistics, focusing on its application in education. It explains how correlation helps in understanding the relationship between two variables, either positive or negative, and how to calculate it manually. The video covers both Pearson’s Product Moment and Spearman’s Rank Correlation for different types of data. Through examples, viewers learn to interpret correlation coefficients, test hypotheses, and determine the strength of relationships between variables, offering a clear guide for students in educational statistics courses.
Takeaways
- 😀 Correlation analysis is used to determine the strength and direction of relationships between two or more variables.
- 😀 The correlation coefficient represents the degree of relationship, with values ranging from -1 to 1. Positive values indicate a direct relationship, and negative values indicate an inverse relationship.
- 😀 A positive relationship means as one variable increases, the other also increases. An example is the relationship between study motivation and academic performance.
- 😀 A negative relationship means as one variable increases, the other decreases. An example is the relationship between the duration of the COVID-19 pandemic and students' online learning engagement.
- 😀 Correlation analysis is categorized into simple correlation (for two variables) and multiple correlation (for more than two variables).
- 😀 In simple correlation, Pearson's Product-Moment is used for interval or ratio data, and Spearman's Rank Correlation is used for ordinal data.
- 😀 The formula for Pearson's Product-Moment correlation is based on the sum of products of paired scores, and it measures linear relationships between variables.
- 😀 The hypothesis test for correlation involves testing the null hypothesis (no relationship) and the alternative hypothesis (there is a relationship).
- 😀 When calculating Pearson’s correlation, it is important to distinguish between the sum of squares of individual variables (Σx², Σy²) and the square of the sum of the variables (Σx)² and (Σy)².
- 😀 The calculated correlation coefficient (r) is compared with the critical value (r-table) to determine if the null hypothesis should be rejected or accepted. If r is larger than the critical value, the null hypothesis is rejected.
- 😀 Spearman’s Rank Correlation is used when data is ordinal, and it involves ranking the data before applying the formula. It is calculated using the differences between ranks of paired data points.
Q & A
What is correlation analysis used for?
-Correlation analysis is used to determine the degree of relationship between two or more variables. It helps to understand how one variable may influence or relate to another.
How is the degree of correlation represented?
-The degree of correlation is represented by the correlation coefficient, which indicates both the strength and direction (positive or negative) of the relationship between the variables.
What does a positive correlation mean?
-A positive correlation means that as one variable increases, the other also increases. For example, if motivation to study increases, academic performance also improves.
What is a negative correlation?
-A negative correlation occurs when one variable increases while the other decreases. For example, increased time in a situation like the COVID-19 pandemic may lead to higher boredom, which negatively affects student engagement.
What are the two main types of correlation analysis methods?
-The two main types of correlation analysis are Pearson's Product-Moment correlation (for interval or ratio data) and Spearman's Rank correlation (for ordinal data).
When should Pearson’s Product-Moment correlation be used?
-Pearson's Product-Moment correlation should be used when the data is in interval or ratio form, where the relationship between the two variables can be measured with a continuous scale.
What type of data is Spearman's Rank correlation used for?
-Spearman's Rank correlation is used for ordinal data, which involves variables that have a natural order or ranking, such as ratings or positions.
What is the formula for Pearson’s Product-Moment correlation?
-The formula for Pearson’s Product-Moment correlation is: r = (nΣxy - ΣxΣy) / √[(nΣx² - (Σx)²)(nΣy² - (Σy)²)], where n is the number of data points, Σxy is the sum of the product of x and y, and Σx and Σy are the sums of x and y respectively.
How do you interpret the result of Pearson’s correlation coefficient?
-The result of Pearson's correlation coefficient (r) ranges from -1 to +1. A value close to +1 indicates a strong positive correlation, while a value close to -1 indicates a strong negative correlation. A value around 0 indicates no correlation.
What steps are involved in calculating correlation using Pearson’s method?
-The steps in calculating Pearson's correlation include: (1) formulating the null and alternative hypotheses, (2) collecting and organizing data, (3) calculating the necessary sums (Σx, Σy, Σxy), (4) applying the formula for the correlation coefficient, and (5) comparing the calculated value with the critical value from the table to determine significance.
What is the role of the critical value (r-table) in hypothesis testing?
-The critical value (r-table) is used to compare with the calculated correlation coefficient. If the calculated r is greater than the critical value, the null hypothesis (no correlation) is rejected, and it is concluded that there is a statistically significant relationship between the variables.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
一夜。統計學:敘述統計
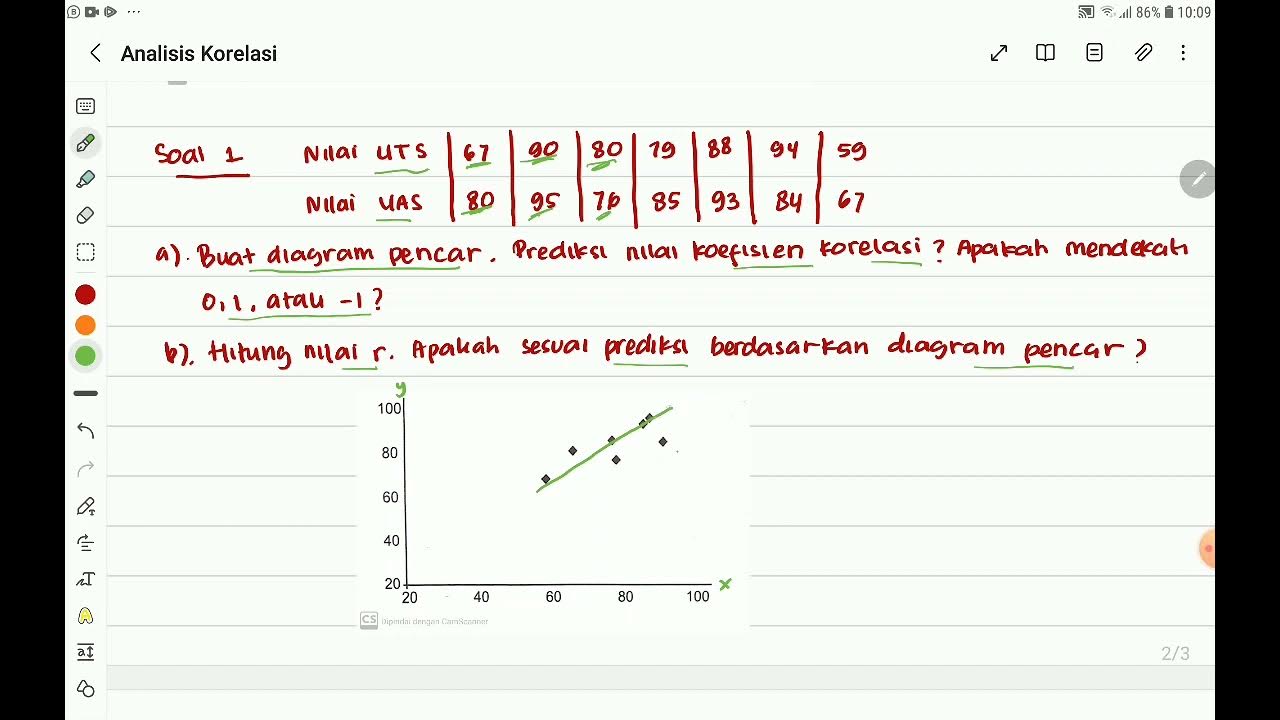
Analisis Korelasi "Nilai Koefisien Korelasi dan Tingkat Korelasi" Part 1 Mtk 11 SMA Kmerdeka

Statistika Bivariat: Mengungkap Hubungan Dua Variabel!

Correlation Analysis - Full Course in 30 min

Analisis Korelasi#STIE GICI

Pearson Correlation Analysis using SPSS - Running, Interpreting, and Reporting
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)