Detail construction of transformer with animation | transformer construction with animation
Summary
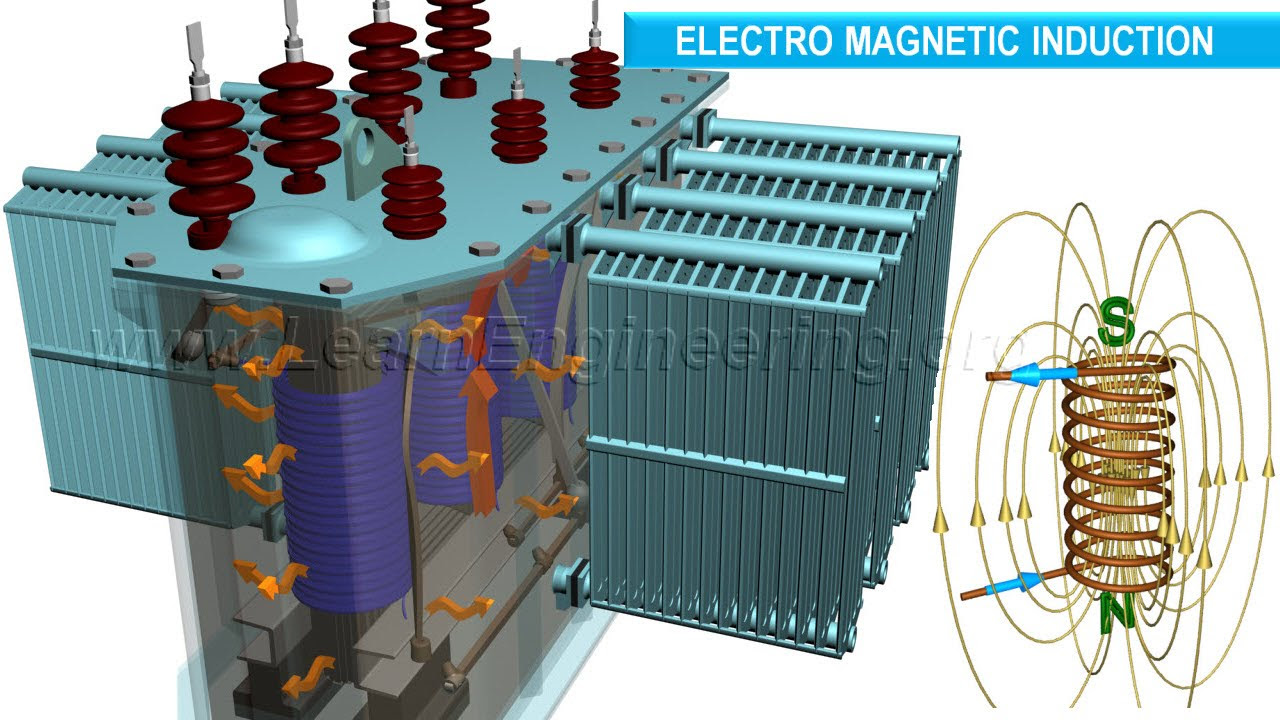
TLDRThis video provides a detailed and animated breakdown of transformer construction, covering essential components such as windings, core, bushings, oil, and the outer body. It explains the function and material choices for each part, including copper and aluminum windings, silicon steel cores, and transformer oil. The video also explores how these parts work together to transfer magnetic flux, manage heat, and ensure safety. Additionally, it highlights protective features like the breather, conservator tank, and explosion vent, offering a comprehensive understanding of the transformer's structure and function.
Takeaways
- 😀 The transformer has multiple components, including windings, a core, and an outer body, each serving important roles in its operation.
- 😀 Windings in a transformer are typically made of copper or aluminum, with copper being preferred for its higher efficiency.
- 😀 The primary winding of a transformer is connected to the source, while the secondary winding is connected to the load.
- 😀 The transformer core is made of laminated sheets of silicon steel, which help in carrying magnetic flux efficiently.
- 😀 There are two main types of transformer core designs: core-type and shell-type. Core-type has windings on the outside, while shell-type has windings on the inside.
- 😀 The outer body of the transformer serves to protect the internal components, contain transformer oil, and provide support for accessories.
- 😀 Transformer oil has two main purposes: insulation and heat dissipation. It circulates inside the transformer and cools down the windings through radiators.
- 😀 The conservator tank, mounted above the transformer, helps accommodate oil expansion and contraction due to temperature changes.
- 😀 A breather connected to the conservator tank uses silica gel to absorb moisture from the air, preventing moisture from mixing with the oil and reducing dielectric strength.
- 😀 Explosion vents are included in transformers to release excess pressure, ensuring the transformer doesn't suffer damage due to sudden faults.
Q & A
What is the primary material used to construct transformer windings?
-The primary material used to construct transformer windings is copper. However, in cases where cost is a major factor, aluminum can also be used.
What is the purpose of the primary winding in a transformer?
-The primary winding's purpose is to produce a magnetic field in the transformer.
How do we distinguish between the primary and secondary windings in a transformer?
-The primary winding is connected to the source, while the secondary winding is connected to the load.
What material is used for the transformer core, and why is it used?
-The transformer core is made up of silicon steel material. This material is used due to its high permeability, which helps in efficiently transferring magnetic flux between the primary and secondary windings.
What are the two types of transformer core designs mentioned in the video?
-The two types of transformer core designs are core type and shell type transformers.
In a core-type transformer, how are the windings arranged?
-In a core-type transformer, the low-voltage (LV) winding is placed inside, while the high-voltage (HV) winding is placed outside due to insulation considerations.
What is the role of transformer oil?
-Transformer oil serves two main purposes: providing insulation and dissipating heat generated by the current flowing through the windings.
What is the function of the conservator tank in a transformer?
-The conservator tank is mounted on top of the transformer and provides space for oil to expand and contract due to temperature changes, ensuring that the transformer remains at a safe operational pressure.
What is the purpose of the breather in a transformer?
-The breather absorbs moisture from the air before it enters the conservator tank, preventing moisture from mixing with transformer oil, which could degrade its dielectric strength.
What is the function of the explosion vent in a transformer?
-The explosion vent provides an emergency exit for gases or oil in case of excessive pressure buildup within the transformer, protecting it from further damage.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

KOMPONEN TRANSFORMER | TRAFO DISTRIBUSI 20KV

How Power Transformers work ? | Epic 3D Animation #transformers

Construction of DC Machine and Its Components - DC Machines - Basic Electrical Engineering

transformer design part 1 SINGLE PHASE CORE TYPE TRANSFORMER.

IPA Kelas 9 Semester 2 : Kemagnetan (part 5 : Transformator)
How does a Transformer work ?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)