POPULASI DAN SAMPEL - STATISTIKA SOSIAL
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the essential concepts of population and sample in social statistics for a journalism program. It distinguishes between the two, emphasizing that a population includes the entire group of subjects under study, while a sample is a subset of that population. The video covers various data collection methods like census and survey, and dives deep into sampling techniques, such as probability sampling (e.g., random, systematic, and stratified sampling) and non-probability sampling (e.g., quota and snowball sampling). Key considerations in sampling, including population homogeneity and sample size, are also discussed.
Takeaways
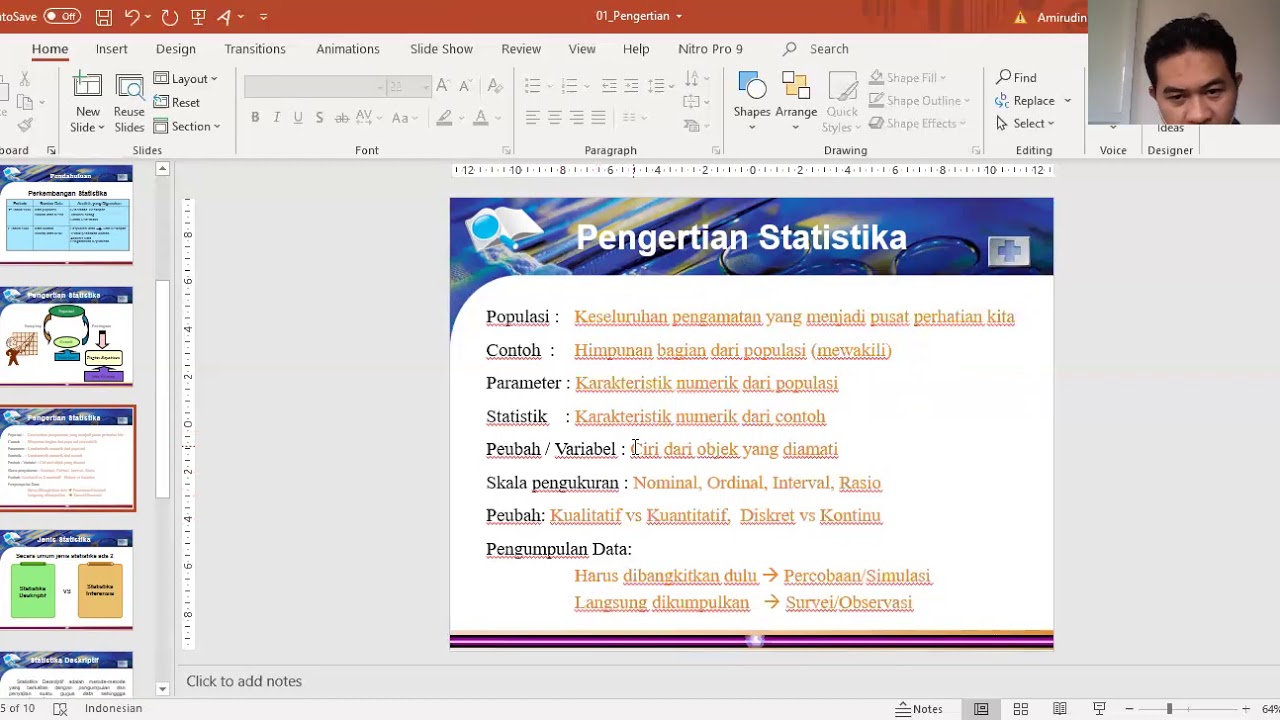
- 😀 Populations represent the entire set of subjects or objects under study, while samples are subsets of the population selected for observation.
- 😀 A **census** is used to collect data from the entire population, whereas a **survey** is used for sample data collection.
- 😀 Population data provides **parameters**, whereas sample data yields **statistics**.
- 😀 Defining your population correctly is crucial before starting research; it sets the foundation for accurate data collection.
- 😀 Examples of populations can include all viewers of a YouTube TV show or students using social media to follow politics.
- 😀 Sampling involves identifying the target population and creating a sample framework to draw conclusions.
- 😀 **Probability sampling** techniques ensure every member of the population has a chance of being selected. Methods include **simple random**, **systematic**, **stratified**, and **cluster sampling**.
- 😀 **Non-probability sampling** is subjective and doesn't guarantee representative samples. Techniques include **accidental sampling**, **quota sampling**, **purposeful sampling**, and **snowball sampling**.
- 😀 Ensuring **homogeneity** in the population means the sample closely mirrors the characteristics of the population.
- 😀 Sample size and error tolerance play a key role in ensuring the representativeness and accuracy of a sample.
- 😀 **Stratified sampling** considers proportions of different subgroups in the population, while **cluster** and **area sampling** are used when the population is large and difficult to handle.
Q & A
What is the difference between population and sample in research?
-Population refers to the entire group of subjects or objects that are being studied, while a sample is a smaller subset of the population selected for observation or analysis.
What are the methods to collect data for population and sample?
-For data related to a population, the method used is a census. For data related to a sample, the method used is a survey.
How do you define a population accurately in research?
-To define a population accurately, researchers must determine the entire group that matches the specific criteria relevant to their study. This is done by clearly specifying the target group based on factors like location, behavior, or characteristics.
What is the significance of identifying a target population?
-Identifying the target population is crucial for ensuring the research focuses on the relevant group, which helps in collecting meaningful and representative data.
What is the role of sample frame in research?
-A sample frame is a list or a comprehensive record of all members of the population. It's necessary when using probability sampling to select a representative sample.
What factors affect the representativeness of a sample?
-The factors that affect the representativeness of a sample include the homogeneity of the population, the sample size, and the technique used for sampling.
What is the difference between probability sampling and non-probability sampling?
-In probability sampling, every individual has a known and equal chance of being selected, while in non-probability sampling, selection is subjective and does not ensure every individual has an equal chance.
What are the types of probability sampling?
-The types of probability sampling include simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and two-stage sampling (cluster and area sampling).
What is the difference between proportional and disproportional stratified sampling?
-Proportional stratified sampling ensures that the sample reflects the population's proportions, while disproportional stratified sampling allocates the same number of samples to each group regardless of their population size.
When should non-probability sampling be used?
-Non-probability sampling should be used when the goal of the research is not to generalize findings to the broader population but to gain deeper insights into specific groups or phenomena, typically in exploratory or qualitative research.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Statistics for Social Work Lecture 01

Perbedaan Antara Statistika Deduktif dan Statistika Induktif dalam Analisis Data

POBLACIÓN, MUESTRA Y MUESTREO

KUPAS TUNTAS: Apakah Perbedaan Statistik Inferensial dengan Statistik Deskriptif ?

KUPAS TUNTAS: Apakah Perbedaan Statistik Inferensial dengan Statistik Deskriptif ?
Pertemuan 1 Statistika sosial
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)