Physics 13.3.2b - Examples
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script explains the calculation of heat produced by electrical appliances using Ohm's Law and power formulas. It covers four examples: a 15-ohm oven heating at 120 volts, a 75-watt light bulb left on for 10 hours, a toaster needing 54,000 joules in 90 seconds, and a 12-volt hairdryer drawing 12 amps for 1 minute. Each example demonstrates how to find current, resistance, power, and heat (in joules), illustrating the energy consumption of household appliances.
Takeaways
- 🔌 The given oven has a heating element with a resistance of 15 ohms and operates at a standard household voltage of 120 volts.
- ⚡ To find the current (I) flowing through the oven, Ohm's law (I = V/R) is used, resulting in a current of 8 amps.
- 🔥 The heat (H) produced by the oven in 30 minutes (1800 seconds) can be calculated using the formula H = I^2 * R * t, yielding 1,728,000 joules (jewels).
- 💡 For a 75-watt, 120-volt light bulb left on for 10 hours, the heat produced is calculated using the formula H = P * t, resulting in 2,700,000 joules (jewels).
- ⏱ The toaster example involves calculating the resistance and current needed to produce 54,000 joules of heat in 90 seconds using standard household electricity.
- 🍞 The power (P) used by the toaster is found by dividing the energy (54,000 joules) by the time (90 seconds), resulting in 600 watts.
- 🛠 The resistance (R) of the toaster is calculated using the formula R = V^2 / P, giving a resistance of 24 ohms.
- 🔌 The current (I) drawn by the toaster is found using the formula I = P / V, resulting in 5 amps.
- 🌬 A 12-volt hair dryer drawing 12 amps of current is used to find the heat produced in 1 minute using the formula H = I * V * t.
- ⏳ The heat produced by the hair dryer in 1 minute is calculated as 86,400 joules (jewels).
- 📚 The script demonstrates the application of electrical formulas to calculate heat produced in various household appliances, emphasizing the relationship between power, resistance, current, and time.
Q & A
What is the resistance of the oven's heating element mentioned in the script?
-The resistance of the oven's heating element is 15 ohms.
What is the standard voltage in a household electrical outlet in the United States as per the script?
-The standard voltage in a household electrical outlet in the United States is 120 volts.
How can you calculate the current (I) flowing through the oven using Ohm's Law?
-You can calculate the current (I) using Ohm's Law, which states I = V/R, where V is the voltage and R is the resistance. In this case, I = 120 volts / 15 ohms, which equals 8 amps.
What formula is used to calculate the heat (H) produced by the oven?
-The formula used to calculate the heat (H) produced by the oven is H = I^2 * R * T, where I is the current in amps, R is the resistance in ohms, and T is the time in seconds.
How many joules of heat does the oven produce in 30 minutes?
-The oven produces 1,728,000 joules of heat in 30 minutes.
What is the power rating of the light bulb in the second example?
-The power rating of the light bulb in the second example is 75 watts.
How many joules of heat does a 75-watt light bulb produce if left on for 10 hours?
-A 75-watt light bulb produces 2,700,000 joules of heat if left on for 10 hours.
What is the formula to calculate the resistance (R) of the toaster in the third example?
-The formula to calculate the resistance (R) of the toaster is R = V^2 / P, where V is the voltage and P is the power.
How many ohms of resistance does the toaster have, and what current does it draw according to the script?
-The toaster has 24 ohms of resistance and draws 5 amps of current.
What is the heat produced by a 12-volt hair dryer drawing 12 amps of current in 1 minute?
-The heat produced by a 12-volt hair dryer drawing 12 amps of current in 1 minute is 864,000 joules.
How can you express the power (P) of an electrical device in terms of current (I) and voltage (V)?
-You can express the power (P) of an electrical device as P = I * V, where I is the current in amps and V is the voltage in volts.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

FISIKA Kelas 12 - Energi dan Daya Listrik | GIA Academy

All FORMULAS Of ELECTRICITY Class 10 in 60 Sec🔥| CBSE 10th Electricity Important Formulas #Cbse2024
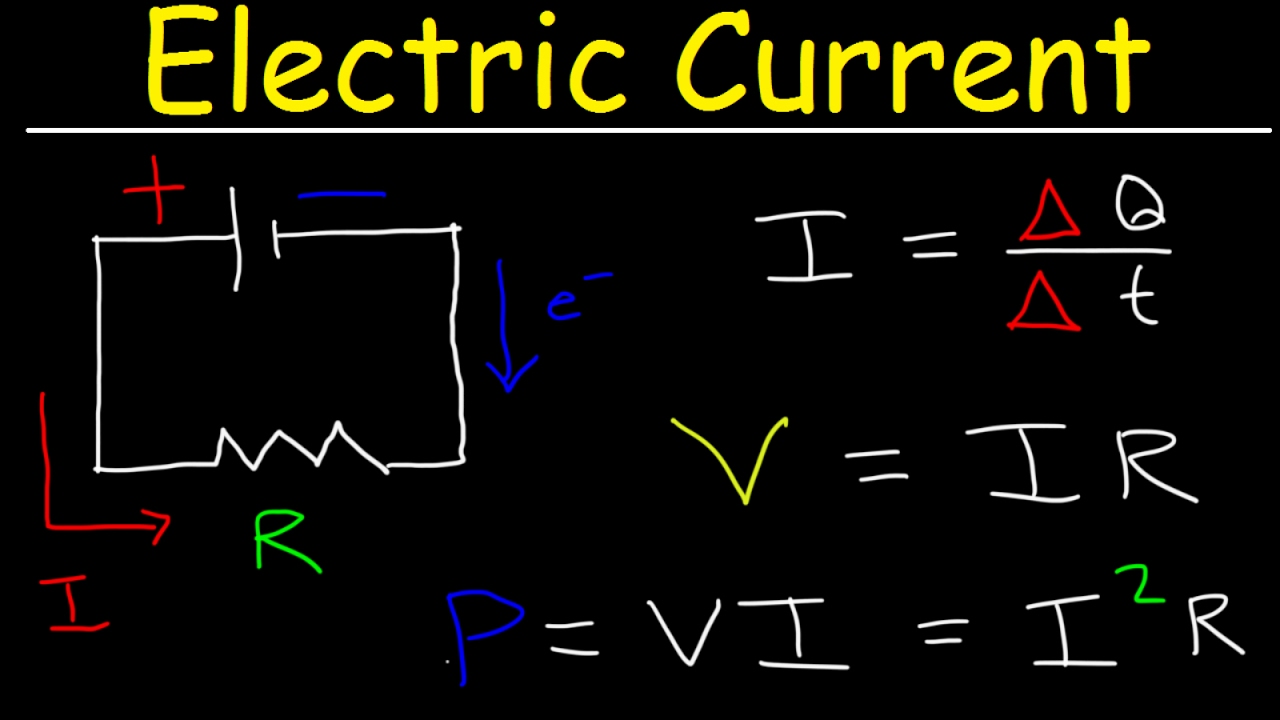
Electric Current & Circuits Explained, Ohm's Law, Charge, Power, Physics Problems, Basic Electricity

Intro to Ohms Law

GCSE Physics Revision "Energy Transfer by Appliances"

Basic Electricity - Resistance and Ohm's law
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)