Sebuah benda bermassa 10 kg bergerak dengan kecepatan 20 mls: Dengan mengabaikan gaya gesek yang ...
Summary
TLDRIn this physics tutorial, the topic of work, energy, and kinetic energy is explored through a problem involving an object with a mass of 10 kg moving from an initial velocity of 20 m/s to a final velocity of 30 m/s. The change in kinetic energy is calculated using the formula ΔEK = 1/2 * m * (v2² - v1²), resulting in a value of 2.5 kJ. The explanation highlights the relationship between an object's mass, velocity, and kinetic energy, demonstrating how changes in velocity can significantly affect the energy of an object.
Takeaways
- 😀 The problem involves calculating the change in kinetic energy (ΔEK) for a 10 kg object moving at different speeds.
- 😀 The initial velocity (V1) of the object is 20 m/s and the final velocity (V2) is 30 m/s.
- 😀 The formula for kinetic energy (EK) is EK = 1/2 * m * v^2, where m is mass and v is velocity.
- 😀 The change in kinetic energy (ΔEK) is found by subtracting the initial kinetic energy from the final kinetic energy.
- 😀 The formula for ΔEK can be simplified to ΔEK = 1/2 * m * (V2^2 - V1^2).
- 😀 The given mass of the object is 10 kg, which remains constant throughout the calculation.
- 😀 Plugging in the values into the formula: ΔEK = 1/2 * 10 * (30^2 - 20^2).
- 😀 The velocities squared are 900 (for V2) and 400 (for V1), so ΔEK = 1/2 * 10 * 500.
- 😀 This simplifies to ΔEK = 2500 Joules, which is the change in kinetic energy of the object.
- 😀 The change in kinetic energy is also equivalent to 2.5 kJ, as 1000 Joules equals 1 kJ.
- 😀 The result shows that kinetic energy is directly proportional to the mass and the square of the velocity of an object.
Q & A
What is the formula for kinetic energy?
-The formula for kinetic energy is Ek = 1/2 * m * v^2, where 'm' is the mass of the object and 'v' is its velocity.
How do you calculate the change in kinetic energy (ΔEk)?
-The change in kinetic energy is calculated as ΔEk = Ek2 - Ek1, where Ek2 is the final kinetic energy and Ek1 is the initial kinetic energy.
What are the given values in this problem?
-The given values are: mass (m) = 10 kg, initial speed (v1) = 20 m/s, and final speed (v2) = 30 m/s.
Why is the mass of the object considered constant in this problem?
-The mass of the object remains constant in this problem because no forces (such as friction or external forces) are affecting its mass during the motion.
How is the change in kinetic energy calculated in this problem?
-The change in kinetic energy is calculated as ΔEk = 1/2 * m * (v2^2 - v1^2), substituting the given values gives ΔEk = 5 * (900 - 400) = 2500 Joules.
What does the result of 2500 Joules represent in this context?
-The result of 2500 Joules represents the increase in the kinetic energy of the object as it accelerates from 20 m/s to 30 m/s.
Why is the energy change linear with respect to velocity?
-The change in kinetic energy is quadratic with respect to velocity, as kinetic energy is proportional to the square of velocity. Therefore, any change in velocity has a squared effect on the energy change.
What would happen to the kinetic energy if the object's mass were increased?
-If the mass of the object were increased, the kinetic energy would also increase, as kinetic energy is directly proportional to mass.
Why is friction ignored in this calculation?
-Friction is ignored in this calculation to simplify the problem and focus only on the change in kinetic energy due to the change in velocity.
How is the final answer of 2.5 KJ derived from the initial 2500 Joules?
-Since 1000 Joules equals 1 kilojoule (KJ), 2500 Joules is equivalent to 2.5 KJ.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Physics 10 Momentum and Impulse (5 of 30) Why you Don't Want to Collide with a Semi Truck
Kinetic energy derivation | Work & Energy | Physics | Khan Academy
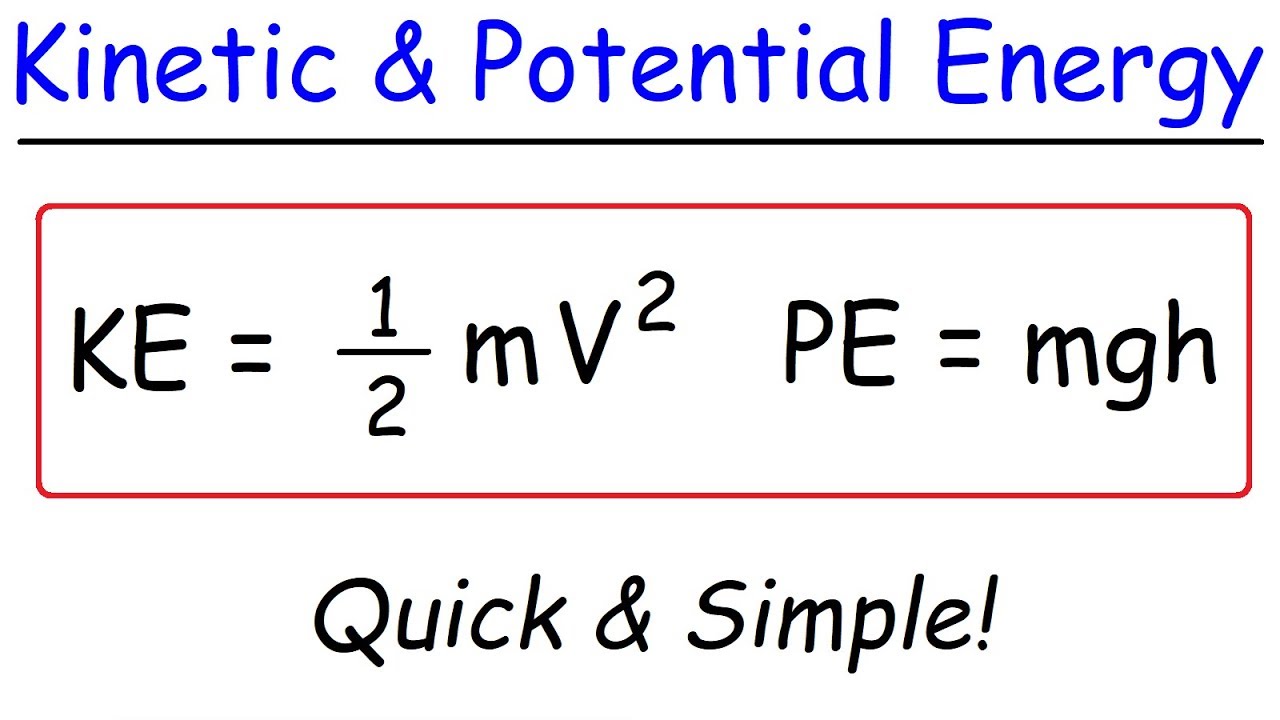
Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy

Free Fall Problems

HUBUNGAN USAHA DAN ENERGI KINETIK

Teorema da energia cinética - Trabalho e variação de energia cinética
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)