Kinetic energy derivation | Work & Energy | Physics | Khan Academy
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the concept of kinetic energy is explored through the example of a 2 kg cricket ball moving at 10 meters per second. The video explains how kinetic energy is the capacity of a moving object to do work, using the ball's interaction with a hand as an example. By applying Newton’s laws and the equations of motion, the formula for kinetic energy—1/2 mv²—is derived. The video concludes by calculating the kinetic energy of the cricket ball to be 100 joules, demonstrating how mass and velocity influence an object’s energy and ability to do work.
Takeaways
- 😀 Kinetic energy is the capacity of a moving object to do work.
- 😀 The kinetic energy of an object depends on its mass and velocity.
- 😀 The formula for kinetic energy is KE = 1/2 m u², where m is mass and u is velocity.
- 😀 The maximum kinetic energy is determined by the maximum work an object can do, such as when it comes to a stop after hitting something.
- 😀 To calculate kinetic energy, you must first calculate the work done, which is force times displacement.
- 😀 Newton's second law (F = ma) is used to relate force to mass and acceleration, but in this context, force on the hand is replaced by force on the ball using Newton's third law.
- 😀 Work is done when an object (like a ball) exerts force on another object (like a hand) and causes displacement.
- 😀 The velocity of an object is a crucial factor in determining its kinetic energy—higher velocity means more kinetic energy.
- 😀 An object with a higher mass will also have more kinetic energy at the same velocity, as it can exert a stronger force.
- 😀 Example: A 2 kg cricket ball moving at 10 m/s has a kinetic energy of 100 joules, meaning it can do 100 joules of work when it hits something.
Q & A
What is kinetic energy?
-Kinetic energy is the energy possessed by an object due to its motion. It is the capacity of the object to do work as a result of its movement.
How do you calculate the kinetic energy of an object?
-Kinetic energy is calculated using the formula: KE = 1/2 * m * u², where 'm' is the mass of the object and 'u' is its velocity.
What is the definition of work in the context of kinetic energy?
-Work is defined as the force exerted on an object over a displacement. In the context of kinetic energy, work is done when a moving object transfers energy by exerting force on another object, causing displacement.
Why is the velocity squared in the kinetic energy formula?
-The velocity is squared because the kinetic energy increases with the square of the velocity. This reflects the fact that as the speed of an object increases, its ability to do work increases exponentially.
How does the mass of an object affect its kinetic energy?
-The mass of an object is directly proportional to its kinetic energy. A heavier object (with more mass) moving at the same speed will have more kinetic energy because it has more capacity to do work.
How does the concept of 'capacity to do work' relate to kinetic energy?
-Kinetic energy represents the maximum amount of work an object can do when it collides with another object or comes to a stop. The more work it can do, the greater its kinetic energy.
What is the role of Newton's second law in deriving the formula for kinetic energy?
-Newton's second law (F = ma) helps connect force with motion, allowing the derivation of kinetic energy by linking mass, acceleration, and displacement in the formula for work.
How does Newton's third law of motion apply to calculating kinetic energy?
-Newton's third law states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. In the context of kinetic energy, it means that the force exerted by a moving object on another object is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force exerted back on the moving object.
Why do we need to use the equations of motion in deriving kinetic energy?
-The equations of motion help us connect velocity, acceleration, and displacement, which are needed to eliminate acceleration and displacement from the equation and obtain a formula that involves only mass and velocity.
What does the kinetic energy of an object tell us about its potential to do work?
-The kinetic energy of an object tells us the maximum work it can do when it comes to a stop. For example, if a moving object with high kinetic energy strikes an object, it can transfer its energy, causing displacement or deformation of the object it strikes.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
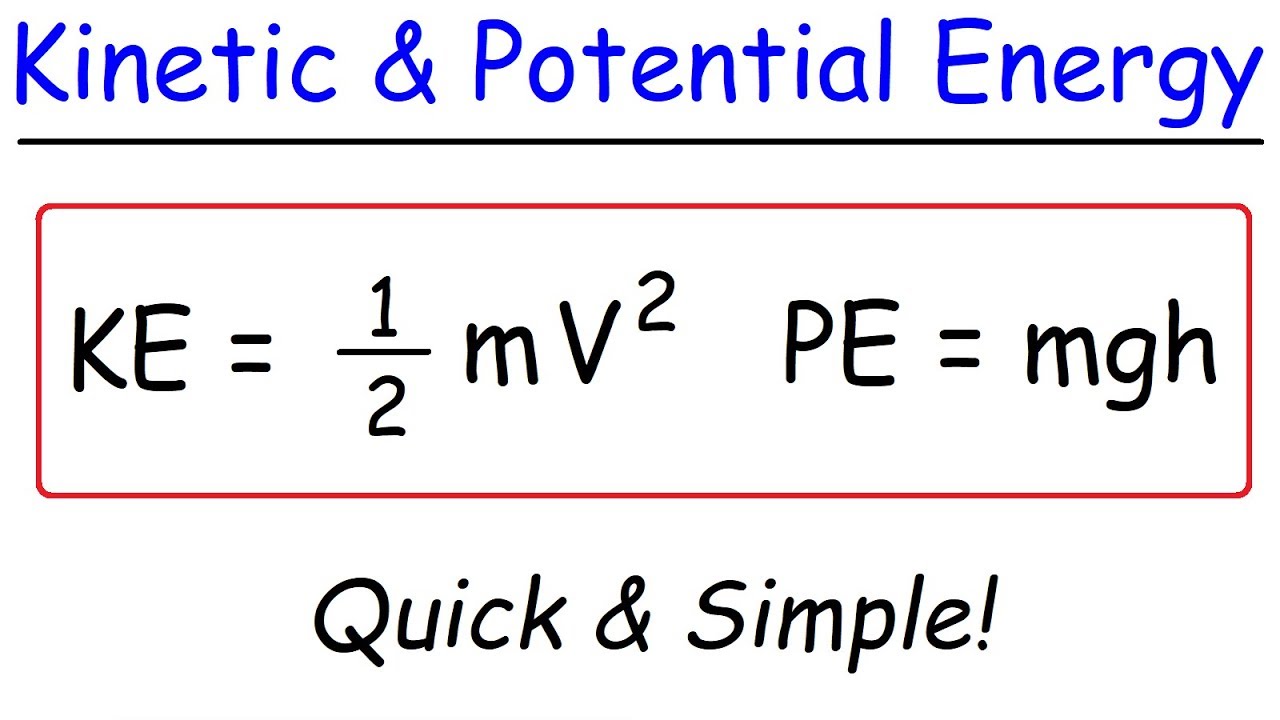
Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy

Sebuah benda bermassa 10 kg bergerak dengan kecepatan 20 mls: Dengan mengabaikan gaya gesek yang ...
Rapidez y velocidad angular | Física | Khan Academy en Español

HUBUNGAN USAHA DAN ENERGI KINETIK

Introduction to Conservation of Mechanical Energy with Demonstrations

Work and Energy | Grade 8 Science DepEd MELC Quarter 1 Module 3 Part 3 Kinetic Energy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)