Toxic multinodular goiter - causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, pathology
Summary
TLDRToxic multinodular goiter, also known as plumber's disease, is a condition where the thyroid gland enlarges and forms multiple nodules that overproduce thyroid hormones, leading to hyperthyroidism. It often starts with iodine deficiency and results in uneven growth of thyroid tissue. The condition can lead to a range of symptoms, including weight loss, rapid heart rate, heat intolerance, and even life-threatening complications like thyroid storm. Diagnosis involves blood tests and imaging, while treatment options include beta blockers, surgery, and radioactive iodine therapy to target the overactive nodules.
Takeaways
- 😀 Toxic multinodular goiter (plumber's disease) is a condition where the thyroid gland enlarges and forms multiple nodules that overproduce thyroid hormones, leading to harmful effects on the body.
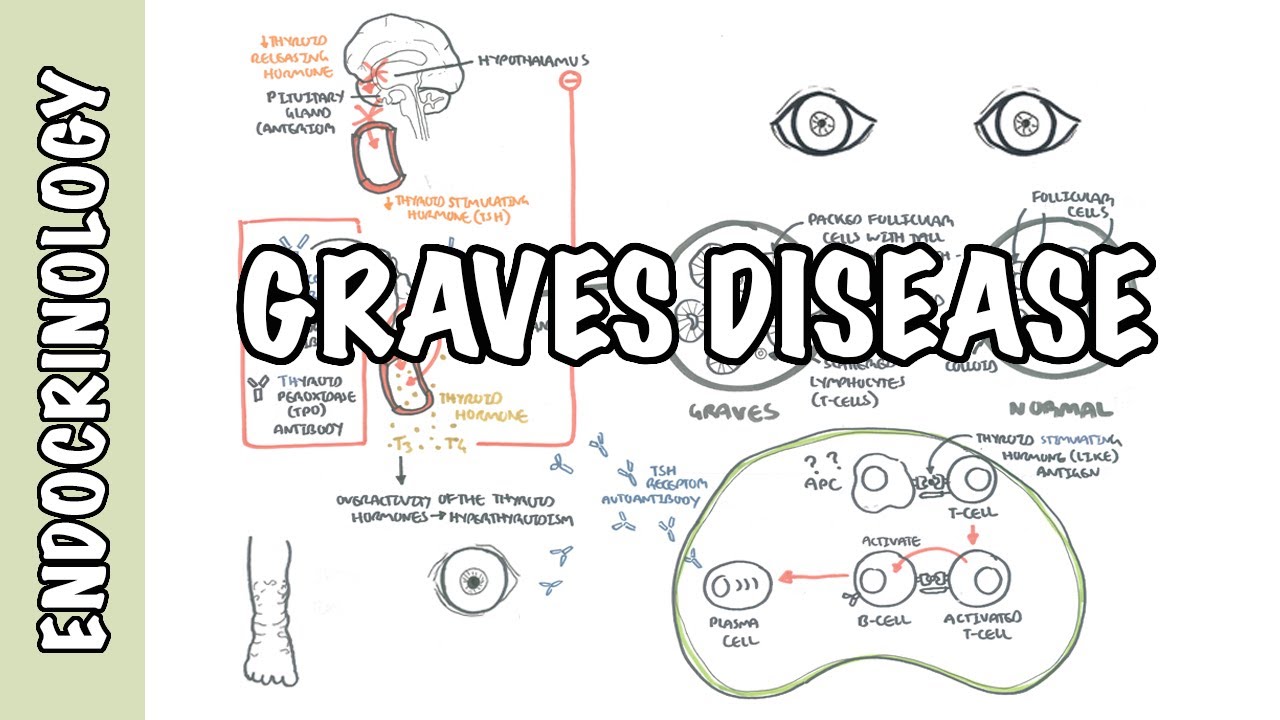
- 😀 The thyroid hormone production process begins in the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, which regulate the thyroid by releasing TSH that stimulates the thyroid gland.
- 😀 The thyroid gland consists of follicular cells that convert thyroglobulin into thyroid hormones T3 and T4, which regulate metabolism throughout the body.
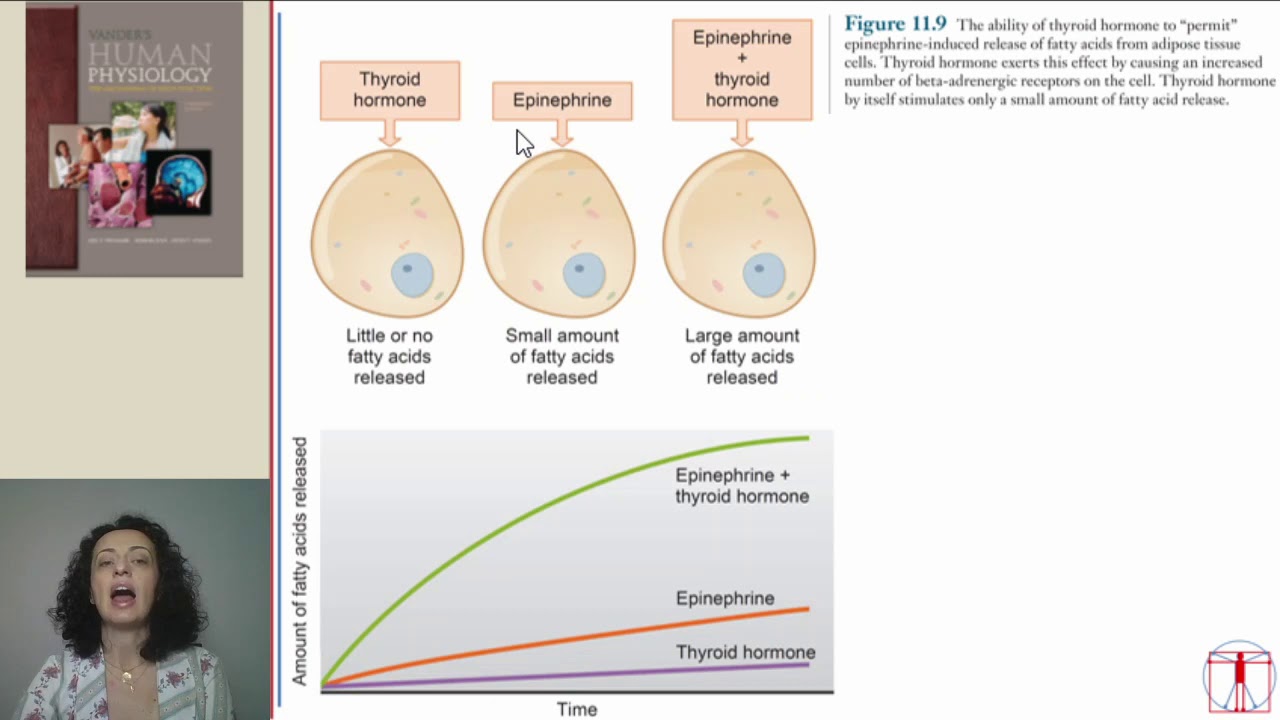
- 😀 T3 speeds up metabolism by increasing energy production, burning sugars and fats, and stimulating the sympathetic nervous system for a 'fight-or-flight' response.
- 😀 Toxic multinodular goiter often starts with iodine deficiency, which leads to thyroid hypertrophy (growth) and hyperplasia (increase in cell numbers).
- 😀 A non-toxic multinodular goiter occurs when the thyroid adapts by growing more cells to maintain hormone levels despite the iodine deficiency.
- 😀 Toxic multinodular goiter becomes harmful when a genetic mutation causes some follicular cells to continuously produce thyroid hormones, leading to hyperthyroidism.
- 😀 Symptoms of toxic multinodular goiter include an enlarged thyroid, hyperthyroidism-related weight loss, rapid heart rate, heat intolerance, and anxiety.
- 😀 Hyperthyroidism in toxic multinodular goiter can lead to complications like superior vena cava syndrome, hoarseness, and thyroid storm, a life-threatening condition.
- 😀 Diagnosis involves measuring blood levels of TSH, T3, and T4, using ultrasonography to detect nodules, and conducting a radio iodine uptake test to identify hyper-functioning nodules.
Q & A
What is toxic multinodular goiter (TMNG)?
-Toxic multinodular goiter (TMNG), also known as Plummer's disease, is a condition where the thyroid gland becomes enlarged and develops multiple nodules that produce excessive thyroid hormone, leading to harmful effects on the body.
How does the body normally regulate thyroid hormone production?
-The hypothalamus detects low levels of thyroid hormones in the blood and releases thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), which stimulates the anterior pituitary to release thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). TSH then stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones T3 and T4.
What role do thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) play in the body?
-Thyroid hormones, primarily T3, increase the basal metabolic rate, promoting protein production, burning more energy, and speeding up cellular reactions. They also increase cardiac output, stimulate bone resorption, and activate the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the fight-or-flight response.
How does a lack of iodine lead to multinodular goiter?
-A chronic iodine deficiency causes follicular cells in the thyroid to produce less thyroid hormone. In response, the anterior pituitary releases more TSH, which causes the thyroid to enlarge and form multiple nodules. Over time, the thyroid goes through cycles of growth and balance, eventually leading to a multinodular goiter.
What causes a multinodular goiter to become toxic?
-A multinodular goiter becomes toxic when a genetic mutation occurs in one of the dividing follicular cells, particularly affecting the TSH receptor. If the mutation causes the receptor to remain constantly active, the affected cells continue to produce excessive thyroid hormone, leading to hyperthyroidism.
What are the symptoms of toxic multinodular goiter?
-Symptoms include an enlarged thyroid, hyperthyroidism (weight loss, increased appetite, heat intolerance, rapid heart rate, sweating, anxiety, insomnia), difficulty swallowing, hoarseness, facial and arm swelling, and bulging eyes due to overstimulation of eye muscles.
What is thyroid storm, and how is it related to toxic multinodular goiter?
-Thyroid storm is a life-threatening complication of hyperthyroidism, where the body experiences severe hypermetabolism. It can develop when someone with hyperthyroidism stops treatment, develops an infection, or undergoes surgery, leading to exaggerated symptoms like high fever and cardiac arrhythmia.
How is toxic multinodular goiter diagnosed?
-TMNG is diagnosed by measuring blood levels of TSH, T3, and T4, and through ultrasonography to confirm the presence of multinodular goiter. A radioiodine uptake test can also help identify independent nodules that are producing excess thyroid hormone.
What are the common treatments for toxic multinodular goiter?
-Treatment options include beta blockers to manage symptoms, surgery to remove part or all of the thyroid gland, and radioiodine therapy, which uses radioactive iodine to destroy hyperfunctioning nodules while sparing the rest of the thyroid. Anti-thyroid drugs are used in cases where other treatments are not suitable.
Why is iodine important for thyroid hormone production?
-Iodine is a crucial component for the synthesis of thyroid hormones T3 and T4. Without adequate iodine, the thyroid cannot produce sufficient hormones, leading to the compensatory enlargement of the thyroid and the formation of nodules in an attempt to maintain hormone production.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)