Mekanisme Patofisiologi Hipertiroid & Tirotoksikosis
Summary
TLDRThis educational video covers hyperthyroidism, a pathological condition characterized by excessive production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland. The primary cause of hyperthyroidism is Graves' disease, followed by toxic nodular goiter. The video explains the mechanisms behind these conditions, including the role of thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins in Graves' disease, and highlights the clinical symptoms such as tremors, sweating, and increased heart rate. Additionally, the video touches on treatment options like surgery and radioactive iodine for managing these thyroid disorders.
Takeaways
- 😀 Hyperthyroidism is a condition characterized by excessive thyroid hormone synthesis and secretion by the thyroid gland.
- 😀 The most common cause of hyperthyroidism is Graves' disease, responsible for 60-80% of cases globally.
- 😀 Thyrotoxicosis refers to excess thyroid hormones in the bloodstream, which can occur without actual hyperthyroidism, such as in thyroiditis.
- 😀 Graves' disease is an autoimmune disorder where thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins (TSI) stimulate the thyroid gland to produce excess hormones.
- 😀 The prevalence of Graves' disease in women is 2-2.5%, and in men it is 0.2-0.6%, with a prevalence of 0.4% in Indonesia.
- 😀 The main clinical features of Graves' disease include hyperthyroidism, goiter (enlarged thyroid), ophthalmopathy (eye issues), and dermopathy (skin abnormalities).
- 😀 Hyperthyroidism in Graves' disease is caused by autoantibodies binding to the thyroid stimulating hormone receptor (TSHR), stimulating excessive thyroid hormone production.
- 😀 Radioactive iodine uptake studies show that the thyroid in hyperthyroidism secretes hormones at rates 5-15 times higher than normal.
- 😀 Toxic nodular goiter (Plummer's disease) is another cause of hyperthyroidism, characterized by autonomous thyroid nodules that secrete hormones independently of the pituitary feedback.
- 😀 Other causes of hyperthyroidism include hydatidiform moles or choriocarcinoma, conditions that raise human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) levels and stimulate the thyroid.
- 😀 Common symptoms of hyperthyroidism include excessive sweating, heat intolerance, tremors, tachycardia, weight loss, and exophthalmos (bulging eyes).
Q & A
What is hyperthyroidism?
-Hyperthyroidism is a pathological condition where there is excessive synthesis and secretion of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland.
What is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism?
-The most common cause of hyperthyroidism is Graves' disease, which accounts for 60 to 80% of cases globally.
What is toxic thyroid goiter (Plummer's disease)?
-Toxic thyroid goiter, or Plummer's disease, involves autonomous nodules in the thyroid that produce excessive thyroid hormones independently of feedback mechanisms.
What is thyrotoxicosis?
-Thyrotoxicosis is a clinical syndrome caused by an excess of thyroid hormones in the circulation, regardless of the underlying cause.
Can thyrotoxicosis occur without hyperthyroidism?
-Yes, thyrotoxicosis can occur in conditions like thyroiditis, where thyroid hormone is released due to thyroid cell damage, rather than increased production.
What is Graves' disease?
-Graves' disease is an autoimmune disorder that causes hyperthyroidism. It involves thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins binding to thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) receptors on the thyroid gland.
What are the clinical features of Graves' disease?
-The main clinical features of Graves' disease include hyperthyroidism, goiter (enlarged thyroid), ophthalmopathy (eye involvement), and dermopathy (skin changes), known as the 'triad of Graves'.
How does Graves' disease lead to hyperthyroidism?
-In Graves' disease, autoantibodies bind to the TSH receptor, leading to excessive thyroid hormone secretion and causing hyperthyroidism.
What is the treatment for toxic thyroid goiter (Plummer's disease)?
-The treatment for toxic thyroid goiter often involves the removal of the autonomous nodules through surgery or radioactive iodine therapy.
What are the common symptoms of hyperthyroidism?
-Common symptoms of hyperthyroidism include excessive sweating, sensitivity to heat, increased heart rate (tachycardia), fine tremors, weight loss, difficulty sleeping, and sometimes exophthalmos (bulging eyes).
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Hyperthyroidism Overview (causes, pathophysiology)

How does the thyroid manage your metabolism? - Emma Bryce

Thyroïde et Hormones Thyroïdiennes - Métabolisme, Régulation, Hyperthyroïdie et Hypothyroïdie
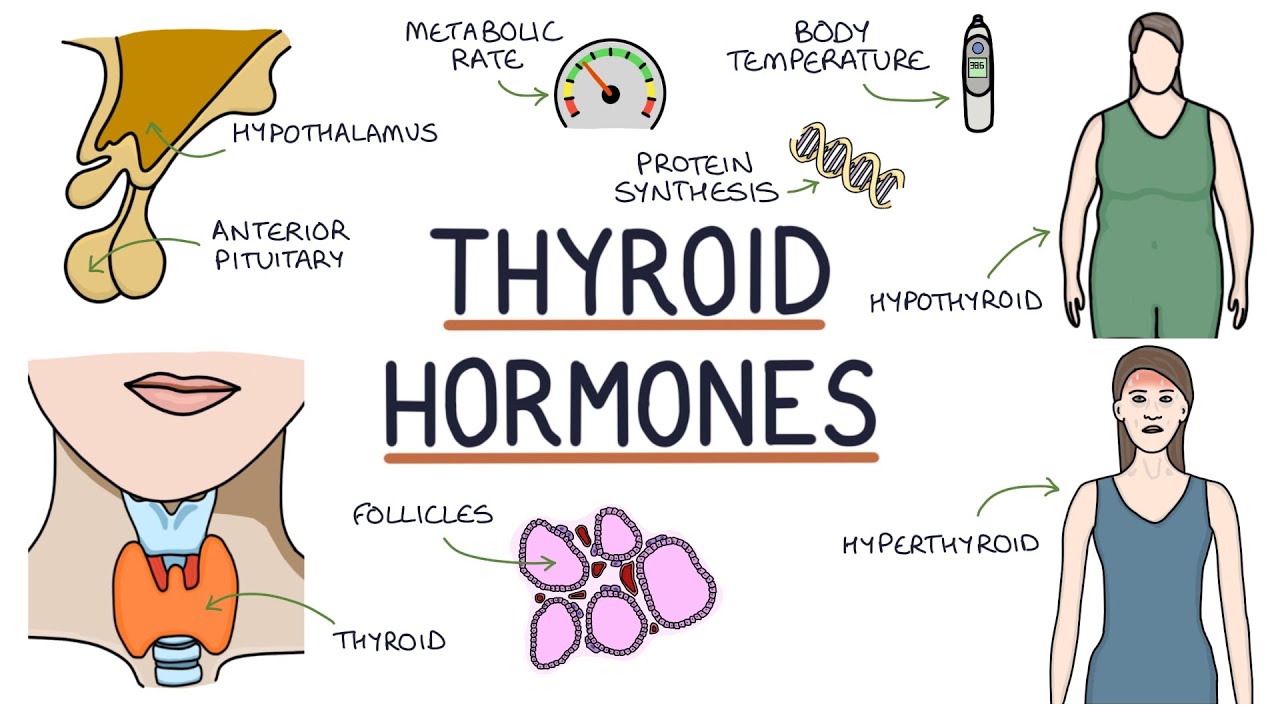
Understanding Thyroid Hormones

TIREOIDE - HIPERTIREOIDISMO E HIPOTIREOIDISMO | Biologia com Samuel Cunha

Toxic multinodular goiter - causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, pathology
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)