How to Read a Topo Map
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces the basics of reading topographic maps, covering key elements like contour lines, scale, and map symbols. Viewers will learn how contour lines represent elevation changes and how their spacing indicates terrain steepness. The video also explains map scale and the importance of the legend, including color codes for vegetation and water features. It highlights how to visualize terrain features and calculate distances effectively, making topographic maps an essential tool for backcountry navigation. By combining these skills, viewers can better plan their outdoor trips and navigate with confidence.
Takeaways
- 😀 Topographic maps show both 2D and 3D terrain features, helping you visualize the land's shape.
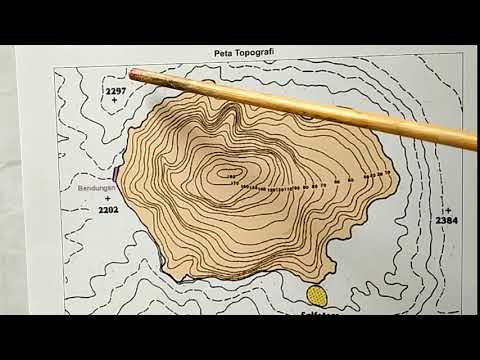
- 😀 Contour lines connect points of the same elevation, giving you a sense of the terrain's steepness or flatness.
- 😀 When contour lines are close together, the terrain is steep. When they are farther apart, the slope is more gradual.
- 😀 Smaller circles in contour lines indicate peaks, and a series of these lines helps you visualize terrain shapes.
- 😀 Index lines are thicker contour lines that show key elevations at regular intervals on the map.
- 😀 Contour intervals are the vertical distance between contour lines, often set at 40 or 80 feet, depending on the map.
- 😀 A map's scale shows the relative distance between locations, e.g., 1:12,000 means 1 inch on the map equals 12,000 inches in real life.
- 😀 Maps with smaller scales show more detail but cover smaller areas, while larger scales cover wider areas with less detail.
- 😀 The map's legend is crucial for interpreting symbols, colors, and lines used to represent terrain and other features.
- 😀 The color gradient on maps typically indicates vegetation density, with darker colors showing denser forests and lighter colors showing more open terrain.
- 😀 The map legend also includes important information like the map's revision date and magnetic declination, which helps with compass navigation.
Q & A
What makes topographic maps different from regular maps?
-Topographic maps are different because they not only show locations like roads and trails but also help visualize three-dimensional terrain using contour lines, scale, and symbols.
What do contour lines represent on a topographic map?
-Contour lines represent the elevation of the terrain. They connect points of equal elevation, and the spacing between them indicates the steepness of the slope.
How can you determine the steepness of terrain using contour lines?
-When contour lines are close together, the terrain is steep. When the lines are spread further apart, the terrain is more gradual and the slope is less steep.
What do smaller and smaller contour line circles represent?
-Smaller and smaller contour line circles typically indicate a peak or summit of the terrain.
What is the purpose of index lines on a topographic map?
-Index lines are thicker contour lines that are spaced every fifth line. They usually have the elevation marked, helping to identify specific elevations at regular intervals.
What is the significance of the contour interval on a topographic map?
-The contour interval refers to the difference in elevation between consecutive contour lines, and it is consistent throughout the map. Common intervals are 40ft or 80ft.
How does scale affect the level of detail on a topographic map?
-A smaller scale (e.g., 1:12,000) shows more detail over a smaller area, while a larger scale (e.g., 1:50,000) covers a larger area with less detail.
What is a representative scale, and how can it be used?
-A representative scale is a visual guide that shows the equivalent distance in miles or kilometers on the map. It helps calculate real-world distances using tools like a compass or piece of string.
What is the role of the map's legend?
-The legend explains the symbols, colors, and lines on the map, including definitions for contour lines, colors for vegetation, and representations of lakes and streams.
Why is the magnetic declination information important on a topographic map?
-Magnetic declination is important because it helps you adjust your compass to match the map’s magnetic north, ensuring accurate navigation.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)