How Jet Engine Works | Part 1 : Starting
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an in-depth explanation of the Boeing 777's GE90 engine start-up process. The engine's intricate components, such as the high and low-pressure shafts, fan, turbines, and fuel systems, are carefully examined. The script outlines the step-by-step procedure for starting the engine, from configuring the aircraft to initiating the APU, managing fuel systems, and activating the ignition. It highlights the engine’s automatic start feature, explaining how the EEC controls fuel flow, ignition, and combustion, leading to stable engine operation and thrust generation. The video concludes by emphasizing the successful completion of the start-up process, setting the stage for further exploration.
Takeaways
- 😀 The GE90 engine is the world's most powerful commercial jet engine in service, paired with the Boeing 777, the best-selling wide-body aircraft.
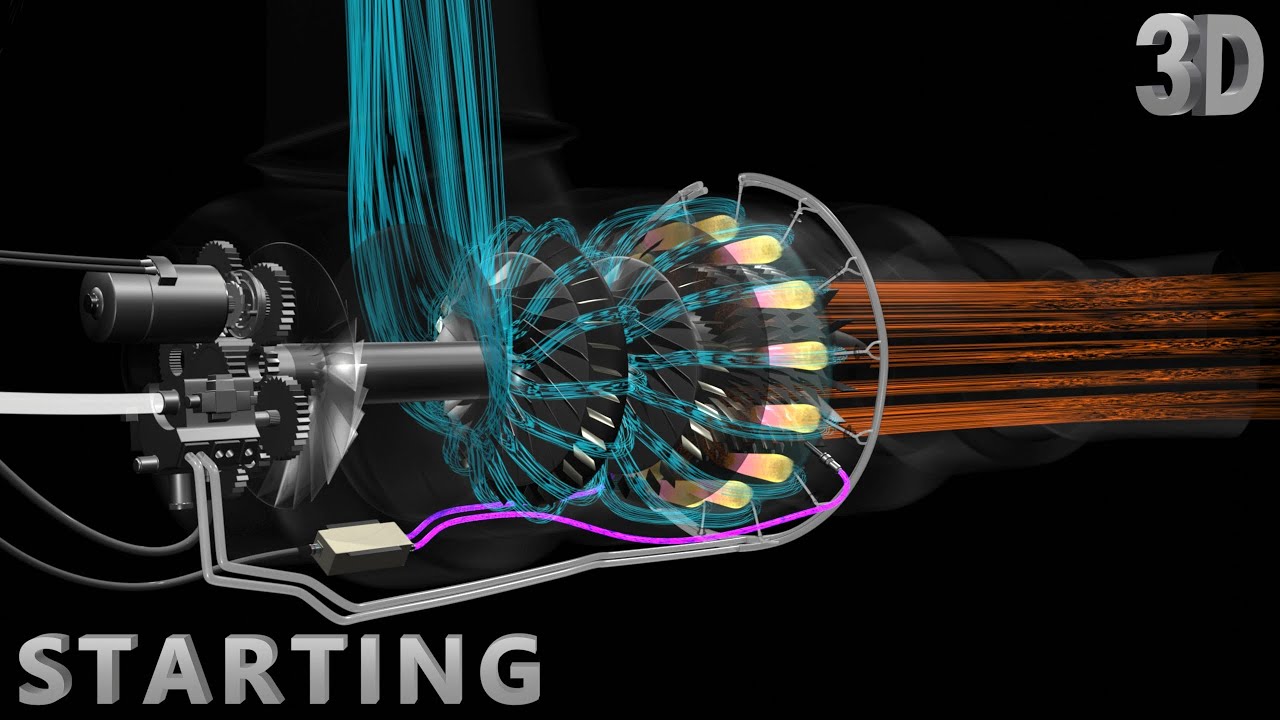
- 😀 The engine consists of two rotor shafts, a high-pressure shaft (N2) and a low-pressure shaft (N1), with various stages of compressors and turbines.
- 😀 To start the engine, the APU (Auxiliary Power Unit) is activated to provide electrical and pneumatic power, including powering the electronic engine control (EEC).
- 😀 The engine uses an automatic start feature, where the EEC manages the entire engine startup process once initiated.
- 😀 The N2 shaft controls airflow through the core of the engine, while the N1 shaft controls the fan, which creates bypass airflow for thrust.
- 😀 The engine fuel flow process starts with the fuel being sent from the left main tank to the engine fuel system via pumps, filters, and heat exchangers.
- 😀 The HMU (Hydromechanical Unit) regulates fuel flow to the engine, and excess fuel is returned to the pump for reuse.
- 😀 Ignition is initiated by the EEC activating an ignition exciter and igniter plug, which ignites the fuel-air mixture inside the combustion chamber.
- 😀 Combustion gases force the high-pressure and low-pressure turbines to rotate, increasing airflow through the engine and generating thrust.
- 😀 The EEC manages the engine start sequence, deactivating ignition and closing valves as the engine reaches stable idle power, signaling the completion of the start process.
Q & A
What is the GE90, and why is it significant?
-The GE90 is the world's most powerful commercial jet engine in service. It is known for its incredible performance when paired with the Boeing 777, the best-selling wide-body aircraft of all time.
How is the engine structured, and what are the key components?
-The engine has two rotor shafts: the high-pressure N2 shaft and the low-pressure N1 shaft. The N2 shaft consists of nine stages of high-pressure compressors and two stages of high-pressure turbines. The N1 shaft consists of six stages of low-pressure turbines and four stages of low-pressure compressors.
What is the purpose of the APU in the engine start procedure?
-The APU (Auxiliary Power Unit) provides the necessary electrical and pneumatic power to start the engine. It is a small engine located in the empennage of the aircraft that powers the systems during the start-up phase.
How does the electrical power system support the engine start?
-The APU generates electrical power, which is used by the aircraft systems. Once the APU is online, it supplies power to the electronic engine control (EEC), which manages the engine's start-up process.
What role do the fuel panels and pumps play in starting the engine?
-The fuel panels are configured to select the left main tank's fuel pumps. The pumps transfer fuel to the engine spar valve, which then directs it to the engine's fuel system, including the main fuel pump and fuel oil heat exchanger.
What is the significance of the HMU (Hydromechanical Unit) during engine start?
-The HMU controls the fuel flow to the engine for combustion. It works with the EEC to ensure fuel is supplied at the proper rate and pressure, and excess fuel is bypassed back to the pump.
How does the EEC manage the ignition system during engine start?
-The EEC activates one of the ignition exciters and controls the fuel shut-off valve to start combustion. Once ignition is initiated, the EEC deactivates the ignition system once the engine stabilizes at idle power.
What is the function of the combustion chamber in the engine?
-The combustion chamber is where the fuel and air mixture undergoes combustion. This process generates high-temperature gas that powers the turbines, leading to increased airflow and thrust.
What happens when N2 reaches 21% during engine start?
-When N2 reaches 21%, the EEC opens the fuel shut-off valve, allowing fuel to flow to the combustion chamber for ignition. The ignition exciter is activated to start the combustion process.
How does the engine reach and stabilize at idle power?
-The engine reaches idle power as the N2 shaft stabilizes and the combustion process is fully established. The EEC then disengages the starter and finalizes the engine start sequence.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
How Auxiliary Power Units Work | Part 1 : Starting
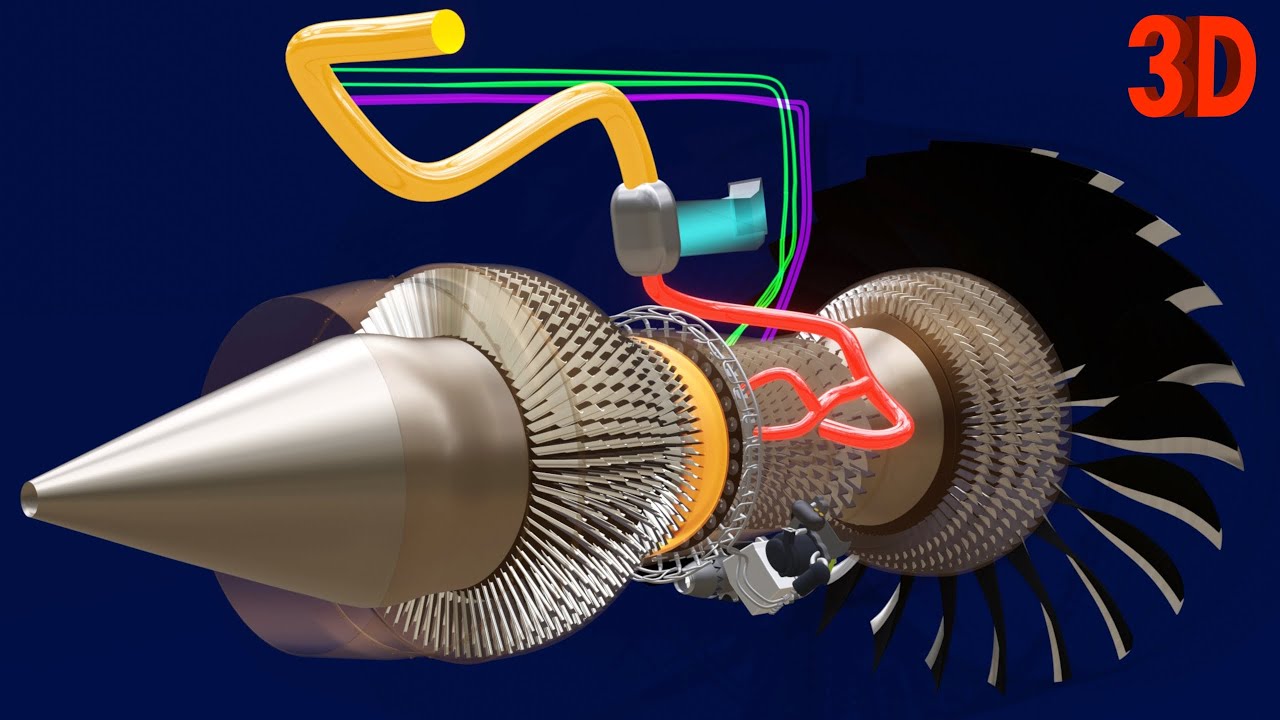
How Jet Engine Works | Part 2 : Outputs

Planespotting 101: How To Identify Each Major Commercial Aircraft Type

How Jet Engine Works | Part 3 : Performance

Aircraft Doors and Door assist ATA 52

What Really Happened to the Missing Malaysian Airlines Flight 370
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)