TEKNIK DNA REKOMBINAN (Bioteknologi Modern)
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Widyaningsih explains the concept of recombinant DNA technology, focusing on its application in creating transgenic organisms. The process involves three main stages: DNA isolation, gene transplantation, and the insertion of recombinant DNA into living cells. The steps of DNA isolation include tissue isolation, cell wall lysis, extraction, purification, and precipitation. Gene transplantation uses ligase to insert isolated genes into plasmids, which are circular DNA in bacteria. The recombinant DNA is then introduced into cells through methods like heat shock or electroporation. The video also touches on plant tissue culture as another form of modern biotechnology.
Takeaways
- 😀 Recombinant DNA technology involves modifying an organism’s DNA by inserting foreign genes to create new traits.
- 😀 The process of recombinant DNA technology results in the creation of transgenic organisms.
- 😀 The first step in recombinant DNA technology is DNA isolation from the organism.
- 😀 DNA isolation involves isolating tissue, breaking open cell walls, extracting DNA, purifying it, and precipitating the histone proteins.
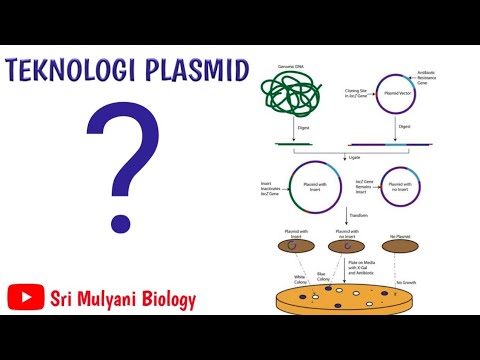
- 😀 The second step is gene or DNA transplantation, where the isolated gene is inserted into a plasmid using the enzyme ligase.
- 😀 Ligase acts as 'glue' to join the foreign gene to the plasmid, facilitating the insertion process.
- 😀 The third step involves inserting the recombinant DNA into living cells, typically using heat shock or electroporation techniques.
- 😀 Plasmids are circular pieces of DNA found in bacteria, and they are used as vectors to carry the foreign gene into the host organism.
- 😀 Recombinant DNA is often introduced into bacterial or viral cells, allowing them to replicate and propagate the new gene.
- 😀 After successful DNA insertion, the host organism will express the new traits introduced through recombinant DNA technology.
- 😀 The video concludes by previewing the next topic: plant tissue culture, and encourages viewers to like and subscribe.
Q & A
What is recombinant DNA technology?
-Recombinant DNA technology is a technique used to alter the DNA sequence of an organism by inserting foreign genes, resulting in the organism acquiring new traits it didn't originally possess.
What does recombinant DNA technology produce?
-Recombinant DNA technology produces transgenic organisms, which are organisms with genetically modified DNA that includes genes from other species.
What are the three main stages of recombinant DNA technology?
-The three main stages are DNA isolation, gene transplantation or DNA insertion, and the introduction of recombinant DNA into living cells.
What is involved in the DNA isolation process?
-DNA isolation involves several steps: isolating tissue, lysing the cell wall and membrane, extracting the DNA into a solution, purifying the extract, and precipitating the DNA to separate it from proteins.
What is the purpose of purifying the DNA during isolation?
-Purifying the DNA ensures that the extracted DNA is free from other substances, such as proteins or lipids, making it suitable for further experimentation.
How is gene transplantation achieved in recombinant DNA technology?
-Gene transplantation involves inserting a gene into a plasmid, which is a small circular DNA molecule found in bacteria. This insertion is facilitated using an enzyme called ligase.
What is the role of the enzyme ligase in gene transplantation?
-Ligase acts like a glue, connecting the foreign gene to the plasmid DNA, ensuring the gene is securely inserted for later introduction into a host organism.
How is recombinant DNA introduced into living cells?
-Recombinant DNA can be introduced into living cells through heat shock in a sodium chloride (NaCl) solution or by using a method called electroporation.
What is a plasmid, and why is it used in recombinant DNA technology?
-A plasmid is a small, circular DNA molecule found in bacteria. It is used in recombinant DNA technology as a vector to carry the inserted foreign gene, which then replicates inside the host cell.
What happens once recombinant DNA is inside a bacterium?
-Once inside the bacterium, the recombinant DNA can replicate along with the bacterial DNA, producing many copies of the foreign gene, which can be used for various applications, including research and biotechnological innovations.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)