TEKTONISME ( Gerak Epirogenetik dan Orogenetik)
Summary
TLDRThis video explains tectonic movements, distinguishing between epirogenetic and orogenetic movements. Epirogenetic movement is slow and affects large areas, including positive and negative movements of the Earth's surface. In contrast, orogenetic movement is faster and leads to the formation of mountains through folding and faulting. The video also covers plate movements, including convergent, divergent, and transform boundaries, and their resulting geological features such as subduction zones, mountain ranges, volcanic activity, and earthquakes. Notable examples include the Himalayas, the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, and the San Andreas Fault, offering an insightful overview of Earth's dynamic geological processes.
Takeaways
- 😀 Tectonic movements are classified into two types: epirogenetic and orogenetic movements.
- 😀 Epirogenetic movement refers to slow shifts in Earth's crust over large areas, which can either raise or lower landmasses, making it appear as if sea levels are changing.
- 😀 Orogenetic movement is faster and is associated with mountain formation, often resulting in folding and faulting of the Earth's crust.
- 😀 Folding occurs when horizontal pressure causes Earth's crust to wrinkle, while faulting occurs due to horizontal or vertical pressure, causing the crust to crack.
- 😀 Tectonic plate movements can be categorized into three types: convergent, divergent, and transform movements.
- 😀 Convergent plate movement involves colliding plates, which can form mountain ranges, ocean trenches, and cause volcanic activity.
- 😀 Convergent boundaries can result in oceanic plates subducting beneath continental plates, forming ocean trenches and volcanic arcs.
- 😀 Divergent plate movement occurs when plates move apart, leading to the creation of new oceanic crust, mid-ocean ridges, and volcanic activity.
- 😀 Transform plate movement happens when plates slide past each other, often resulting in fault lines like the San Andreas Fault in North America.
- 😀 In Indonesia, both subduction zones and fault lines caused by tectonic movements contribute to the formation of mountain ranges like the Barisan Mountains along Sumatra.
Q & A
What are the two main types of tectonic movements mentioned in the script?
-The two main types of tectonic movements mentioned are epirogenic and orogenic movements.
What is an example of a phenomenon caused by epirogenic positive movement?
-An example of a phenomenon caused by epirogenic positive movement is the appearance of water level rising as the land sinks.
How does orogenic movement differ from epirogenic movement?
-Orogenic movement is faster than epirogenic movement and is responsible for the formation of mountains.
What are the two types of pressure that cause geological formations like folds and faults?
-The two types of pressure are horizontal pressure, which causes folding, and vertical or horizontal pressure that causes faults.
What happens when tectonic plates converge?
-When tectonic plates converge, they collide, forming phenomena such as ocean trenches, mountain chains, volcanic activity, and subduction zones.
Which area is an example of a convergent boundary between oceanic and continental plates?
-An example of a convergent boundary between oceanic and continental plates is the subduction zone between the Philippine Sea Plate and the Eurasian Plate, leading to volcanic islands like the Philippines.
What geological formation is caused by the convergence of two continental plates?
-The convergence of two continental plates forms mountain ranges, such as the Himalayas, which includes Mount Everest.
What is the result of divergent plate movement, as discussed in the transcript?
-Divergent plate movement causes the plates to move apart, leading to phenomena like the formation of ocean ridges, volcanic activity, and earthquakes.
Can you give an example of divergent movement between two landmasses?
-An example of divergent movement between two landmasses is the separation of South America and Africa, which led to the formation of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge.
What is the geological result of transform fault movement?
-Transform fault movement leads to horizontal displacement, forming features such as the San Andreas Fault in California and the Semangko Fault in Sumatra.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
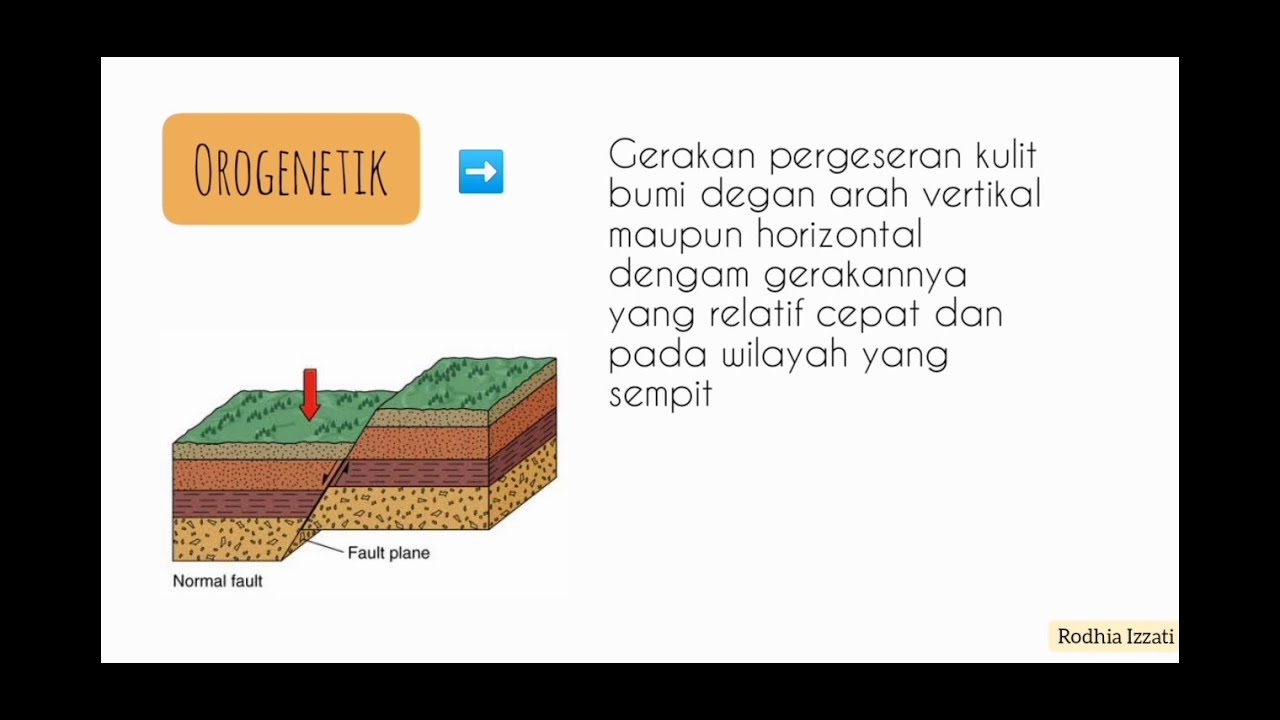
Tenaga Endogen Part 1 : TEKTONISME

Tenaga Endogen: Tektonisme | Geografi | Alternatifa

Geo X. 20. Tektonisme & Pengaruhnya Terhadap Kehidupan Manusia.
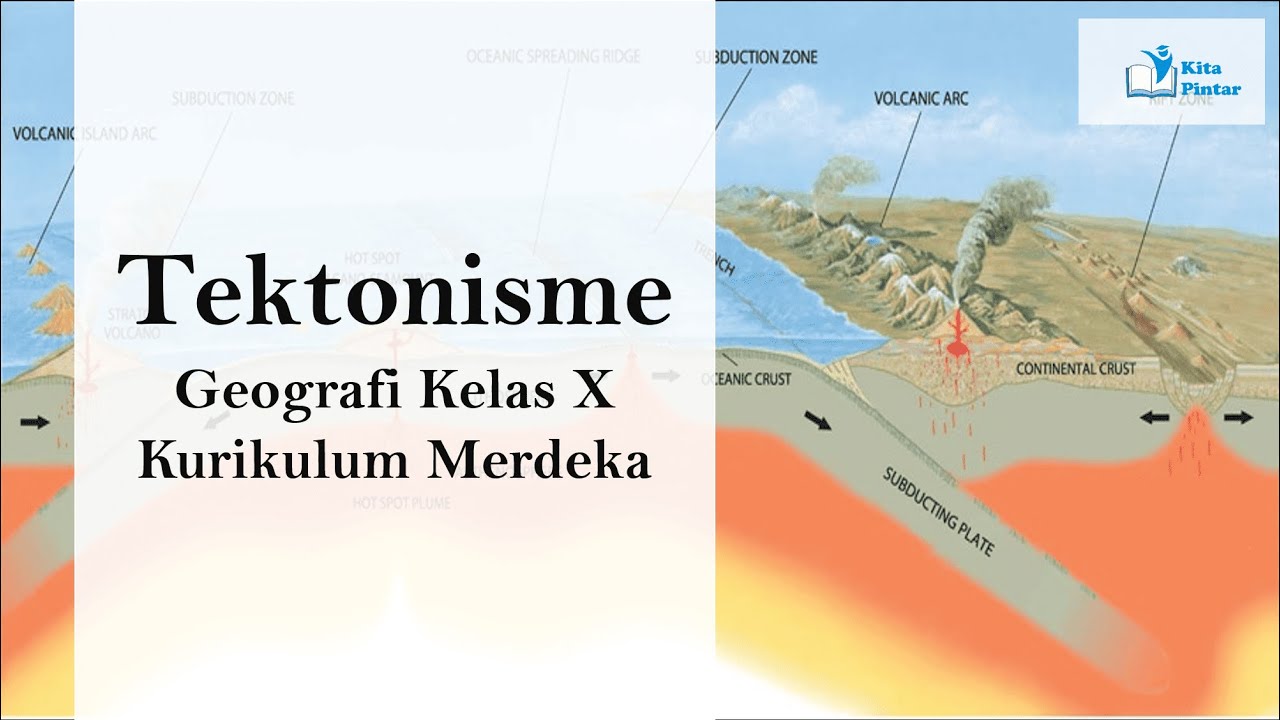
Tektonisme/ Tenaga Endogen/ Geografi Kelas X SMA/ Kurikulum Merdeka

Tektonisme: Pengertian – Proses dan Dampaknya

TEKTONISME DAN PENGARUHNYA TERHADAP KEHIDUPAN (TUGAS GEOGRAFI SMA NEGERI 1 TABANAN)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)