Tenaga Endogen: Tektonisme | Geografi | Alternatifa
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the host explains the concept of 'Tektonisme,' or tectonic forces, focusing on their horizontal and vertical movements. The video covers key concepts like epirogenetic and orogenetic movements, highlighting their differences with the help of examples such as mountain formations and land shifts. The video also introduces the three types of plate tectonic movements: convergent, divergent, and transform. The host provides visuals and simple explanations to help viewers understand these complex geological processes, such as how plate interactions lead to phenomena like mountain building, ocean ridges, and earthquakes.
Takeaways
- 😀 Tectonism is the force caused by the movement or displacement of rock layers on the Earth's surface, both horizontally and vertically.
- 😀 Horizontal movement occurs when land masses shift, such as the movement of Madagascar away from the African continent between 1980 and 2022.
- 😀 Vertical movement is when land is pushed up, forming features like hills due to pressure from within the Earth.
- 😀 Tectonic movements are categorized into two types: epirogenetic (slow and widespread) and orogenetic (faster and more localized).
- 😀 Epirogenetic movements involve slow, long-term shifts across large areas, with both positive (land subsidence) and negative (land rising) movements.
- 😀 Orogenetic movements are characterized by rapid, localized shifts and can lead to mountain-building through processes like folding and faulting.
- 😀 Folding, a form of orogenetic movement, occurs when rock layers are subjected to unidirectional pressure, leading to formations like anticlines and synclines.
- 😀 Faulting, on the other hand, happens when rocks experience compressional forces from two opposite directions, resulting in fractures in the Earth's crust.
- 😀 The Earth’s lithosphere can be uplifted by orogenic movements, forming fold mountains, especially in areas with softer rock materials.
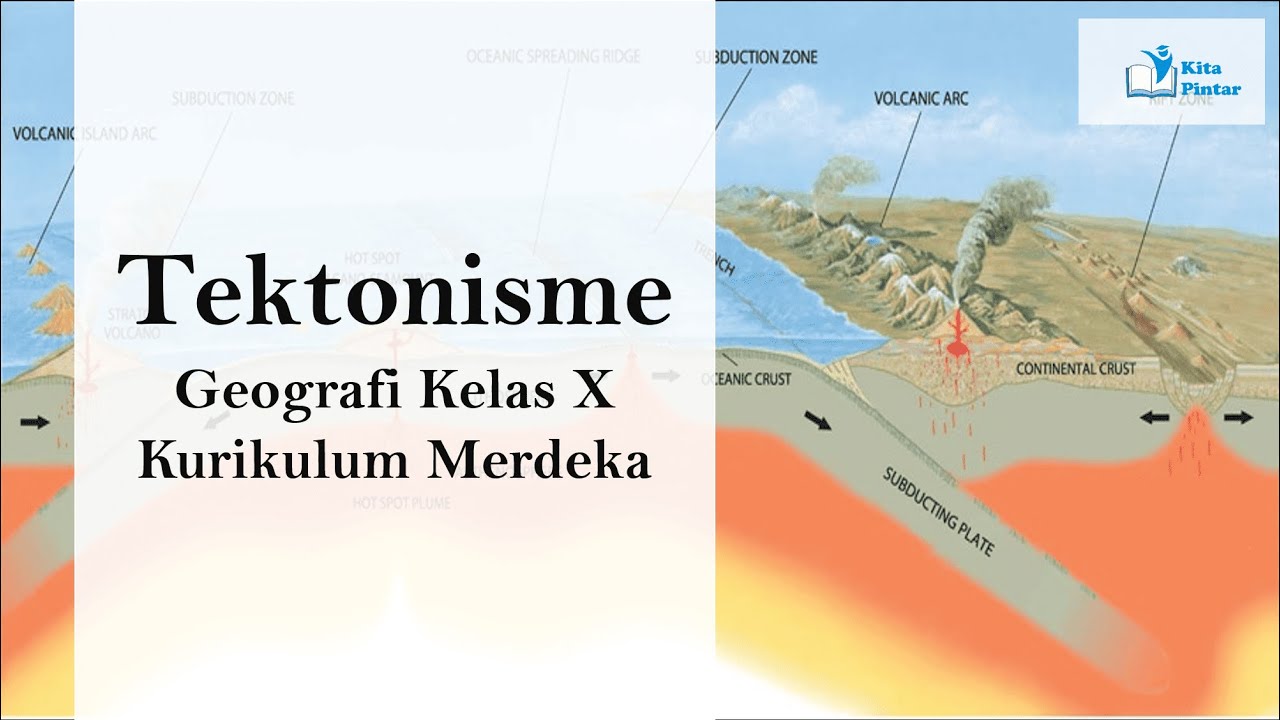
- 😀 Earth's tectonic plates move in three main ways: convergent (plates collide), divergent (plates move apart), and transform (plates slide horizontally).
Q & A
What is tectonism?
-Tectonism refers to the forces generated by the movement or shifting of rock layers on the Earth's surface, both horizontally and vertically.
What is the difference between horizontal and vertical tectonic movements?
-Horizontal movements involve the shifting of landforms, such as the separation of Madagascar and Africa, where the distance between them increased over time. Vertical movements occur when pressure from within the Earth causes flat landforms to rise, forming features like hills.
What are the two types of tectonic movements discussed?
-The two main types of tectonic movements are horizontal movements and vertical movements.
How can you differentiate between epirogenetic and orogenetic movements?
-Epirogenetic movements are slow, gradual, and affect wide areas over a long time, while orogenetic movements are faster, more localized, and occur in smaller regions.
What is the key difference between positive and negative epirogenetic movements?
-In positive epirogenetic movements, land sinks, creating the illusion that the sea level has risen. In negative movements, land rises, making it appear that the sea level has decreased.
What is the main characteristic of orogenetic movements?
-Orogenetic movements typically involve the folding or faulting of the Earth's crust, driven by pressure from two opposing directions. They are characterized by narrow regions and can result in mountain formations.
What is the difference between folding and faulting in tectonics?
-Folding occurs when rocks are compressed and bend, often forming anticlinals (upward folds) and synclinals (downward folds). Faulting involves the fracturing and displacement of rock layers due to stress, which can result in horizontal or vertical displacements.
What is the impact of tectonic plate movement, particularly in terms of convergent, divergent, and transform boundaries?
-At convergent boundaries, plates move towards each other, leading to subduction or mountain formation. At divergent boundaries, plates move apart, creating new oceanic crust like the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. At transform boundaries, plates slide past each other, causing earthquakes, like the San Andreas Fault.
What geological features are associated with divergent plate boundaries?
-Divergent plate boundaries typically lead to the formation of mid-ocean ridges and new oceanic crust, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge.
What causes the Himalayan mountains to form?
-The Himalayan mountains were formed by the convergent movement of tectonic plates, where the Indian Plate collided with the Eurasian Plate, causing the crust to fold and form a mountain range.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

MACAM-MACAM TUMPUAN (ROL, SENDI DAN JEPIT) MEKANIKA TEKNIK KELAS X SMK BANGUNAN

Geografia pro ENEM - Agentes Internos (endógenos) Modeladores do Relevo - Resumo

TEKTONISME DAN PENGARUHNYA TERHADAP KEHIDUPAN (TUGAS GEOGRAFI SMA NEGERI 1 TABANAN)
Tektonisme/ Tenaga Endogen/ Geografi Kelas X SMA/ Kurikulum Merdeka

5.2 Lateral Load resisting system design – Part 1

Horizontal and Vertical Integration (Business Growth Strategy)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)