Types of Geographic Data [AP Human Geography Review Unit 1 Topic 2]
Summary
TLDRThis video explores how geospatial technologies like remote sensing, GPS, and GIS help collect and analyze geographic data. It discusses how farmers, individuals, and governments benefit from these tools for tasks such as improving crop yields, navigation, and urban planning. The video also covers other methods of data collection, including field observations, media reports, government documents, travel narratives, and personal interviews. The difference between qualitative and quantitative data is explained, showcasing how geographers use various tools to understand and interpret the world. Viewers are encouraged to engage with the content and further explore AP Human Geography.
Takeaways
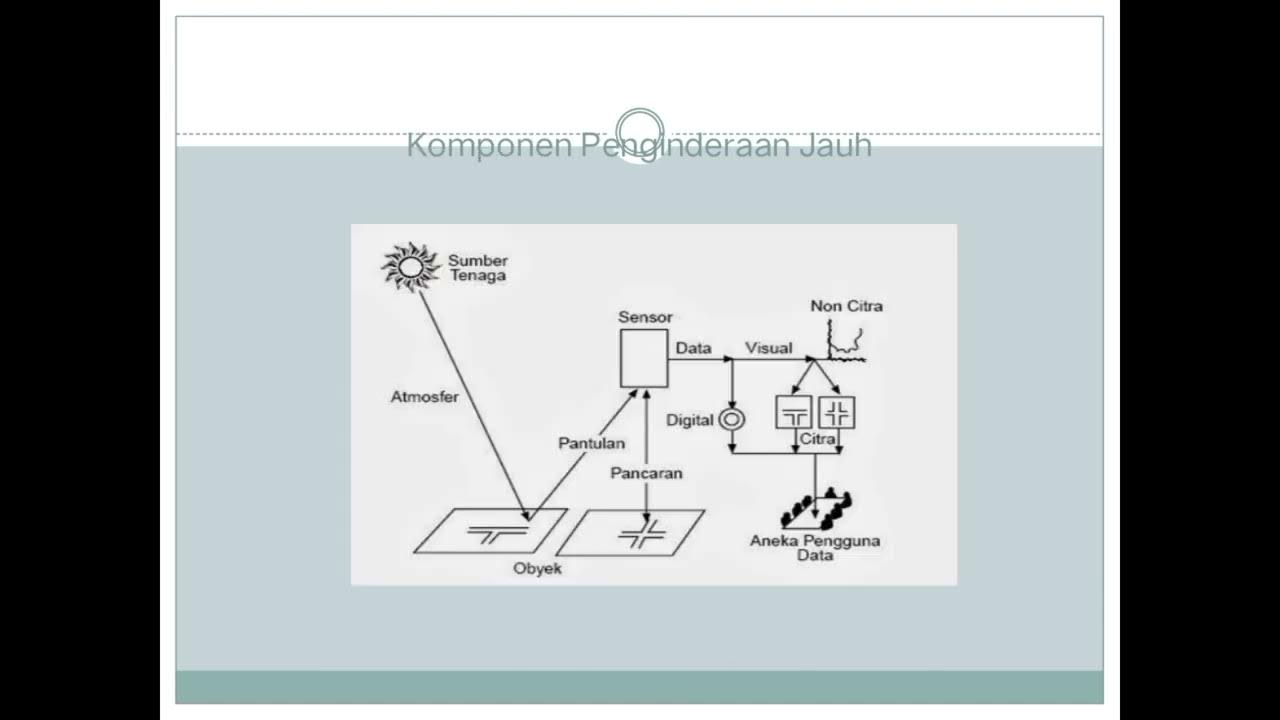
- 😀 Remote sensing helps monitor changes in the environment, like deforestation and ice cap melting, by collecting data from satellites orbiting the Earth.
- 😀 Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are used to analyze and display geographic data, offering insights into spatial patterns, trends, and associations.
- 😀 Farmers use remote sensing and GIS to optimize crop yield by identifying areas in need of more water, pesticides, or attention.
- 😀 GPS technology helps individuals navigate and allows farmers to precisely guide their tractors using longitude and latitude to optimize planting and fertilizer application.
- 😀 Geospatial technologies provide valuable insights for governments, organizations, and individuals to locate places and visualize geographic data to benefit society.
- 😀 Geographers can collect firsthand data through field observations, which offer accurate and detailed insights into specific places and their characteristics.
- 😀 When field observations aren't possible, geographers can rely on media reports, government documents, travel narratives, and interviews to gather data.
- 😀 Media reports, such as online articles and news broadcasts, provide valuable insights into what people are experiencing in different areas and help geographers understand local conditions.
- 😀 Travel narratives give geographers an unfiltered perspective of a place and reveal the experiences of people who have visited or lived in specific locations.
- 😀 Photo analysis allows geographers to understand cultural practices, demographics, and geographic conditions, such as conflict, religious practices, or climate-related features.
Q & A
What is remote sensing and how is it used?
-Remote sensing is the process of collecting information about the Earth from satellites orbiting the planet. It is used to gather geographic data and can help track changes such as urban growth, deforestation, and climate change.
What role does Geographic Information Systems (GIS) play in analyzing geographic data?
-GIS is a computer system that analyzes, collects, and displays geographic data. It creates layered maps that provide insights into spatial associations, trends, and patterns, helping individuals, governments, and organizations make informed decisions.
How do farmers use remote sensing and GIS to improve crop yield?
-Farmers use remote sensing and GIS to monitor their fields, identifying areas that need more water, pesticides, or attention. This helps optimize the use of resources and increase crop yield.
What is GPS and how is it used by farmers?
-GPS (Global Positioning System) is used for navigation and helps farmers guide their equipment, such as tractors, by using latitude and longitude. This ensures precise placement of crops and application of fertilizers and pesticides, improving efficiency and yield.
What are field observations, and how are they used by geographers?
-Field observations are firsthand data collected by geographers when visiting a place. They provide accurate and detailed information about a location, though they may not always be feasible due to cost or practicality.
What other sources can geographers use when field observations are not possible?
-When field observations aren't feasible, geographers can use media reports, travel narratives, government documents, and personal interviews to gather geographic data remotely.
How do media reports help geographers collect geographic data?
-Media reports, such as articles, newspapers, and local news, offer insight into the experiences of people in an area. They help geographers understand current events, trends, and societal issues related to a specific place.
What insights can geographers gain from travel narratives?
-Travel narratives provide unfiltered perspectives of people’s experiences and observations while visiting or living in an area. They offer valuable insights into the local culture, environment, and everyday life.
What is the significance of analyzing photos in geographic studies?
-Photo analysis allows geographers to understand aspects like culture, population density, and environmental features. For example, photos can reveal signs of conflict, cultural landmarks, or physical characteristics of a place.
What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative data?
-Qualitative data includes subjective observations, interviews, and opinions, while quantitative data consists of objective numerical facts such as population figures, age cohorts, and religious breakdowns. Qualitative data is open to interpretation, while quantitative data is factual and verifiable.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)