Computação Quântica - Fundamentos e Aplicações - Aula 03
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into key concepts of quantum computing, such as quantum superposition, quantum entanglement, and quantum gates. It explains how qubits, unlike classical bits, can exist in multiple states simultaneously, as illustrated by Schrödinger's cat thought experiment. The concept of quantum entanglement is also discussed, where qubits become linked, and measuring one instantly affects the other, regardless of distance. Additionally, quantum gates are introduced, enabling the manipulation of qubits in quantum circuits. These phenomena are foundational to quantum computing's potential, offering insights into how quantum systems differ from classical ones.
Takeaways
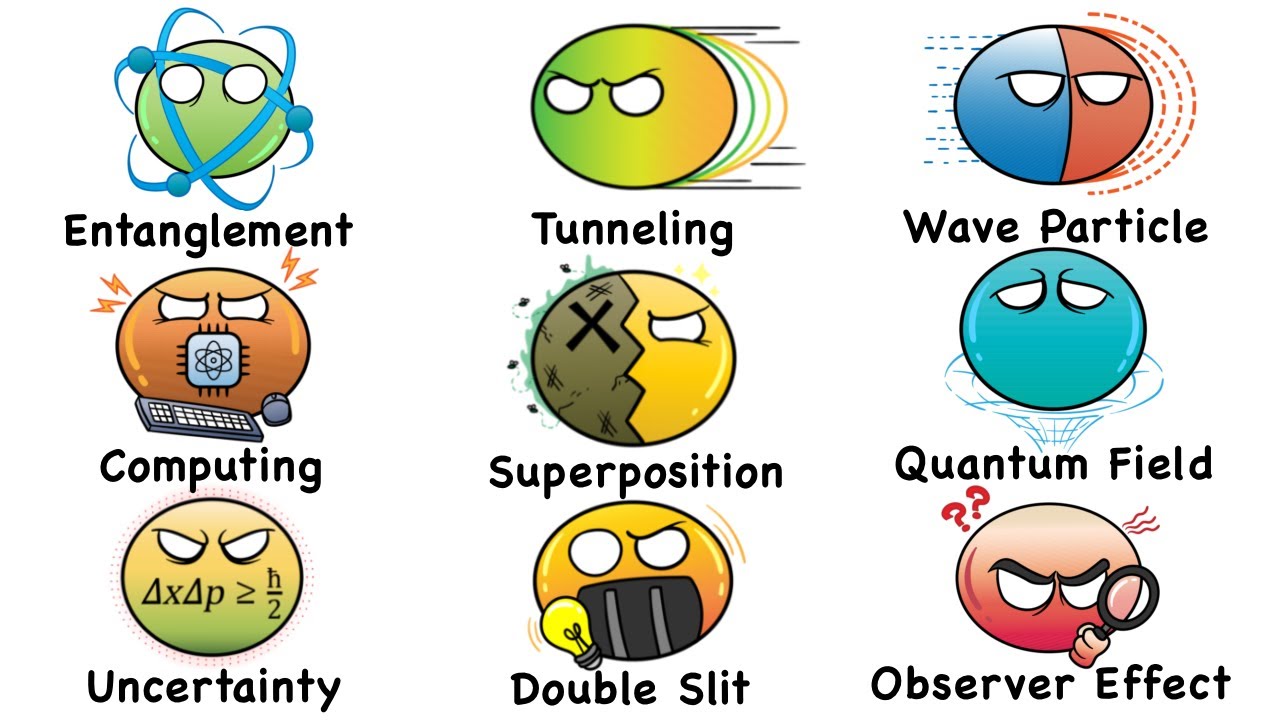
- 😀 Superposition allows quantum bits (qubits) to exist in multiple states simultaneously, unlike classical bits that are either 0 or 1.
- 😀 Schrödinger's cat thought experiment is a popular example of superposition, where the cat can be both dead and alive until observed.
- 😀 Quantum entanglement describes how two qubits can be correlated in such a way that the state of one qubit instantly determines the state of the other, regardless of distance.
- 😀 Albert Einstein referred to quantum entanglement as 'spooky action at a distance' because it challenges classical physics and relativity.
- 😀 Even though quantum entanglement allows instant state determination between qubits, information about the state still requires communication at the speed of light to confirm it.
- 😀 Quantum operations or gates, similar to classical logical gates, are used to manipulate qubits and change their states in quantum computers.
- 😀 Some quantum gates, like the controlled NOT gate (CNOT), can operate on multiple qubits simultaneously, affecting the state of one qubit based on the state of another.
- 😀 Quantum operations are reversible, meaning that the system can return to its previous state by applying the opposite operation.
- 😀 Unlike classical computing, where hardware and gates are standardized, quantum computing hardware and gates can vary depending on the system used.
- 😀 Analysts working with quantum computing need to consider the specific hardware model when designing quantum circuits, as different models may have different gate sets.
- 😀 Quantum computing is still in an experimental phase, with different quantum computing systems having unique configurations, but this diversity also presents opportunities for innovation.
Q & A
What is the concept of superposition in quantum computing?
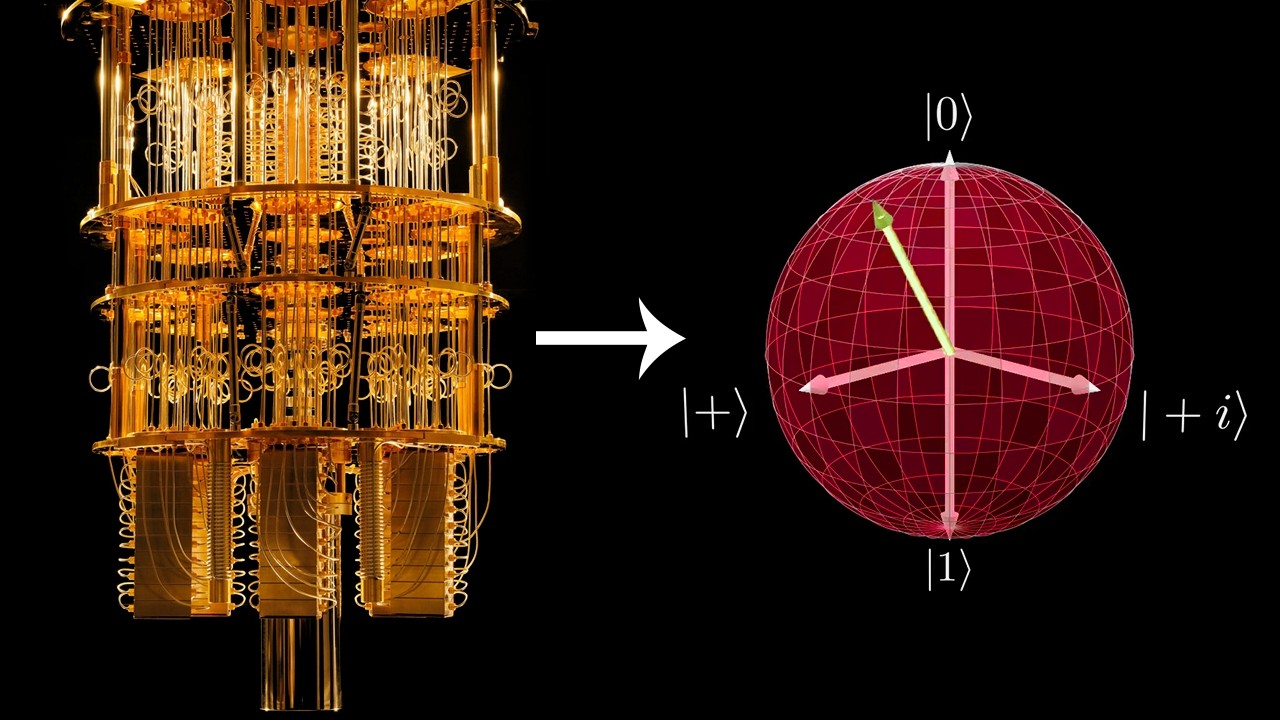
-Superposition refers to the ability of quantum bits (qubits) to exist in multiple states simultaneously. Unlike classical bits, which are either 0 or 1, qubits can represent a combination of both states at once, allowing for more information to be processed at once.
How does Schrödinger’s cat experiment relate to quantum superposition?
-Schrödinger’s cat experiment is a thought experiment used to illustrate quantum superposition. In the experiment, a cat in a box can be both alive and dead at the same time due to the superposition of a radioactive particle's decaying state. The cat's fate is only determined when the box is opened and observed.
What is quantum entanglement and how does it work?
-Quantum entanglement occurs when two qubits become linked in such a way that the state of one qubit directly influences the state of the other, no matter the distance between them. When one qubit is measured, the other qubit's state collapses instantly, even if it is far away, such as across the globe.
How does the example of shoes in boxes explain quantum entanglement?
-The shoe analogy helps explain entanglement by imagining two shoes, a left and a right one, placed in two separate boxes. If one box is opened and a left shoe is found, it is immediately known that the other box contains the right shoe, regardless of the distance between the two boxes. This illustrates how entangled qubits work, where the measurement of one instantaneously affects the other.
What did Albert Einstein think about quantum entanglement?
-Albert Einstein was skeptical of quantum entanglement, calling it 'spooky action at a distance.' He was concerned because the phenomenon seemed to challenge the theory of relativity, particularly the notion that information cannot travel faster than the speed of light.
What role do quantum gates play in quantum computing?
-Quantum gates perform operations on qubits, manipulating their states. Similar to classical logical gates, quantum gates allow for transformations such as putting a qubit into superposition or flipping its state. They are fundamental for constructing quantum circuits and algorithms.
How are quantum gates different from classical logical gates?
-Quantum gates operate on qubits and can perform operations like creating superposition or entangling qubits. Unlike classical gates, quantum gates are reversible and work with quantum phenomena such as superposition and entanglement. They can also operate on multiple qubits simultaneously.
What is a Controlled NOT (CNOT) gate in quantum computing?
-A Controlled NOT (CNOT) gate is a quantum gate that involves two qubits. It flips the state of the second qubit (target qubit) based on the state of the first qubit (control qubit). If the control qubit is in state 1, the target qubit is flipped; if the control qubit is in state 0, the target qubit remains unchanged.
What happens during the measurement of a qubit?
-When a qubit is measured, it collapses into one of its possible states (0 or 1). Prior to measurement, the qubit may exist in a superposition, representing a combination of both 0 and 1, but once measured, the outcome is definite.
Why is quantum communication still limited by the speed of light?
-While quantum entanglement suggests instantaneous information transfer, verifying the state of an entangled qubit still requires classical communication, which is limited by the speed of light. This means that even though the entanglement is instant, confirming the result requires light-speed communication.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)