ANALISIS PERILAKU BIAYA
Summary
TLDRThis lecture delves into cost accounting, focusing on cost behavior analysis. It explains the classification of costs into fixed, variable, and semi-variable categories, highlighting how each type behaves in relation to business activity. The video also covers three key methods for estimating costs: the High-Low Method, Scattergraph Method, and Least Squares Method, emphasizing their role in cost analysis, budgeting, and profitability evaluations. These techniques help in separating fixed and variable components of semi-variable costs, crucial for informed decision-making in business operations.
Takeaways
- 😀 Costs can be classified into three categories: fixed costs, variable costs, and semi-variable costs.
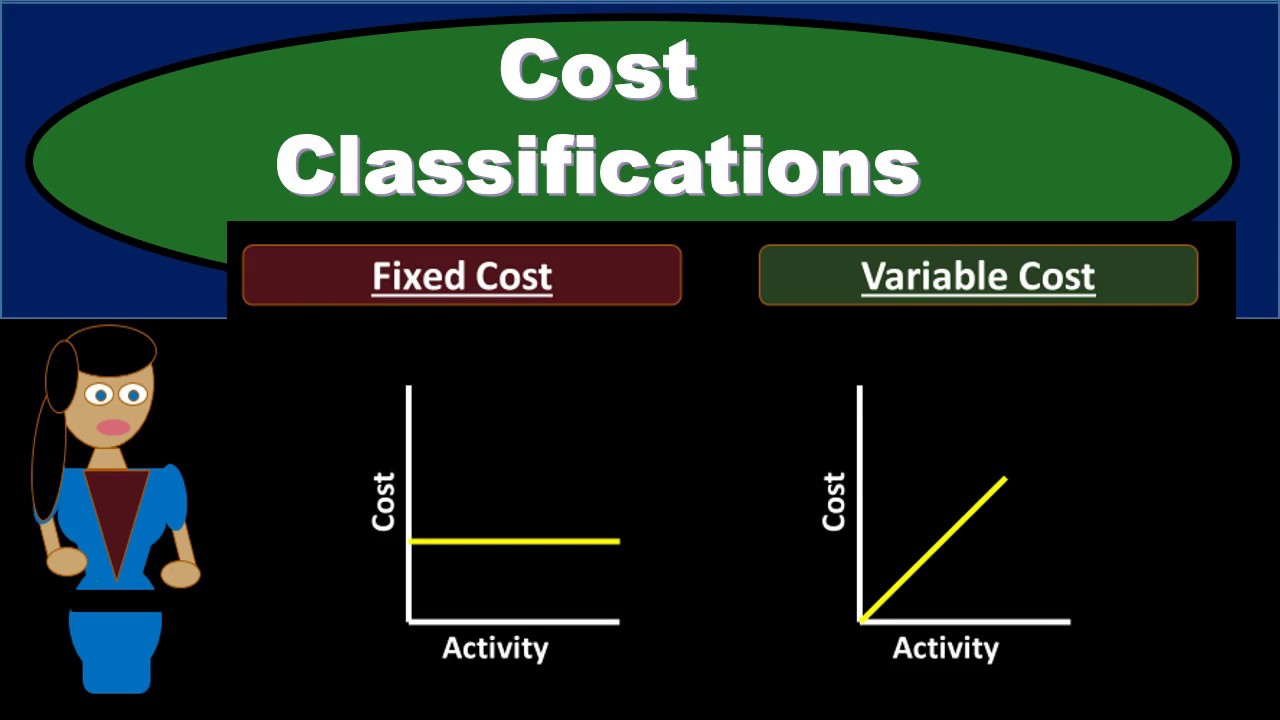
- 😀 Fixed costs remain constant despite changes in business activity, but they may increase if business activity grows beyond a certain relevant range.
- 😀 Examples of fixed costs include advertising expenses and long-term debt interest.
- 😀 Variable costs increase in proportion to business activity, such as raw materials and direct labor costs.
- 😀 Semi-variable costs exhibit characteristics of both fixed and variable costs, such as utility bills and certain employee benefits.
- 😀 It's important to separate fixed and variable costs for accurate cost analysis and decision-making.
- 😀 Three methods to separate semi-variable costs include: the High-Low Method, Scattergraph, and Least Squares Method.
- 😀 The High-Low Method uses the highest and lowest levels of activity to estimate fixed and variable cost components.
- 😀 The Scattergraph method involves plotting data points on a graph to visualize the relationship between costs and activity levels.
- 😀 The Least Squares Method uses regression analysis to find the best-fitting line through data points and calculate the variable and fixed cost components mathematically.
- 😀 Analyzing costs at different activity levels helps in budgeting, break-even analysis, and profitability maximization.
Q & A
What are the main objectives of cost behavior analysis in accounting?
-The main objectives are to classify costs as fixed, variable, or semi-variable, and to understand how changes in business activity levels affect these costs. Additionally, it involves learning how to estimate fixed and variable costs using different methods and calculating confidence intervals for cost estimations.
What are fixed costs, and how are they classified?
-Fixed costs are costs that remain constant regardless of changes in the level of business activity. They can be classified into two types: discretionary fixed costs (e.g., advertising, social donations) set by management and committed fixed costs (e.g., long-term debts, lease payments) which are ongoing and not easily adjusted.
What are variable costs, and how do they behave?
-Variable costs change directly in proportion to the level of business activity. As production or sales increase, variable costs rise, and as activity decreases, these costs fall. Common examples include raw materials and direct labor.
What are semi-variable costs, and how do they differ from fixed and variable costs?
-Semi-variable costs exhibit both fixed and variable characteristics. They have a fixed component that does not change with activity levels and a variable component that changes with activity. Examples include utilities like electricity or water, which have a fixed monthly charge and a variable cost based on usage.
Why is it important to separate fixed and variable costs?
-Separating fixed and variable costs is crucial for accurate financial analysis, budgeting, and decision-making. It helps in calculating overhead rates, preparing flexible budgets, performing break-even analysis, and determining profitability. Understanding this separation is also essential for cost-volume-profit (CVP) analysis.
What are the three methods used to separate semi-variable costs into fixed and variable components?
-The three methods are: 1) the High-Low method, which uses the highest and lowest levels of activity to estimate fixed and variable costs; 2) the Scattergraph method, which plots data points and draws a line to estimate cost behavior; and 3) the Least Squares method, a statistical technique that uses regression analysis to estimate the line of best fit.
How does the High-Low method work to separate fixed and variable costs?
-The High-Low method identifies the highest and lowest levels of activity and the corresponding costs. By subtracting the low-cost point from the high-cost point and the low-activity level from the high-activity level, the variable cost per unit is calculated. The fixed cost is then determined by subtracting the total variable cost at a given activity level from the total cost at that level.
What is the Scattergraph method, and how is it used to analyze cost behavior?
-The Scattergraph method involves plotting data points on a graph with the cost on the y-axis and the activity level on the x-axis. The data points are then visually analyzed, and a line is drawn to represent the relationship between cost and activity. This helps in estimating the fixed and variable cost components.
What is the Least Squares method, and how is it different from the High-Low and Scattergraph methods?
-The Least Squares method is a regression analysis technique used to determine the best-fitting line through a set of data points. Unlike the High-Low and Scattergraph methods, which are based on visual or simple calculations, the Least Squares method uses statistical formulas to minimize the sum of squared errors and derive more accurate estimates of fixed and variable costs.
What is the formula used in the Least Squares method, and what do the variables represent?
-The formula used in the Least Squares method is: y = a + bx. In this equation, 'y' represents the predicted cost, 'a' is the fixed cost (intercept), 'b' is the variable cost per unit (slope), and 'x' is the activity level. The formula helps in estimating the cost based on the relationship between the activity level and the cost.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Akuntansi Biaya Bab 3: Analisis Perilaku Biaya

Perilaku Biaya | Wahyu Pramesti, S.E., M.Si,. Ak., C.A
Cost Classifications - Managerial Accounting- Fixed Costs Variable Costs Direct & Indirect Costs

Perhitungan Biaya Produk Sampingan (By Product) | Akuntansi Biaya

2023 Meet 3 Akuntasi Manajemen : Konsep dan Prilaku Biaya

PERAN AKUNTAN DALAM ORGANISASI
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)