PRINSIP KERJA TRANSFORMATOR
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the working principles of a transformer, focusing on its key components: primary and secondary coils. It discusses how alternating current (AC) creates a magnetic flux that induces voltage in the secondary coil. The video highlights the factors affecting voltage in transformers, such as flux and the number of turns in the coils. It also touches on the efficiency of transformers, emphasizing energy losses and the importance of proper design for minimizing power loss. The video concludes with a discussion on the equations governing transformers and the concept of efficiency.
Takeaways
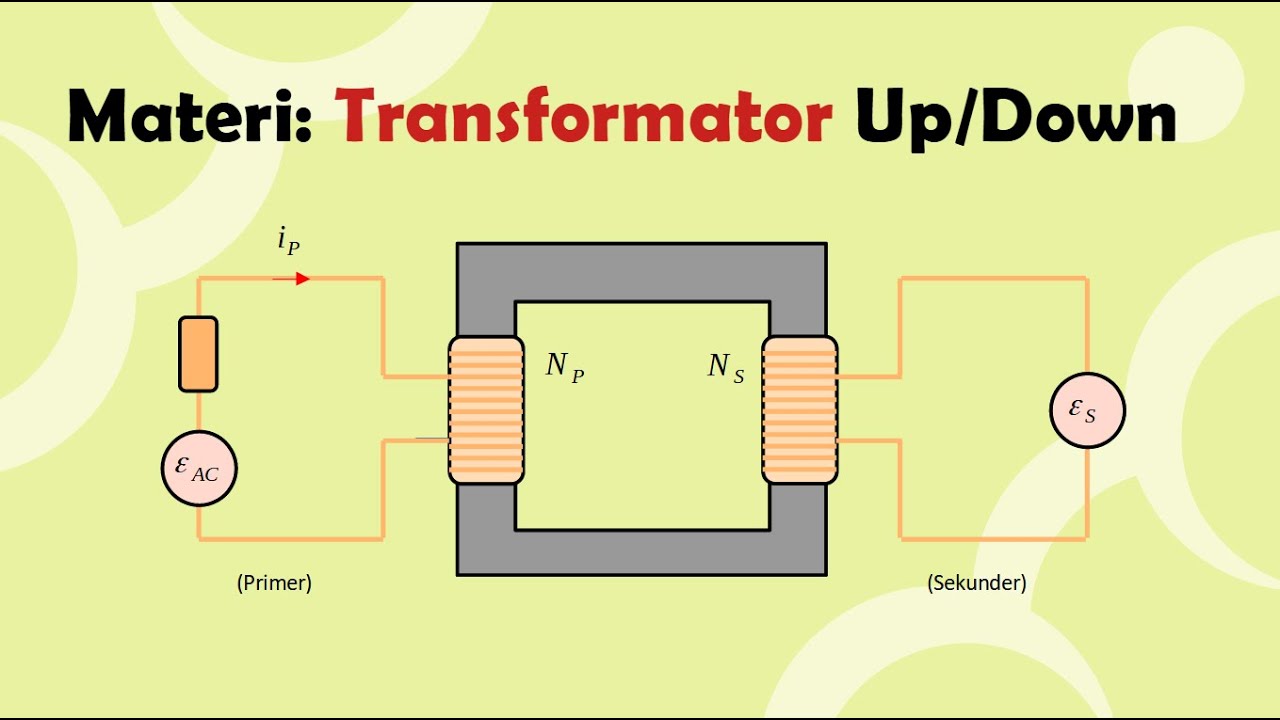
- 😀 Transformers consist of two coils: the primary coil (kumparan primer) and the secondary coil (kumparan sekunder).
- 😀 A transformer works by using electromagnetic induction to transfer energy from the primary to the secondary coil.
- 😀 AC (alternating current) passing through the primary coil generates a magnetic field, which induces voltage in the secondary coil.
- 😀 DC (direct current) in the primary coil creates a static magnetic field, which does not induce voltage in the secondary coil.
- 😀 The amount of induced voltage in the secondary coil depends on the magnetic flux and the number of turns in the coil.
- 😀 The more turns in the secondary coil, the higher the induced voltage.
- 😀 The transformer can either step up or step down the voltage, depending on the ratio of turns in the primary and secondary coils.
- 😀 The voltage ratio between the primary and secondary coils is given by the formula: V_primary / V_secondary = N_primary / N_secondary.
- 😀 Power loss occurs in transformers due to heat generated by resistance and magnetic flux leakage.
- 😀 Transformer efficiency is the ratio of power output (secondary) to power input (primary), and it is calculated as: Efficiency = (Power output / Power input) * 100%.
- 😀 Transformers are crucial for power transmission and distribution, enabling voltage conversion while minimizing losses in energy.
Q & A
What are the main components of a transformer?
-The main components of a transformer are the primary coil (kumparan primer) and the secondary coil (kumparan sekunder), which are wound around a core. The primary coil receives alternating current (AC), which generates a fluctuating magnetic field that induces current in the secondary coil.
How does alternating current (AC) work in the transformer?
-In a transformer, alternating current (AC) flows through the primary coil, creating a changing magnetic flux. This changing magnetic flux is transferred to the secondary coil, inducing a voltage and current in the secondary coil through electromagnetic induction.
Why does a transformer require alternating current (AC) to function effectively?
-A transformer requires alternating current (AC) because AC generates a fluctuating magnetic field. A fluctuating magnetic field is necessary for electromagnetic induction to occur, which is the fundamental process through which a transformer operates. If direct current (DC) were used, the magnetic field would remain constant, and no induced voltage would be generated in the secondary coil.
What happens if direct current (DC) is applied to a transformer?
-If direct current (DC) is applied to the primary coil of a transformer, the magnetic field generated would be constant, not fluctuating. This means no voltage would be induced in the secondary coil, and the transformer would not work as intended.
How does the number of turns in the coils affect the output voltage of a transformer?
-The number of turns in the coils affects the voltage induced in the secondary coil. The voltage in the secondary coil is directly proportional to the ratio of the number of turns between the primary and secondary coils. If the secondary coil has more turns than the primary, the output voltage will be higher (step-up transformer). If the secondary coil has fewer turns, the output voltage will be lower (step-down transformer).
What is the relationship between the voltage and number of turns in a transformer?
-The relationship between the voltage and the number of turns in a transformer is described by the formula: Vp/Vs = Np/Ns, where Vp is the primary voltage, Vs is the secondary voltage, Np is the number of turns on the primary coil, and Ns is the number of turns on the secondary coil. This means the voltage ratio between the primary and secondary coils is proportional to the ratio of the number of turns.
What factors influence the induced voltage in the secondary coil of a transformer?
-The induced voltage in the secondary coil is influenced by several factors: the number of turns in the secondary coil, the magnetic flux that is transferred from the primary coil, and the strength of the magnetic field. The closer the coils are to each other and the more turns the secondary coil has, the greater the induced voltage will be.
What is meant by the efficiency of a transformer, and how is it calculated?
-The efficiency of a transformer refers to how effectively it converts input electrical power into output electrical power without significant losses. It is calculated using the formula: Efficiency = (Power Output / Power Input) × 100%. Efficiency is often less than 100% due to losses like heat generation in the transformer.
What are the primary sources of power loss in a transformer?
-The primary sources of power loss in a transformer are core losses (hysteresis and eddy currents in the core material) and copper losses (resistance of the wires in the coils). These losses result in the generation of heat, reducing the overall efficiency of the transformer.
What is the role of magnetic flux in the operation of a transformer?
-Magnetic flux plays a crucial role in the operation of a transformer. When alternating current flows through the primary coil, it generates a fluctuating magnetic flux. This magnetic flux is transferred to the secondary coil, where it induces a voltage and current through the process of electromagnetic induction.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Materi Kemagnetan Kelas 9 (Part-6) Transformator

IPA Kelas 9 Semester 2 : Kemagnetan (part 5 : Transformator)

Como funciona um Transformador?

APA ITU TRANSFORMATOR | CARA KERJA DAN CARA HITUNG TRAFO
Apa yang dimaksud transformator step up dan step down induksi elekromagnet kelas 12

How LVDT Works | Construction and Working
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)