[PART 1] KONSEP DASAR STATISTIKA INFERENSIA
Summary
TLDRIn this lecture on inferential statistics, the instructor explains key concepts such as data, population, sample, and hypothesis testing, guiding students through the transition from descriptive to inferential statistics. The lecture emphasizes understanding quantitative data, selecting appropriate research variables, and choosing suitable data collection methods, using a research example about the impact of reciprocal learning on students' creative thinking. Students are encouraged to formulate hypotheses, collect data, and apply statistical techniques to draw conclusions. The focus is on preparing students to analyze and interpret data in quantitative research effectively.
Takeaways
- 😀 Inferential Statistics builds upon Descriptive Statistics learned in the previous semester.
- 😀 The goal of Inferential Statistics is to analyze data and draw conclusions about a population based on a sample.
- 😀 Understanding **data**, **populations**, **samples**, and **hypotheses** are the foundation for conducting inferential statistical analysis.
- 😀 Inferential Statistics involves three main activities: **hypothesis testing**, **estimating** parameters, and **drawing conclusions**.
- 😀 Data in Inferential Statistics is typically quantitative and can be obtained through various methods like tests, surveys, or observations.
- 😀 The **hypothesis** is central to statistical inference, and researchers must formulate hypotheses before testing them with statistical tools.
- 😀 It's important to understand the **data types** (nominal, ordinal, interval, ratio) and the scale of measurement when designing a study.
- 😀 **Populations** represent the entire group being studied, and **samples** are the subsets used to make inferences about the population.
- 😀 The lecture provides an example of a quantitative research study involving the impact of a learning model on students' creative thinking.
- 😀 Researchers must carefully select data that answers the research questions posed in the study, ensuring the data aligns with the problem being investigated.
Q & A
What is the focus of the Statistika Inferensia (Inferential Statistics) course mentioned in the transcript?
-The focus of the Statistika Inferensia course is to introduce students to inferential statistics, particularly in the context of quantitative research. The course emphasizes understanding data analysis techniques, hypothesis testing, and drawing conclusions from sample data to infer characteristics of a larger population.
How does Inferential Statistics differ from Descriptive Statistics?
-Inferential Statistics, which is the focus of the course, is used to make predictions or inferences about a population based on sample data. Descriptive Statistics, covered in the previous course (Statistics 1), is focused on summarizing and presenting data without drawing broader conclusions.
What are the three key elements highlighted in the lecture for understanding Inferential Statistics?
-The three key elements highlighted are: 1) Data, 2) Populations and Samples, and 3) Hypothesis. These concepts are critical for understanding the process of inferential statistics, which involves collecting data, analyzing it, and making conclusions about a larger population.
What is the importance of understanding the concept of 'data' in Inferential Statistics?
-Understanding 'data' is essential in Inferential Statistics because data is the foundation of statistical analysis. Knowing the type of data (quantitative or qualitative), the methods of collecting it, and the techniques used to analyze it are crucial for making accurate inferences and conclusions.
What role do populations and samples play in Inferential Statistics?
-In Inferential Statistics, populations refer to the entire group of individuals or items the research aims to study, while samples are smaller, manageable subsets of the population. Understanding the relationship between these two concepts is key for making accurate generalizations from sample data to the larger population.
Why is hypothesis formulation important in Inferential Statistics?
-Hypothesis formulation is crucial in Inferential Statistics because it provides a clear research question or assumption that can be tested using statistical methods. The hypothesis guides the data analysis and helps researchers make decisions about the validity of their assumptions based on the sample data.
What are the three main activities in Inferential Statistics as mentioned in the lecture?
-The three main activities in Inferential Statistics are: 1) Hypothesis testing, 2) Estimation or interpretation, and 3) Drawing conclusions based on statistical evidence. These activities allow researchers to test assumptions, estimate parameters, and make inferences about a population.
How does the example research title ('The effect of PAI learning with reciprocal learning model on creative thinking skills of 10th-grade SMK students') relate to the concepts of Inferential Statistics?
-The example research title highlights two key variables (PAI learning and creative thinking skills) that will be studied in the sample (10th-grade SMK students). It demonstrates the need to identify the appropriate data to collect (e.g., student performance on creative thinking), define the population and sample, and develop a hypothesis to test the relationship between the variables.
What types of data are discussed in the lecture, and which one is relevant for Inferential Statistics?
-The lecture discusses three types of data based on form: 1) Quantitative data, which is the primary data type used in Inferential Statistics, and 2) Qualitative data. Quantitative data, such as numerical measurements or scores, is necessary for applying statistical techniques like hypothesis testing and estimation.
Why is it important for researchers to carefully choose data collection methods, such as surveys or tests, for their research?
-It is important for researchers to choose appropriate data collection methods because the type of data collected must align with the research question and the statistical techniques used. For example, surveys, tests, or observations must be designed to gather the right type of data (e.g., quantitative data) to answer the research questions and support valid conclusions.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
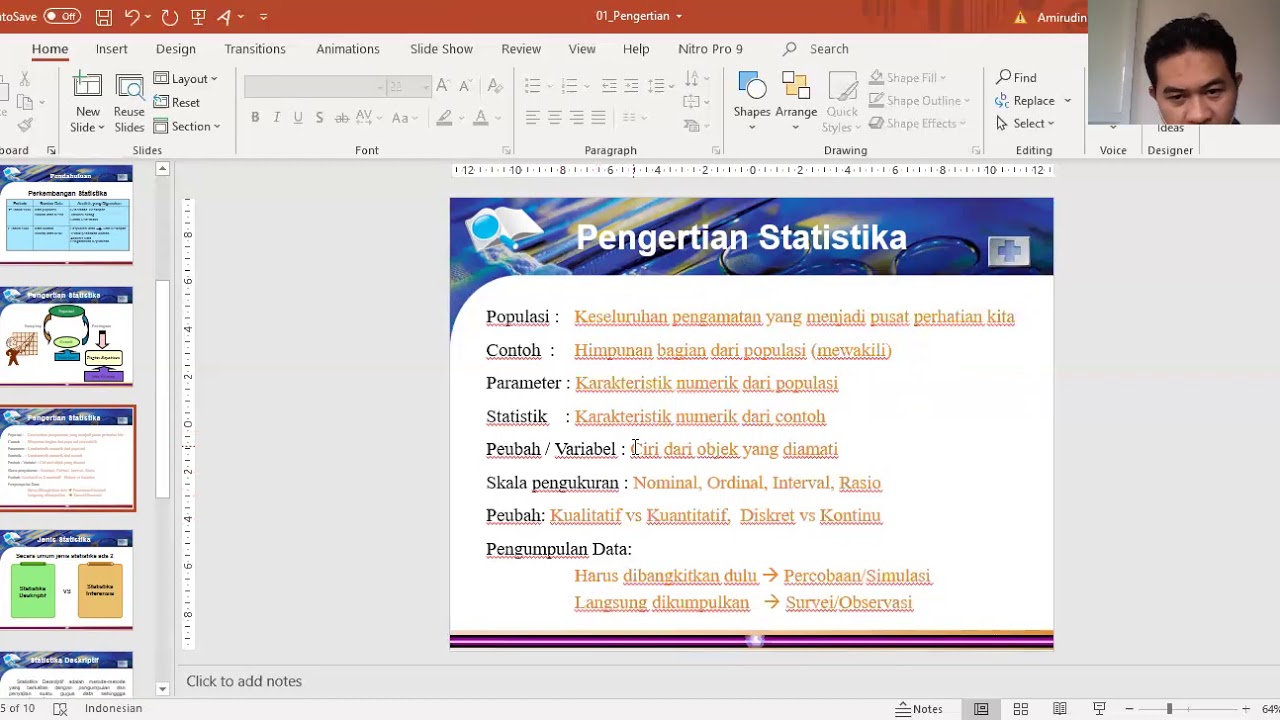
Pertemuan 1 Statistika sosial

Statistik Inferensial

Apa itu Statistika?

KUPAS TUNTAS: Apakah Perbedaan Statistik Inferensial dengan Statistik Deskriptif ?

PERBEDAAN STATISTIKA DESKRIPTIF DAN INFERENSIAL | Dive Deeper | Algoritma 2023
Descriptive Statistics vs Inferential Statistics | Measure of Central Tendency | Types of Statistics
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)