Models of communication
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the principles of communication, outlining three main models: Linear, Interactive, and Transactional. It explains the goal of communication—ensuring the receiver can easily understand the message. The Linear model, exemplified by Aristotle's framework, emphasizes one-way communication. The Interactive model highlights two-way communication, with the Osgood-Schramm model showing mutual roles of sender and receiver. The Transactional model focuses on continuous, real-time feedback, as illustrated by Dan’s Helo model, enhancing communication through immediate responses. These models provide a foundation for understanding how effective communication works in different contexts.
Takeaways
- 😀 The goal of communication is to ensure a successful relay of a message.
- 😀 Effective communication requires that the receiver easily understands the conveyed message.
- 😀 Communication models can be categorized into three types: linear, interactive, and transactional.
- 😀 Linear communication models emphasize one-directional communication, like Aristotle's model.
- 😀 Aristotle's communication model involves five key elements: speaker, speech, occasion, target audience, and effect.
- 😀 Interactive communication models involve two-way communication and emphasize equal roles for both sender and receiver.
- 😀 The Osgood-Schramm model is an example of an interactive model where the sender and receiver exchange roles between encoder and decoder.
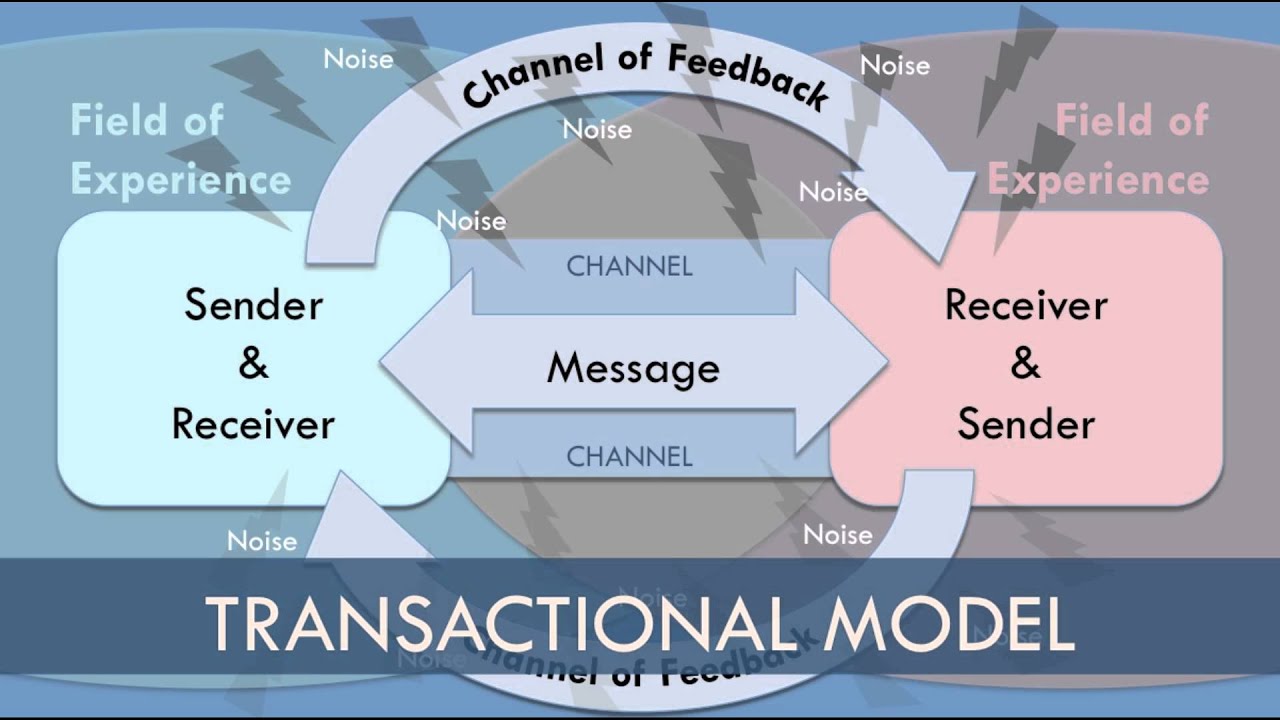
- 😀 Transactional models focus on two-way communication with immediate feedback between participants.
- 😀 Dan's Helo model illustrates the importance of frequent feedback to improve communication in transactional models.
- 😀 In interactive and transactional models, communication is dynamic, with continuous exchange between parties.
Q & A
What is the primary goal of communication?
-The primary goal of communication is the successful relay of a message, ensuring that the receiver can easily understand the message being conveyed.
What are the three categories of communication models?
-The three categories of communication models are linear, interactive, and transactional.
How does a linear communication model function?
-A linear communication model focuses on one-way communication, where a message flows in a single direction from sender to receiver.
Can you provide an example of a linear communication model?
-An example of a linear communication model is Aristotle's communication model, which involves five elements: speaker, speech, occasion, target audience, and effect.
What is the key characteristic of interactive communication models?
-Interactive communication models involve two-way communication, with both the sender and receiver actively participating and alternating between encoding and decoding messages.
What does the Osgood-Schramm model of communication emphasize?
-The Osgood-Schramm model emphasizes that both the sender and receiver are equal participants in communication, constantly fluctuating between the roles of encoder and decoder.
How do transactional communication models differ from interactive ones?
-Transactional communication models go beyond two-way communication by involving immediate feedback between participants, creating a more dynamic and continuous exchange of messages.
What is the focus of Dan's Helo model in communication?
-Dan's Helo model focuses on improving communication through frequent feedback, enhancing clarity and understanding between the parties involved.
How are linear and interactive communication models different in terms of feedback?
-In linear communication models, feedback is not immediate or part of the communication process, whereas in interactive models, feedback is a crucial component that allows for a two-way exchange of messages.
What is the significance of feedback in transactional communication models?
-Feedback in transactional models is significant because it ensures that the message is continuously being processed and adjusted based on real-time responses, creating a more responsive communication process.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)