CORSO NETWORK ITA - Lezione 27 - STP "Spanning Tree Protocol"
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is explained in detail, focusing on its role in creating a loop-free network topology. STP operates at Layer 2 and prevents network loops by selecting a root bridge and assigning roles to switch ports (Root Port, Designated Port, and Blocked Port). The protocol calculates the lowest-cost paths and blocks redundant links while ensuring redundancy in case of failures. The video also covers STP's dynamic nature, with switches exchanging Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) to elect the root bridge and adapt to network changes. A hands-on demonstration using Cisco Packet Tracer illustrates STP in practice.
Takeaways
- 😀 STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) is a Layer 2 protocol that creates a virtual topology to prevent network loops in switched networks.
- 😀 While the physical topology remains unchanged, STP creates a virtual, loop-free structure to ensure efficient network traffic flow.
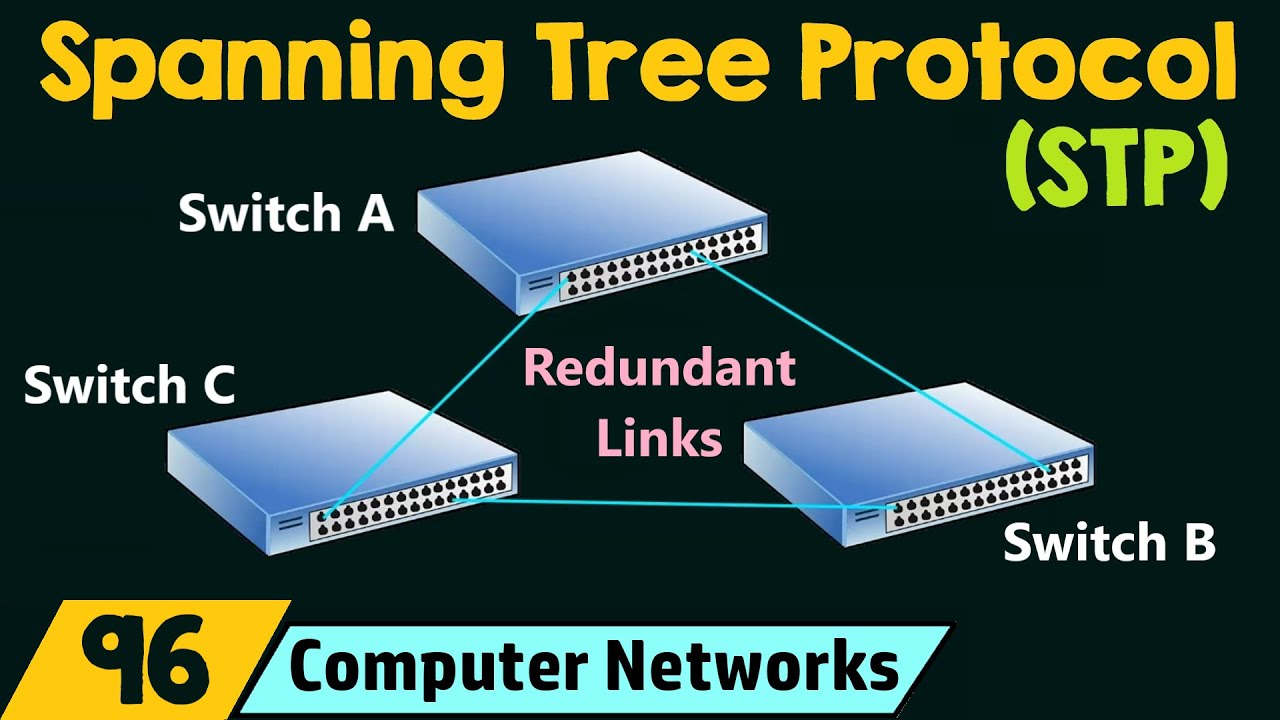
- 😀 The core function of STP is to eliminate network loops, which could lead to broadcast storms or other performance issues.
- 😀 STP utilizes a spanning tree structure, which is a connected graph with the minimum number of links, ensuring redundancy while avoiding loops.
- 😀 A spanning tree is a subgraph that connects all nodes in the network using the least number of edges, ensuring no redundant connections.
- 😀 The first step of STP involves selecting a Root Bridge, which serves as the central reference point for all switches in the network.
- 😀 Once the Root Bridge is selected, all other switches (Non-Root Bridges) calculate the shortest path to the Root Bridge based on link costs.
- 😀 Ports on each switch are assigned roles: Root Port (the port that leads to the Root Bridge) and Designated Port (the port leading away from the Root Bridge).
- 😀 Unnecessary links are blocked to prevent redundancy and potential loops, but they remain as backups in case the primary link fails.
- 😀 STP operates dynamically, meaning it can adapt to network changes like the failure of a link or the Root Bridge itself, by recalculating the best paths and activating backup links if needed.
Please replace the link and try again.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)