Что такое UEFI и BIOS?🤔 КОРОТКО и ЯСНО обо всём!✅
Summary
TLDRThis YouTube video from the 'Компьютерные фишки' channel dives into the differences between BIOS and UEFI, two types of firmware used to boot up computers. BIOS, the Basic Input/Output System, has been around since the 1980s and is limited to booting from hard drives up to 2.1 TB and operates in a 16-bit mode with only 1 MB of memory. UEFI, the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface, is a newer standard that overcomes BIOS's limitations, supporting larger drives and operating in a 32-bit or 64-bit mode. It also introduces a graphical user interface, mouse support, and secure boot options. The video explains how UEFI is a significant upgrade that most modern computers use, making them more efficient and capable of supporting advanced hardware without users needing to understand the underlying firmware changes.
Takeaways
- 🌟 BIOS (Basic Input Output System) is a low-level program stored on a chip on your computer's motherboard that initializes hardware components and starts the operating system.
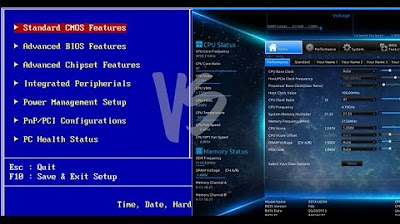
- 🔄 UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) is a newer standard that replaces traditional BIOS, offering faster boot times, support for larger hard drives, and a graphical interface.
- 🚫 Traditional BIOS has limitations, such as only supporting hard drives up to 2.1 TB and operating in a 16-bit processor mode with only 1 MB of memory.
- 🛠️ UEFI supports emulation of BIOS, allowing users to install and run older operating systems that expect BIOS instead of UEFI.
- 💾 BIOS settings are saved in CMOS memory, which is being phased out in favor of flash memory, also known as EEPROM.
- 🔗 UEFI uses GPT (GUID Partition Table) instead of MBR (Master Boot Record), which allows for larger disk sizes and more efficient partitioning.
- 🛡️ UEFI includes features like Secure Boot, which ensures that the operating system has not been tampered with by malicious software.
- 🌐 UEFI can support networking, enabling remote configuration and debugging, which is not possible with traditional BIOS.
- 🖥️ Accessing UEFI settings may require entering the boot menu or using a specific key during startup, which can vary between manufacturers.
- ⚙️ UEFI is essentially a small operating system that runs on top of the computer's firmware, capable of more complex tasks than BIOS.
- ⏱️ Computers with UEFI boot faster and can support modern hardware and features, providing a smoother user experience without needing to understand the underlying firmware changes.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the video script?
-The main topic discussed in the video script is the difference between BIOS (Basic Input Output System) and UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface), and the transition from BIOS to UEFI in modern computers.
What does BIOS stand for?
-BIOS stands for Basic Input Output System, which is a low-level program stored on a chip on the motherboard of a computer.
What is UEFI?
-UEFI stands for Unified Extensible Firmware Interface, a newer solution that replaces the traditional BIOS and provides a more advanced booting process with features like support for larger hard drives, faster boot times, and a graphical interface.
Why is UEFI considered an improvement over BIOS?
-UEFI is considered an improvement over BIOS because it supports larger hard drives, boots faster, is more secure, and features a graphical interface with mouse support, among other enhancements.
What is the main limitation of BIOS that UEFI addresses?
-One of the main limitations of BIOS is that it can only boot from hard drives with a capacity of up to 2.1 TB, while UEFI supports much larger volumes and uses GPT (GUID Partition Table) instead of MBR (Master Boot Record).
How does UEFI support larger hard drives compared to BIOS?
-UEFI supports larger hard drives by using GPT instead of MBR, which allows for the management of hard drives with capacities far beyond the 2.1 TB limit imposed by BIOS.
What is the theoretical limit for storage devices supported by UEFI?
-The theoretical limit for storage devices supported by UEFI is 9.4 Zettabytes, which is significantly larger than the 2.1 TB limit of BIOS.
What is Secure Boot and how does UEFI support it?
-Secure Boot is a feature that allows the verification of the integrity of the operating system during the boot process to prevent tampering by malicious software. UEFI supports Secure Boot, enhancing the security of the boot process.
How does UEFI differ from BIOS in terms of its execution environment?
-UEFI can operate in 32-bit or 64-bit modes, providing a larger addressable space compared to BIOS, which operates in a 16-bit mode. This allows for faster boot times and more advanced features.
Why might some users not notice the transition from BIOS to UEFI on their computers?
-Some users might not notice the transition from BIOS to UEFI because the change is often seamless, with UEFI providing backward compatibility and improved performance without requiring user intervention.
What is the significance of the transition from BIOS to UEFI for modern computers?
-The transition from BIOS to UEFI is significant as it allows modern computers to better support contemporary hardware and software, offering improved performance, security, and compatibility with larger storage devices and advanced booting features.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)