Work and Energy | Grade 8 Science DepEd MELC Quarter 1 Module 3 Part 3 Kinetic Energy
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explores kinetic energy, the energy of a moving object, derived from Greek 'kinetikus' meaning moving. It explains how kinetic energy quantifies the work an object can perform due to its motion, using the example of a bowling ball to illustrate acceleration and force. The script teaches the formulas for calculating acceleration, force, average velocity, and displacement, leading to the derivation of the kinetic energy formula: KE = (1/2)mv^2. Practical examples, like a truck's kinetic energy and a hockey player's mass, are used for clarity. The video concludes with a discussion on energy transformation, emphasizing the law of conservation of energy, which states that energy can only change forms and never be created or destroyed.
Takeaways
- 🚀 Kinetic energy is the energy possessed by an object due to its motion.
- 🔍 The term 'kinetic' is derived from the Greek word 'kinetikos', meaning 'moving'.
- 📚 Kinetic energy can be quantified and is related to the work an object can do because of its motion.
- 🎱 An example given is a bowling ball rolling to hit pins, which has kinetic energy due to its motion.
- ⏱️ Acceleration is defined as the rate of change in velocity, calculated as ( a = (v_f - v_i) / t ), where v_i is initial velocity, v_f is final velocity, and t is time.
- 📉 The formula for force according to Newton's second law is ( F = m * a ), which can be rearranged using the concept of acceleration.
- 📏 The average velocity of an object can be calculated as ( v_f + v_i ) / 2, and when the initial velocity is zero, it simplifies to v_f / 2.
- 📐 Displacement, or the distance an object travels, is found by multiplying the average velocity by time.
- 🔄 The formula for kinetic energy is derived from the work-energy principle, expressed as ( KE = 1/2 * m * v^2 ).
- 📘 A practical example is given where a truck's kinetic energy is calculated using its mass and velocity.
- 🏒 Another example involves calculating the mass of a hockey player using their kinetic energy and velocity.
- 🔄 Energy transformation is illustrated through examples like a roller coaster, where potential and kinetic energy convert back and forth.
- 🌐 The law of conservation of energy is highlighted, stating that energy can only change forms and is neither created nor destroyed.
Q & A
What is kinetic energy?
-Kinetic energy is the energy of a moving object. It quantifies the amount of work an object can do because of its motion.
What is the origin of the word 'kinetic'?
-The word 'kinetic' comes from the Greek word 'kinetikos', which means moving.
How is acceleration defined in the context of the video?
-Acceleration is defined as the rate of change in velocity, calculated as final velocity minus initial velocity divided by time.
What is the formula for force according to the law of acceleration?
-The formula for force according to the law of acceleration is force equals mass times acceleration.
How is average velocity calculated for an object starting from rest?
-If an object starts from rest, the average velocity is calculated as final velocity divided by two.
What is the formula to calculate the distance traveled by an object?
-The distance traveled by an object is calculated as average velocity times time.
How is kinetic energy related to work done on an object?
-The work done in accelerating an object is equal to the kinetic energy gained by the object.
What is the formula for kinetic energy?
-The formula for kinetic energy is mass times velocity squared divided by two.
In the sample problem, what is the kinetic energy of a 3000 kg truck moving at 40 m/s?
-The kinetic energy of the truck is calculated as (3000 kg * (40 m/s)^2) / 2, which equals 2,400,000 Joules or 2.4 million Joules.
How can you find the mass of an object given its kinetic energy and velocity?
-You can find the mass of an object by rearranging the kinetic energy formula to mass equals 2 multiplied by kinetic energy divided by velocity squared.
What is the concept of energy transformation as discussed in the video?
-Energy transformation is the process of converting energy from one form to another, such as from potential to kinetic energy.
What does the law of conservation of energy state?
-The law of conservation of energy states that energy can only be transformed from one form to another and cannot be created or destroyed.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Grade 8 Science Q1 Ep6: Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy
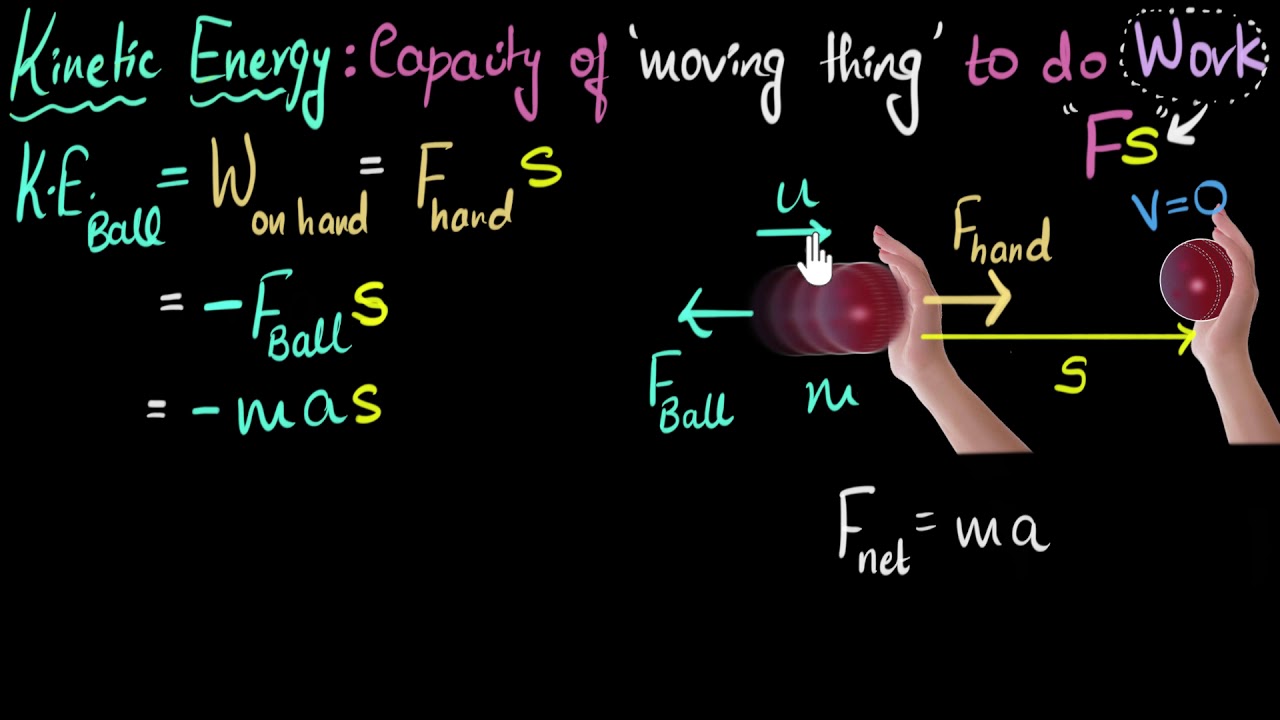
Kinetic energy derivation | Work & Energy | Physics | Khan Academy
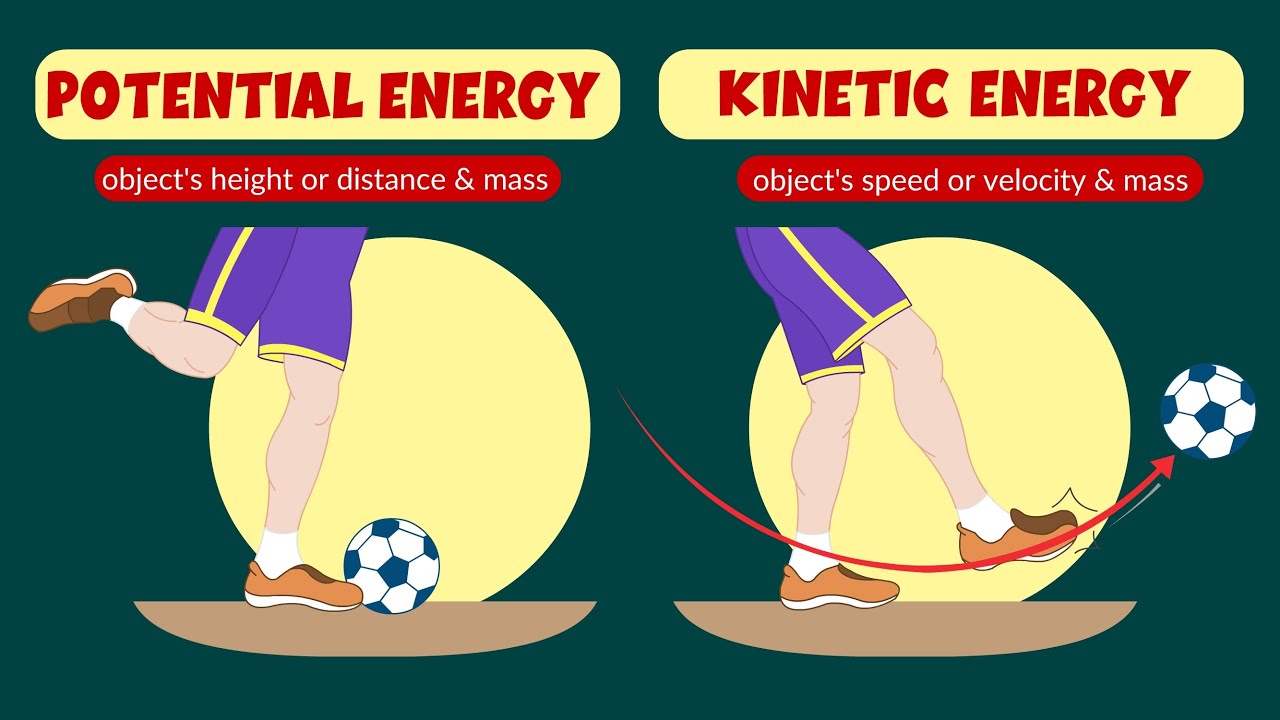
Potential and kinetic energy - Law of conservation of energy - Video for kids
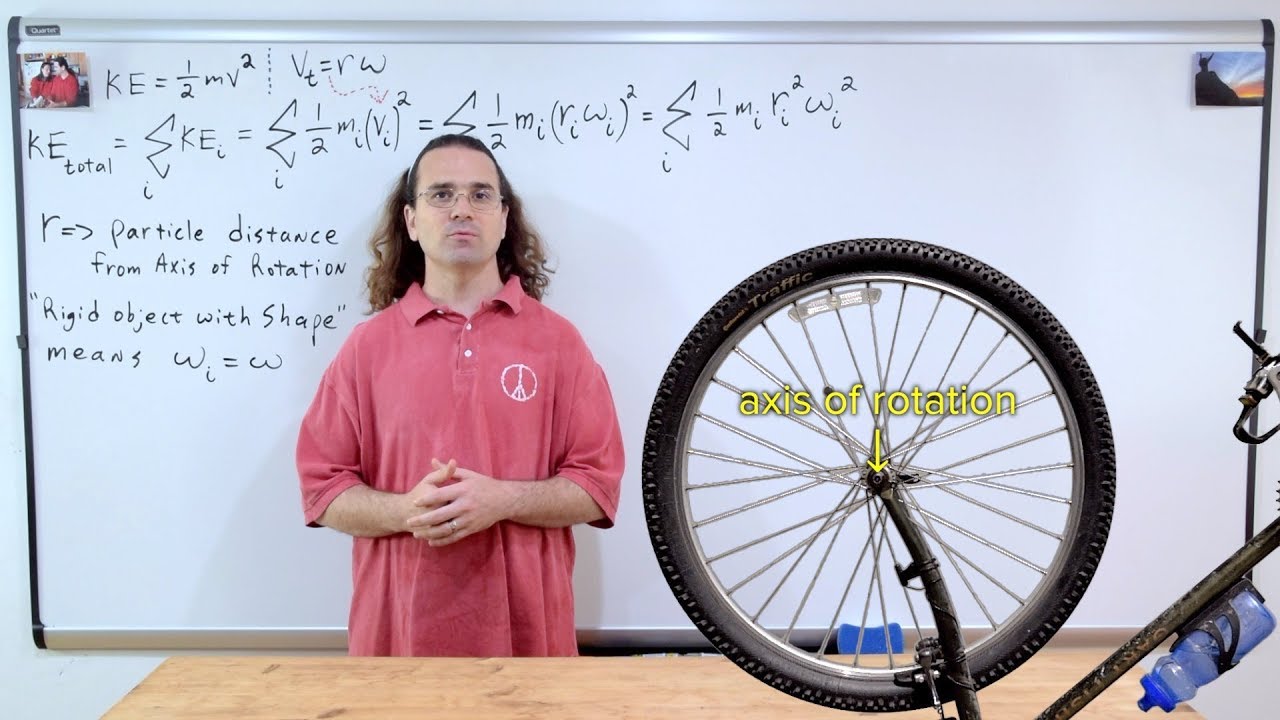

Moment of Inertia Introduction and Rotational Kinetic Energy Derivation

Sebuah benda bermassa 10 kg bergerak dengan kecepatan 20 mls: Dengan mengabaikan gaya gesek yang ...

ENERGI YANG BERGERAK (ENERGI KINETIK)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)