SPEKTROFOTOMETRI UV-Vis | Prinsip Kerja Spektrofotometri UV-Vis
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Professor Aira introduces UV-Vis Spectrophotometry, an analytical technique that uses ultraviolet and visible light to measure the concentration of chemical substances. The process involves measuring the absorption of light by a sample, with the results compared to a standard solution. The video covers the fundamental principles of light absorption, the key components of a spectrophotometer, and how different wavelengths of light interact with molecules. It concludes by explaining the relationship between absorbance, concentration, and the Beer-Lambert Law, offering valuable insights into this essential laboratory technique.
Takeaways
- 😀 Spectrophotometry UV-Vis is a chemical analysis technique using electromagnetic radiation in the UV (200-380 nm) and visible (380-780 nm) ranges.
- 😀 The method relies on the absorption of light by molecules in a sample, which helps determine its concentration by comparing with standard solutions.
- 😀 The term 'spectrophotometry' combines two components: 'spectrometry', which refers to generating light of specific wavelengths, and 'photometry', which refers to measuring light intensity.
- 😀 The basic principle involves the interaction of monochromatic light with the molecules in the sample, which leads to electron excitation and transitions.
- 😀 Molecules absorb light differently based on their energy requirements; shorter wavelengths are absorbed by molecules requiring more energy, and longer wavelengths by those needing less.
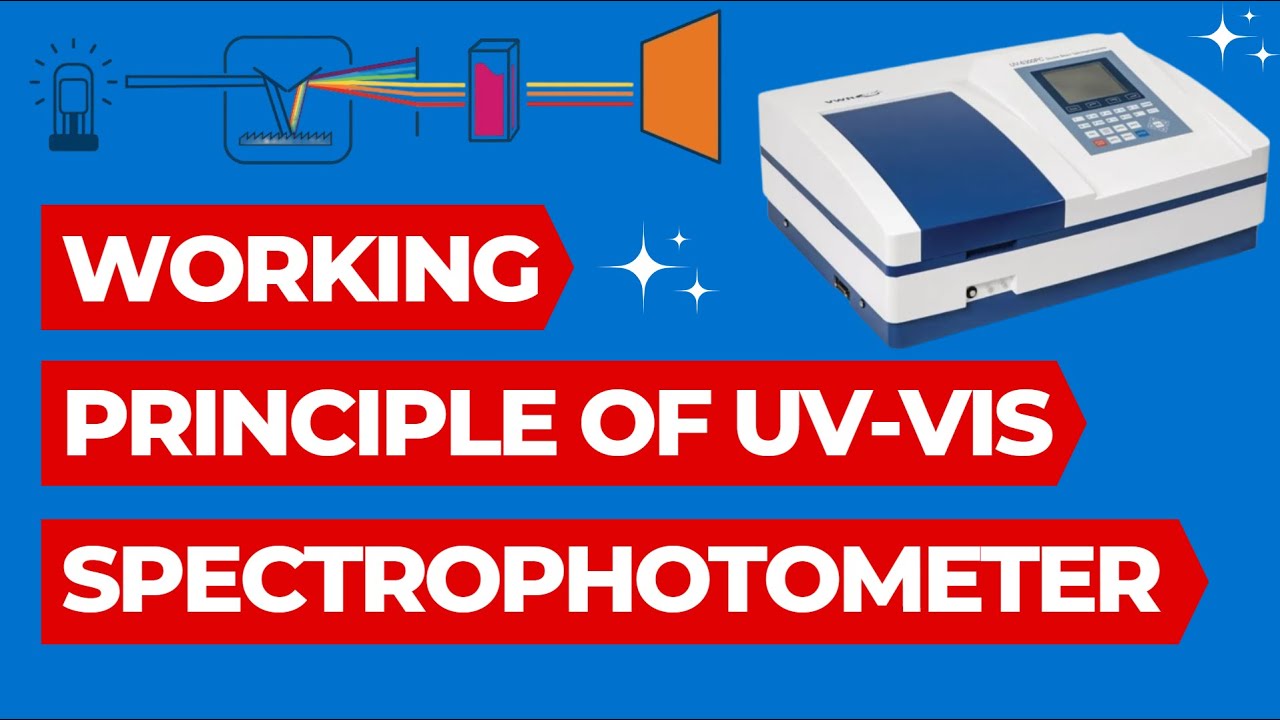
- 😀 UV-Vis spectrophotometry uses two main light sources: Deuterium lamps for UV light (200-380 nm) and Tungsten lamps for visible light (380-2200 nm).
- 😀 The light from the lamps is polychromatic (composed of many wavelengths) and is passed through a prism to separate it into individual wavelengths.
- 😀 The monochromatic light then passes through an optical slit and into a cuvette containing the sample, where some light is absorbed by the sample.
- 😀 The transmitted light is detected by a detector, which converts it into an electrical signal that is processed by a computer or recorder.
- 😀 The results are displayed as a spectrum showing the absorbance or transmittance of light across different wavelengths, providing valuable data for analysis.
- 😀 The cuvette, which holds the sample, can be made of glass for visible light analysis or quartz for UV light analysis due to their different absorption properties.
Q & A
What is UV-Vis spectrophotometry?
-UV-Vis spectrophotometry is an analytical technique that uses ultraviolet (UV) and visible light (VIS) to measure the absorption of light by a sample. The technique helps determine the concentration of a substance by measuring the intensity of light absorbed by the sample at different wavelengths.
What is the principle behind UV-Vis spectrophotometry?
-The principle of UV-Vis spectrophotometry is based on the interaction between electromagnetic radiation (light) and molecules. When light is absorbed by a sample, it can excite electrons from a lower energy state to a higher one. The amount of light absorbed is related to the concentration of the sample.
What are the wavelength ranges for UV and visible light in UV-Vis spectrophotometry?
-In UV-Vis spectrophotometry, UV light ranges from 200 to 380 nm, while visible light ranges from 380 to 780 nm.
What are the two main components of a UV-Vis spectrophotometer?
-The two main components of a UV-Vis spectrophotometer are the spectrometer, which produces the light with specific wavelengths, and the photometer, which measures the intensity of transmitted or absorbed light.
What is the role of the spectrometer in UV-Vis spectrophotometry?
-The spectrometer generates light at specific wavelengths from a radiation source and passes this light through the sample for analysis. It allows the selection of particular wavelengths of light, which are then directed onto the sample.
What happens when light interacts with a sample in UV-Vis spectrophotometry?
-When light interacts with a sample, it is absorbed by the molecules, leading to electronic excitation of the molecules. This results in the absorption of specific wavelengths of light, which can be measured to assess the sample's properties.
How does the UV-Vis spectrophotometer measure light absorption?
-The UV-Vis spectrophotometer measures light absorption using a detector that converts the absorbed light into an electrical signal. This signal is then processed by a computer to provide the absorbance or transmittance values.
What are the functions of the deuterium and tungsten lamps in a UV-Vis spectrophotometer?
-The deuterium lamp emits UV light (200–380 nm) and is used for measurements in the ultraviolet range, while the tungsten lamp emits visible light (380–2200 nm) and is used for measurements in the visible range.
What is a cuvette, and what materials are used for its construction?
-A cuvette is a small, transparent container used to hold the sample in the spectrophotometer. It can be made from different materials, such as glass for visible light measurements or quartz for UV measurements.
What is the significance of the wavelength selection process in UV-Vis spectrophotometry?
-The wavelength selection process is crucial for determining the specific absorption characteristics of a sample. By adjusting the wavelength, a spectrophotometer can measure how much light is absorbed by the sample at different points within the UV and visible spectrum, providing information about the sample's composition and concentration.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)