GCSE Maths - Regular Polygons #99
Summary
TLDRThis video explains regular polygons, focusing on key characteristics such as closed 2D shapes with straight sides, equal side lengths, and equal angles. It contrasts regular and irregular polygons, providing examples like equilateral triangles, squares, and hexagons. The video also covers the symmetry and rotational properties of these shapes, noting that regular polygons have as many lines of symmetry as sides. The video concludes by showcasing various regular polygons, from an equilateral triangle to a decagon, with a focus on their symmetry and rotational symmetry.
Takeaways
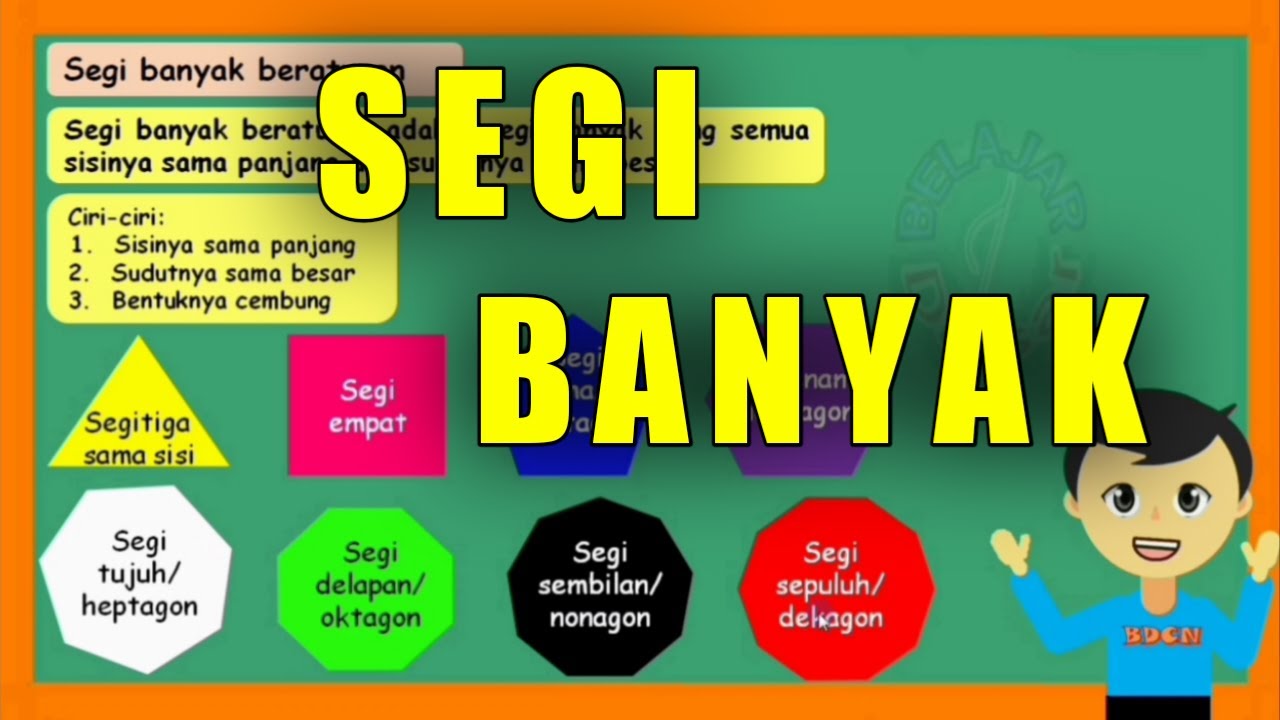
- 😀 A regular polygon is a closed 2D shape made up of straight lines, with equal side lengths and equal angles.
- 😀 Polygons must have straight lines and be closed; shapes with curved lines or open shapes do not qualify as polygons.
- 😀 The term 'regular' in regular polygon means all sides and angles are identical in size and length.
- 😀 An equilateral triangle is a regular polygon, with three equal sides and three 60-degree angles.
- 😀 An irregular polygon has sides or angles that are not equal, like the irregular quadrilateral or irregular pentagon.
- 😀 A regular polygon with four sides is called a square, a regular polygon with five sides is a regular pentagon, and so on.
- 😀 Regular polygons continue in sequence from an equilateral triangle (3 sides) to a decagon (10 sides).
- 😀 Every regular polygon has the same number of lines of symmetry as it has sides (e.g., a regular hexagon has six lines of symmetry).
- 😀 Regular polygons also have rotational symmetry, meaning they look the same at specific rotations (e.g., a square has order 4 rotational symmetry).
- 😀 The order of rotational symmetry of a regular polygon is equal to the number of its sides, such as a heptagon having rotational symmetry of order 7.
Q & A
What defines a regular polygon?
-A regular polygon is a closed 2D shape where all sides are of equal length and all angles are the same size.
What makes a shape a polygon?
-A polygon is a closed 2D shape made up entirely of straight lines. It must be closed (no gaps between the lines), and the lines must be straight.
Why are shapes with curved lines not considered polygons?
-Shapes with curved lines are not considered polygons because, by definition, polygons must only have straight sides.
What is the difference between a regular and an irregular polygon?
-A regular polygon has all sides of equal length and all angles the same size. An irregular polygon has sides or angles that are not all the same.
Can a shape be a polygon but not a regular polygon?
-Yes, a shape can still be a polygon even if it is not a regular polygon. For example, an irregular quadrilateral or pentagon are polygons, but they are not regular polygons.
What is the significance of symmetry in regular polygons?
-Regular polygons have the same number of lines of symmetry as the number of sides. This means that the shape can be folded or mirrored along these lines to match itself perfectly.
How does rotational symmetry apply to regular polygons?
-A regular polygon has an order of rotational symmetry equal to the number of its sides. This means the shape can be rotated that many times within a full 360-degree rotation before it looks the same again.
How many lines of symmetry does a regular hexagon have?
-A regular hexagon has 6 sides, so it also has 6 lines of symmetry.
How many positions of symmetry does a square have during a 360-degree rotation?
-A square has 4 sides, so it has 4 positions of symmetry within a 360-degree rotation, meaning it will look the same in 4 different positions during a full rotation.
What is the order of rotational symmetry for a regular heptagon?
-A regular heptagon has 7 sides, so it has an order of rotational symmetry of 7, meaning it can be rotated 7 times within a full 360-degree rotation before it looks the same.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)