Math Antics - Polygons
Summary
TLDRIn this Math Antics video, viewers are introduced to the world of polygons, learning the key properties that define them. A polygon is a multi-sided, closed, 2D shape with straight sides, vertices, and angles. The video explains the essential components of polygons, such as sides, vertices, and angles, and clarifies the difference between closed and open shapes. It also explores various types of polygons based on the number of sides, like triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, and hexagons. Through interactive examples, the lesson teaches how to identify polygons and highlights their importance in geometry.
Takeaways
- 😀 Polygons are multi-sided shapes that have straight sides, vertices (intersection points of the sides), and angles formed by the intersecting lines.
- 😀 The term 'polygon' comes from the Greek word for 'many-angles', which refers to the angles formed at the vertices.
- 😀 A polygon must be a closed shape, meaning that all its sides are connected without any gaps, separating the inside from the outside.
- 😀 Polygons are 2D shapes, meaning all their vertices lie on the same plane; if any vertex is out of this plane, it's not a polygon.
- 😀 Shapes like circles, which have no straight sides, vertices, or angles, are not considered polygons.
- 😀 A polygon can have sides of different lengths, but it must still be a closed, 2D shape to qualify.
- 😀 Shapes with intersecting lines or curves disqualify them from being polygons (e.g., a star shape with crossed lines or a shape with curved sides).
- 😀 3D shapes like boxes, while made up of polygons, are not polygons themselves because they are not 2-dimensional.
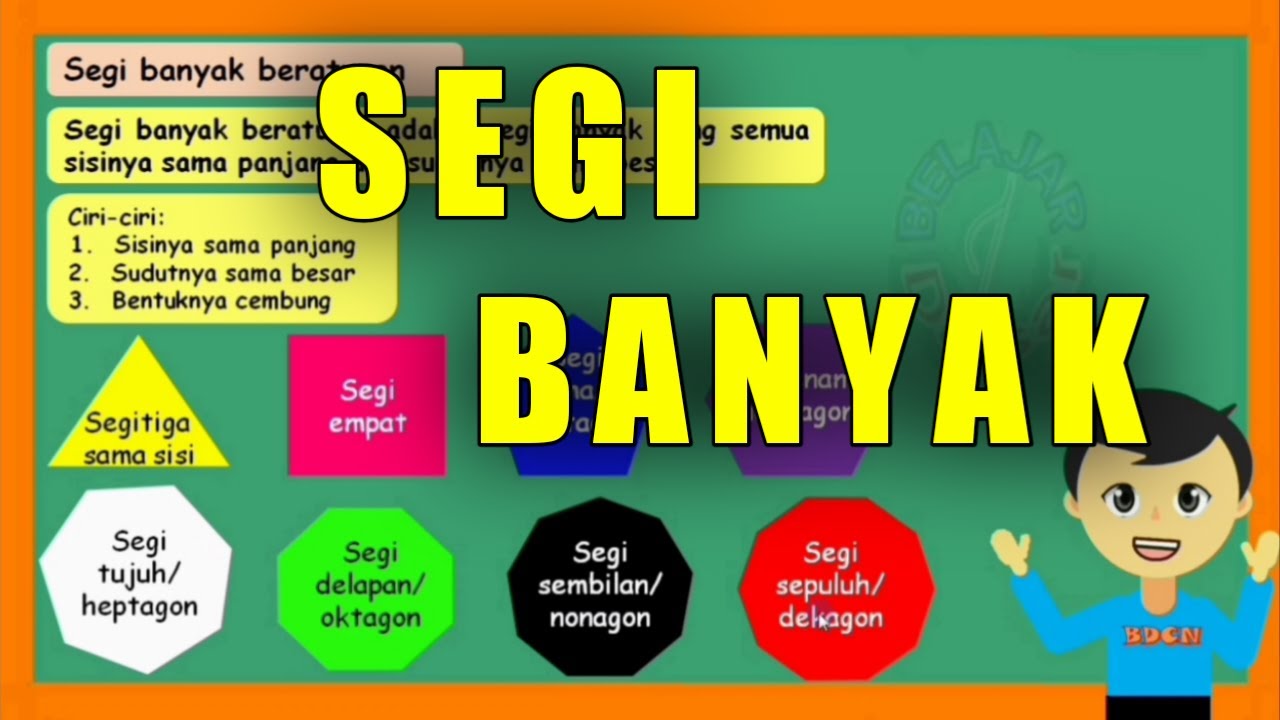
- 😀 Polygons are named based on the number of sides they have: triangles (3 sides), quadrilaterals (4 sides), pentagons (5 sides), hexagons (6 sides), and octagons (8 sides).
- 😀 Regular polygons have equal angles and sides, while irregular polygons have unequal angles or sides.
- 😀 Understanding what qualifies as a polygon helps distinguish between different geometric shapes, making it easier to identify them in various forms.
Q & A
What is the definition of a polygon?
-A polygon is a multi-sided, closed, two-dimensional shape that has straight sides, vertices, and angles.
What are the three parts that make up all polygons?
-The three parts of a polygon are sides (straight line segments), vertices (points where sides intersect), and angles (formed by the intersecting sides).
What does it mean for a polygon to be a closed shape?
-A polygon is considered a closed shape if its sides are connected without gaps, meaning there is no way to get from the inside to the outside without crossing a line.
Why must polygons be two-dimensional?
-Polygons must be two-dimensional because all their vertices must lie on the same plane. If any vertex were moved out of that plane, the shape would no longer be flat.
Can polygons be three-dimensional shapes?
-No, polygons themselves cannot be three-dimensional. However, polygons can be used to form the flat surfaces of three-dimensional shapes, like a box.
Is a circle considered a polygon? Why or why not?
-No, a circle is not a polygon because it does not have straight sides, vertices, or angles. It is a curved shape, which disqualifies it from being a polygon.
What is the difference between a regular polygon and an irregular polygon?
-A regular polygon has equal angles and equal sides, while an irregular polygon has sides and angles of different lengths or measures.
What is the special name for a 3-sided polygon?
-A 3-sided polygon is called a triangle.
What are some examples of 4-sided polygons?
-Examples of 4-sided polygons include squares, rectangles, and parallelograms, all of which are classified as quadrilaterals.
What happens if any sides of a polygon cross each other?
-If any sides of a polygon cross each other, the shape is no longer a polygon. The sides must not intersect or cross to maintain the classification of a polygon.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)