How DSLR Cameras Work
Summary
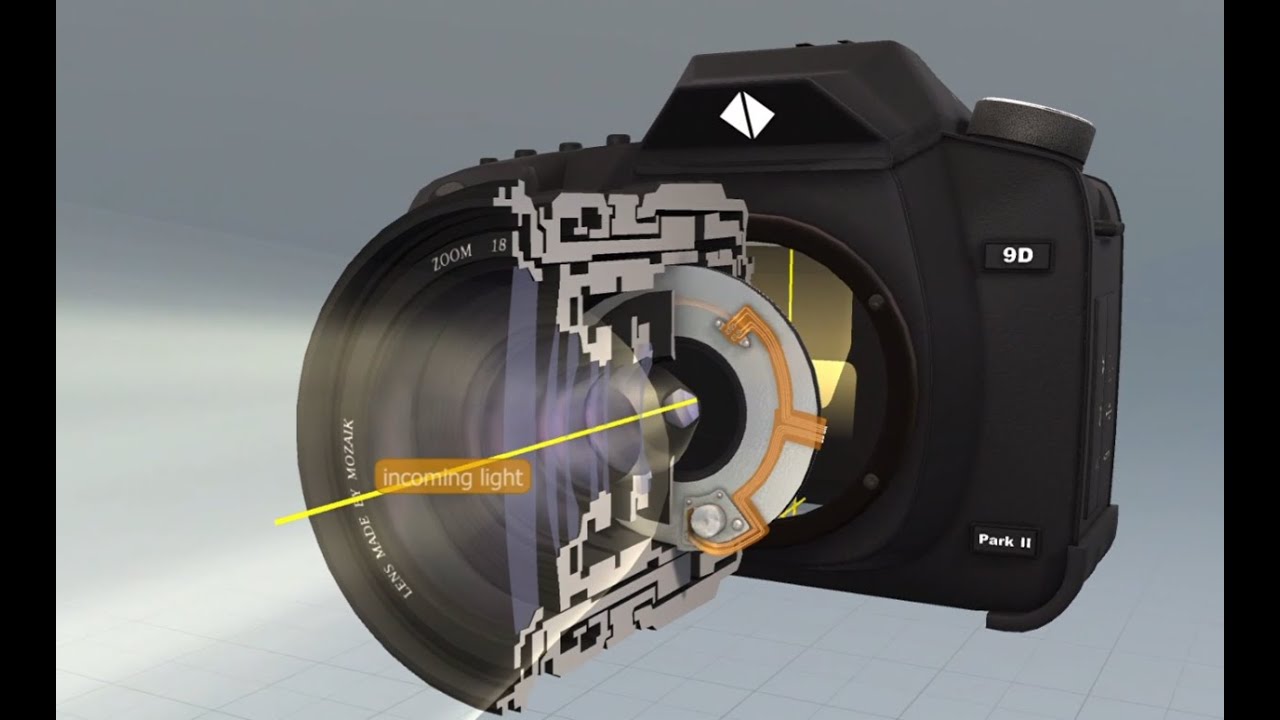
TLDRIn this video, the basics of how DSLR cameras work are explained. Light enters through the lens and hits a reflex mirror, allowing the user to view the scene through the viewfinder. The reflex mirror bounces light into a pentaprism, enabling a clear view. When the shutter is pressed, the mirror flips up, exposing the image sensor to light, capturing the photo. Once the shutter is released, the mirror and shutter close, returning the camera to its viewing state. This quick overview simplifies the inner workings of DSLRs and how they capture images.
Takeaways
- 😀 The first step in a DSLR camera is the lens, where light enters the camera.
- 😀 The light passing through the lens hits the reflex mirror, which directs it to the viewfinder.
- 😀 The viewfinder allows you to see the image through the lens by reflecting light via the reflex mirror and pentaprism.
- 😀 In older cameras, the image sensor is replaced by film, but the process is similar.
- 😀 The shutter controls the exposure, blocking light from reaching the film or image sensor when closed.
- 😀 Pressing the shutter button causes the reflex mirror to flip up and the shutter to open.
- 😀 When the shutter opens, light passes directly through the lens and onto the image sensor, creating the exposure.
- 😀 After the exposure, the reflex mirror returns to its original position, and the shutter closes.
- 😀 Once the shutter closes, the camera returns to its ready state, and the viewfinder is again usable.
- 😀 DSLR cameras use a combination of the reflex mirror, shutter, and image sensor (or film) to capture photos quickly and accurately.
- 😀 This process happens almost instantly, allowing photographers to capture sharp, well-exposed images.
Q & A
What is the first step in the functioning of a DSLR camera?
-The first step is the lens, which is located at the front of the camera. Light enters the camera through the lens.
How does the reflex mirror in a DSLR camera function?
-The reflex mirror reflects the light coming through the lens and directs it upwards into the pentaprism, allowing the user to see the image through the viewfinder.
What role does the pentaprism play in a DSLR camera?
-The pentaprism reflects the light coming from the reflex mirror so that the user can see the image correctly through the viewfinder, simulating what the lens captures.
What happens when you look through the viewfinder of a DSLR camera?
-When you look through the viewfinder, you're seeing the light that comes through the lens, bounces off the reflex mirror, and passes through the pentaprism, showing the image as captured by the lens.
Where is the image sensor located in a DSLR camera?
-The image sensor is located at the rear of the camera, where it captures the light and converts it into a digital image. In older SLRs, this space would contain the film.
How does the shutter function in a DSLR camera?
-The shutter controls the exposure of the image. When the shutter button is pressed, the reflex mirror lifts, the shutter opens, and light passes through the lens onto the image sensor, capturing the photo.
What happens to the reflex mirror when the shutter is pressed?
-When the shutter is pressed, the reflex mirror flips up, allowing light to pass through unobstructed, reaching the image sensor or film for exposure.
What occurs after the shutter is released in a DSLR camera?
-After the shutter is released, the reflex mirror returns to its original position, and the shutter curtains close, blocking light from reaching the sensor again.
Why is there no image visible through the viewfinder when the shutter is pressed?
-When the shutter is pressed, the reflex mirror flips up, blocking the viewfinder from receiving light, which is why no image is visible through it during exposure.
What is the significance of the shutter curtains in a DSLR camera?
-The shutter curtains control the timing of the exposure. When they open, light hits the image sensor to capture the photo, and when they close, the exposure ends.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)