Cognitive Load Theory 3 - intrinsic, extraneous, germane.
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the three types of cognitive load: intrinsic, extraneous, and germane. Intrinsic load refers to the inherent difficulty of a task based on the learner's expertise and working memory capacity. Extraneous load is the additional cognitive burden created by poorly designed materials or irrelevant details. Germane load, on the other hand, is the mental effort directed towards integrating new information with existing knowledge. Effective instructional design aims to manage these types of load by reducing extraneous factors, balancing intrinsic load, and promoting germane load to enhance learning outcomes.
Takeaways
- 😀 Cognitive load comes in three types: intrinsic, extraneous, and germane.
- 😀 Intrinsic load refers to the inherent difficulty of a task based on the learner's knowledge and task complexity.
- 😀 The number of novel elements in a task and how they interact determines intrinsic load.
- 😀 Working memory is limited to handling 3-7 novel elements at a time, while long-term memory can hold much more.
- 😀 Tasks are easier when the learner has more prior knowledge and well-developed schemas in long-term memory.
- 😀 Extraneous load is caused by poorly designed instructional materials, such as irrelevant details or distractions.
- 😀 Examples of extraneous load include flashy animations, irrelevant anecdotes, or using complex vocabulary unnecessarily.
- 😀 Germane load refers to the mental effort used to integrate new information with existing knowledge.
- 😀 The goal of instructional design is to maximize germane load while minimizing intrinsic and extraneous load.
- 😀 Good instructional design should reduce unnecessary distractions (extraneous load) and help learners make connections (germane load).
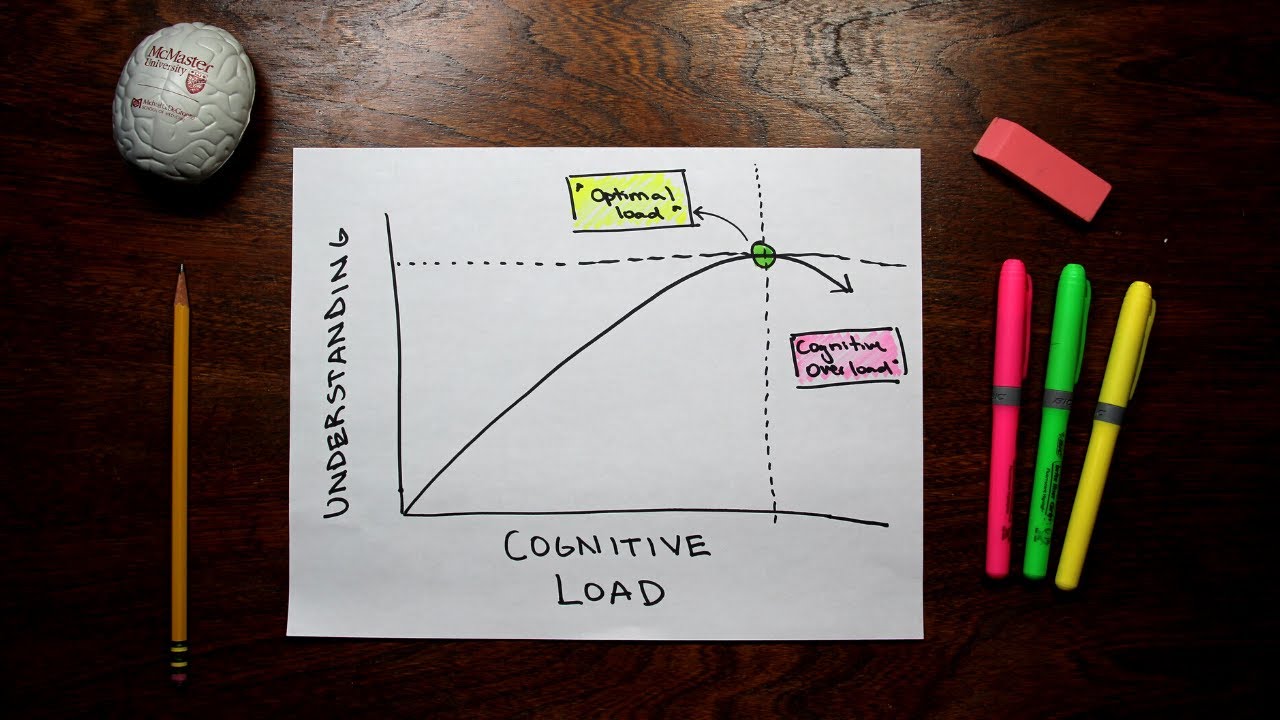
- 😀 Cognitive overload occurs when intrinsic and extraneous loads are too high, leaving no room for germane processing.
Q & A
What are the three types of cognitive load mentioned in the video?
-The three types of cognitive load are intrinsic load, extraneous load, and germane load.
How does intrinsic load affect learning?
-Intrinsic load refers to the inherent difficulty of a task, which depends on the number of novel elements and their interactivity. It is affected by the complexity of the task, the learner's expertise, and their working memory capacity.
What is the relationship between working memory and intrinsic load?
-Working memory is limited to handling 3-7 novel elements at a time, so tasks with more elements or complexity increase intrinsic load. Long-term memory, however, is virtually unlimited and can reduce intrinsic load if the learner has relevant knowledge stored.
What role does long-term memory play in cognitive load?
-Long-term memory helps reduce intrinsic load when learners have more relevant knowledge stored, as they can use this knowledge to handle more complex tasks without overloading their working memory.
What defines extraneous load in the context of instructional design?
-Extraneous load refers to the cognitive load imposed by poorly designed instructional materials or unnecessary details that do not contribute to the learning goals, such as distractions like flashy animations or irrelevant content.
How can extraneous load negatively impact learning?
-Extraneous load consumes cognitive resources that should be dedicated to learning the core material. Distractions like unnecessary anecdotes, poor fonts, or overly complex vocabulary can detract from the learning experience.
What is germane load and why is it important in learning?
-Germane load refers to the cognitive effort directed towards integrating new information with existing knowledge. It plays a key role in promoting deep understanding and meaningful learning.
How can instructional design foster germane load?
-Instructional design can foster germane load by prompting learners to connect new knowledge with prior knowledge, using strategies that encourage meaningful integration of information, such as reminders of previously studied concepts.
Why is it crucial to manage cognitive load in educational settings?
-Managing cognitive load is essential to prevent overload, which can impair learning. Balancing intrinsic, extraneous, and germane load helps ensure that learners can effectively process and integrate new information without overwhelming their cognitive capacity.
What are some practical ways to reduce extraneous load in teaching materials?
-Practical ways to reduce extraneous load include removing unnecessary details, using simple fonts and clear language, minimizing distractions like background music or animations, and ensuring that all content directly supports the learning goals.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
How I got a 4.0 GPA with COGNITIVE LOADING (Better than Active Recall) [LOW BACKGROUND MUSIC]

Cognitive Load Theory (Definition + Examples)

How to achieve more in 1 week than most people do in 3 months

TPAI Materi Pembelajaran 5: Penilaian Saham

Type of muscle contraction

Levers | Skeletal System 09 | Anatomy & Physiology
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)