Type of muscle contraction
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the three main types of muscle contractions: isotonic, isometric, and isokinetic. Isotonic contractions are divided into concentric (muscle shortens under load) and eccentric (muscle lengthens under load) types, with practical examples like bicep curls and box step-ups. Isometric contractions involve no change in muscle length, as seen in exercises like planks. Isokinetic contractions, though rare in daily life, occur when muscle length changes at a constant speed, such as in the breaststroke during swimming. The video provides clear examples to illustrate how these contractions function in various exercises and activities.
Takeaways
- 😀 Isotonic muscle contractions involve a change in muscle length during contraction without a change in load or resistance.
- 😀 Isotonic contractions are divided into two types: concentric and eccentric.
- 😀 Concentric contraction occurs when the muscle shortens under load, such as during the flexion phase of a bicep curl.
- 😀 Eccentric contraction occurs when the muscle lengthens under load, like when lowering the weight during a bicep curl.
- 😀 An example of concentric and eccentric contractions is the quadriceps during a box step-up: concentric when stepping up, eccentric when stepping down.
- 😀 Isometric muscle contraction occurs when the muscle does not change length, such as in a plank exercise where the trunk remains stable.
- 😀 Isometric contraction can also occur during exercises like the bicep curl when holding the weight without flexing or extending the elbow.
- 😀 Isokinetic muscle contraction involves muscle length changes, similar to isotonic contractions, but with the added feature of constant speed movement.
- 😀 An example of isokinetic contraction is the breaststroke in swimming, where water resistance is consistent during the arm adduction movement.
- 😀 Isokinetic contractions require special equipment, such as an isokinetic dynamometer, to maintain constant speed during contraction.
Q & A
What are the three general types of muscle contractions?
-The three general types of muscle contractions are isotonic, isometric, and isokinetic.
What is characteristic of an isotonic muscle contraction?
-An isotonic muscle contraction is characterized by a change in muscle length during contraction without a change in load or resistance.
What are the two types of isotonic muscle contractions?
-The two types of isotonic muscle contractions are concentric contraction and eccentric contraction.
What happens during concentric muscle contraction?
-During concentric muscle contraction, the muscle shortens under load. For example, during a bicep curl, the biceps contract and shorten as the elbow flexes.
Can you provide an example of eccentric muscle contraction?
-An example of eccentric muscle contraction occurs when you lower your elbow during a bicep curl. In this phase, the biceps lengthen under load.
How does eccentric contraction help in exercises like box step-ups?
-In exercises like box step-ups, eccentric contraction occurs when the quadriceps lengthen under load as you step down, which helps to control the movement and prevent injury by resisting the downward force.
What is the defining feature of isometric muscle contraction?
-In isometric muscle contraction, there is no change in muscle length during contraction. The muscle remains static, like when holding a plank position.
What is an example of isometric contraction using the bicep curl?
-In a bicep curl, isometric contraction occurs if you stop during the movement and hold the weight still without flexing or extending the elbow.
What differentiates isokinetic muscle contraction from isotonic muscle contraction?
-Isokinetic muscle contraction, like isotonic, involves a change in muscle length during contraction. However, isokinetic contractions occur at a constant speed of movement, unlike isotonic contractions that may vary in speed.
What is the most common example of isokinetic muscle contraction?
-The best-known example of isokinetic muscle contraction is the breaststroke in swimming, where the water provides a consistent, even resistance during the adduction movement.
What equipment is necessary for isokinetic muscle contraction?
-An isokinetic dynamometer system is required to produce and measure isokinetic muscle contractions.
How do the three types of muscle contractions differ in terms of muscle length change?
-In isotonic contraction, the muscle changes length (either shortening in concentric or lengthening in eccentric); in isometric contraction, the muscle remains the same length; and in isokinetic contraction, the muscle changes length at a constant speed.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Muscle Contraction Types
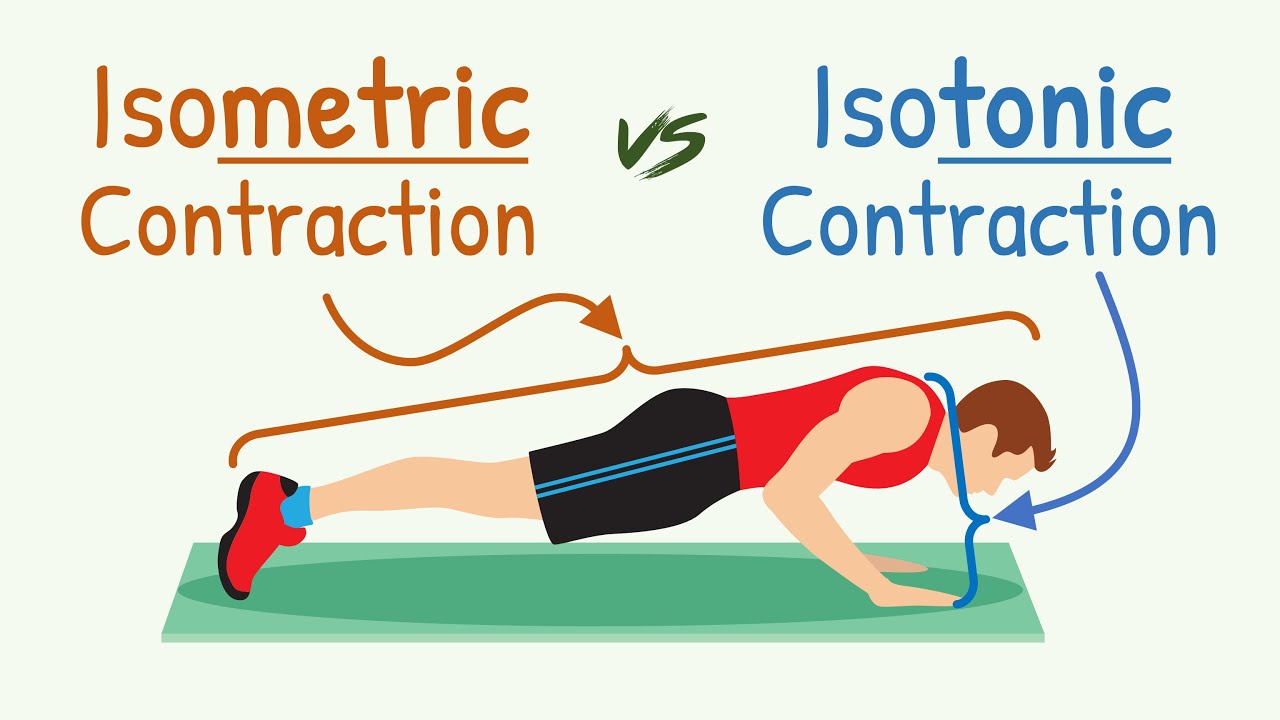
Isometric Contraction vs Isotonic Contraction || Physiology with Animation

Isotonic, Isometric, Eccentric and Concentric Muscle Contractions
Muscles, Part 2 - Organismal Level: Crash Course Anatomy & Physiology #22

Exercise Physiology | Skeletal Muscle Force-Velocity Relationship
Muscular system - Anatomical terminology for healthcare professionals | Kenhub
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)