Fotorespirasi
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the concept of photorespiration in plants, a process that occurs when high temperatures and low carbon dioxide levels lead to inefficiencies in photosynthesis. The enzyme rubisco, which typically fixes carbon dioxide, instead binds oxygen during photorespiration, releasing carbon dioxide and reducing photosynthetic efficiency. While harmful in terms of energy loss, photorespiration can help protect plants from excessive light damage and maintain cellular balance. The script also highlights the higher efficiency of C4 plants in hot, dry climates, which avoid photorespiration, making them better suited for such environments.
Takeaways
- 😀 Photorespiration is a negative process in plants that leads to a loss of carbon and energy during photosynthesis.
- 😀 Rubisco, an enzyme in plants, plays a central role in both photosynthesis and photorespiration by fixing carbon dioxide, but can also bind to oxygen under certain conditions.
- 😀 High temperatures and water stress increase the likelihood of photorespiration in plants, especially C3 plants.
- 😀 Photorespiration occurs when Rubisco starts fixing oxygen instead of carbon dioxide, which reduces the efficiency of photosynthesis by 50-90%.
- 😀 During photorespiration, the plant releases carbon dioxide, similar to cellular respiration, making it an energy-wasting process.
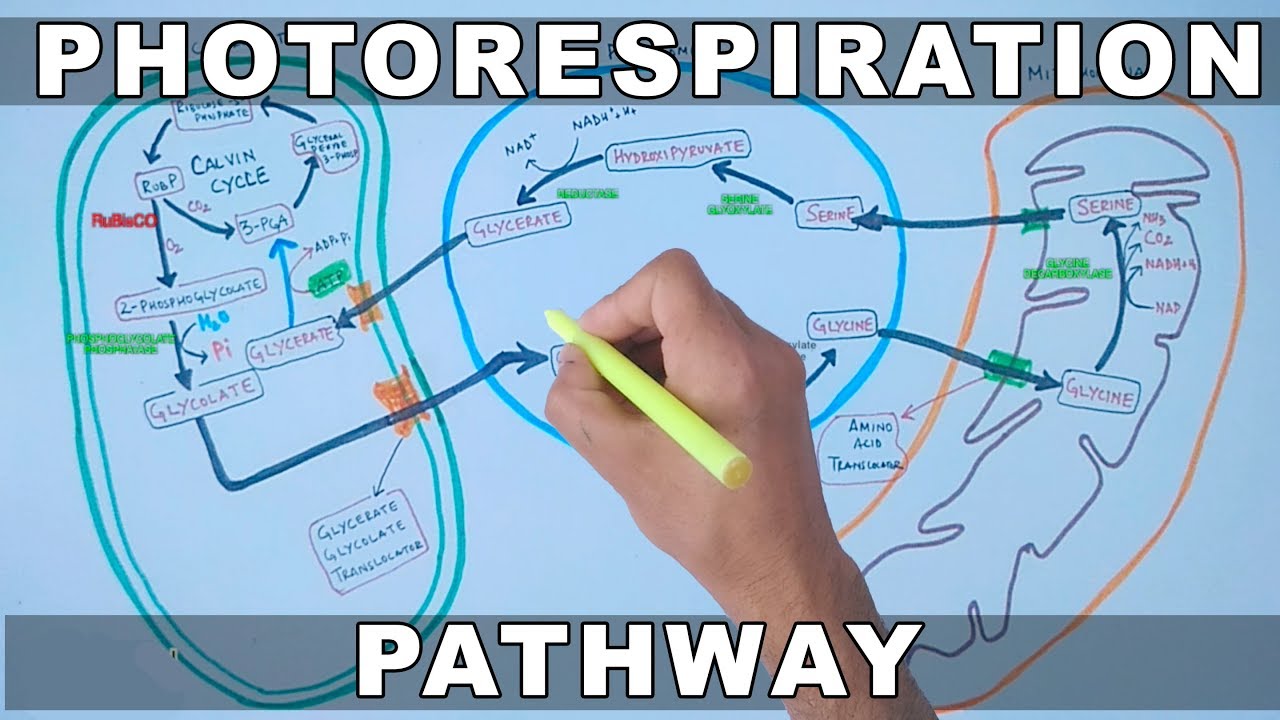
- 😀 The process of photorespiration involves multiple organelles: chloroplasts, peroxisomes, and mitochondria.
- 😀 C3 plants, under normal conditions, can perform photosynthesis efficiently, but in hot and dry environments, photorespiration reduces their effectiveness.
- 😀 In C4 and CAM plants, photorespiration is avoided, allowing them to perform photosynthesis more efficiently in hot and dry climates.
- 😀 Despite its drawbacks, photorespiration provides photoprotection, helping to prevent damage from excess light energy and maintain cellular redox balance.
- 😀 Photorespiration is considered a trade-off, where plants lose some carbon fixation potential but gain protection against environmental stressors.
- 😀 The efficiency of photosynthesis in C3 plants can drop significantly (up to 90%) due to photorespiration, especially under unfavorable environmental conditions.
Q & A
What is photorespiration and how does it differ from normal respiration?
-Photorespiration is a process where the enzyme Rubisco binds oxygen instead of carbon dioxide, leading to inefficient carbon fixation in photosynthesis. Unlike normal respiration, which involves oxygen uptake and carbon dioxide release for energy production, photorespiration wastes energy and carbon by involving oxygen and producing carbon dioxide in the process.
Why is photorespiration considered a negative process for plants?
-Photorespiration is considered negative because it results in the loss of up to 50% of the fixed carbon, using light energy inefficiently. This reduces the overall efficiency of photosynthesis and can decrease the plant's ability to synthesize carbohydrates.
Under what conditions does photorespiration become more problematic for plants?
-Photorespiration becomes more problematic when environmental conditions are hot and dry. In such conditions, plants close their stomata to conserve water, which limits the entry of carbon dioxide and increases the likelihood of Rubisco binding oxygen instead of carbon dioxide.
How does the closure of stomata affect photorespiration?
-When stomata close to prevent water loss during hot and dry conditions, the concentration of carbon dioxide inside the leaf decreases. This leads to Rubisco preferentially binding oxygen, initiating photorespiration, which reduces the efficiency of carbon fixation.
What is the role of Rubisco in photorespiration?
-Rubisco is the enzyme responsible for fixing carbon dioxide in the Calvin cycle. However, during photorespiration, Rubisco mistakenly binds oxygen instead of carbon dioxide, leading to the production of waste products and a decrease in the efficiency of photosynthesis.
What organelles are involved in the photorespiration process?
-Photorespiration involves three main organelles: chloroplasts, peroxisomes, and mitochondria. These organelles work together to process the waste products of photorespiration and attempt to recover some of the carbon, though the process is still inefficient.
How does photorespiration impact the efficiency of photosynthesis?
-Photorespiration decreases the efficiency of photosynthesis by diverting energy and carbon away from the Calvin cycle. Instead of producing carbohydrates, photorespiration results in the loss of fixed carbon and energy, reducing the plant's overall productivity.
Can photorespiration have any positive effects on plants?
-Yes, despite its inefficiency, photorespiration has some positive effects. It serves as a form of photoprotection, preventing damage to the molecules involved in photosynthesis and respiration under high light conditions. Additionally, it helps maintain redox balance in plant cells.
What are C4 plants and how do they avoid photorespiration?
-C4 plants have a specialized carbon fixation pathway that helps them avoid photorespiration. They concentrate carbon dioxide in specialized cells, allowing Rubisco to work more efficiently even in hot and dry conditions, thus preventing photorespiration.
How does photorespiration contribute to the release of carbon dioxide?
-During photorespiration, Rubisco binds oxygen, leading to the oxidation of ribulose bisphosphate into 3-phosphoglycerate and phosphoglycolate. These molecules enter a metabolic pathway that ultimately releases carbon dioxide, similar to the process of cellular respiration.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)