FOTORESPIRASI
Summary
TLDRThe script delves into the process of photorespiration in plants, explaining its definition, mechanisms, and effects. Photorespiration is a form of respiration that occurs during the day when plants are exposed to sunlight. It is initiated by the enzyme Rubisco, which can bind to both oxygen and carbon dioxide, leading to the breakdown of carbohydrates. While photorespiration helps in protecting plants from excessive light and contributes to the formation of amino acids, it is considered inefficient due to energy loss. The script also contrasts photorespiration with regular respiration and highlights differences between C3, C4, and CAM plants.
Takeaways
- 😀 Photorespiration occurs in plants during the daytime and is driven by sunlight. It is a type of respiratory process that involves oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange.
- 😀 The process begins when the enzyme Rubisco binds with oxygen instead of carbon dioxide, leading to the formation of CO2, similar to respiration in plants.
- 😀 Unlike normal respiration, photorespiration occurs when there is more oxygen in the mesophyll than carbon dioxide, especially when stomata are closed to reduce water loss.
- 😀 Photorespiration is a form of energy consumption that is often considered inefficient, as it consumes energy without producing much usable energy for the plant.
- 😀 The main enzyme involved in photorespiration is Rubisco, which can bind either with carbon dioxide or oxygen, and its binding with oxygen leads to photorespiration.
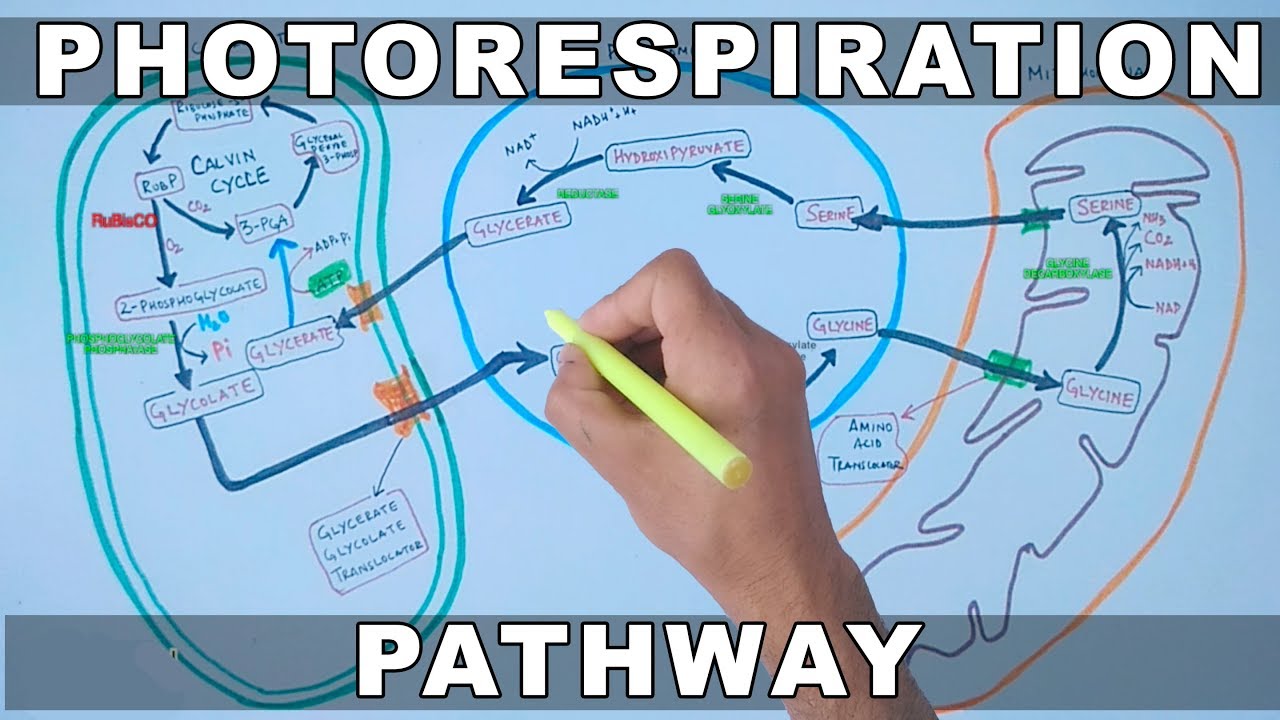
- 😀 In photorespiration, the breakdown of the carbon compound RubP occurs, leading to the formation of both 3-phosphoglycerate and 2-phosphoglycolate.
- 😀 The pathway of photorespiration involves various organelles like peroxisomes and mitochondria, which help process the byproducts like glyoxylate and convert them into useful compounds like glycine.
- 😀 One of the main differences between photorespiration and photosynthesis is the substrate binding preference of Rubisco: it binds oxygen during photorespiration, whereas it binds carbon dioxide during photosynthesis.
- 😀 C4 plants are more efficient in reducing photorespiration compared to C3 plants due to the use of the enzyme PEP carboxylase, which preferentially binds carbon dioxide.
- 😀 Photorespiration is influenced by factors like oxygen and carbon dioxide ratios, light intensity, temperature, and the net photosynthetic rate. Increased oxygen can accelerate photorespiration, while increased light intensity can also heighten its rate.
Q & A
What is photorespiration?
-Photorespiration is a process that occurs in plants during daylight when oxygen is taken up instead of carbon dioxide by the enzyme rubisco. This leads to the production of carbon dioxide and a reduced efficiency of photosynthesis.
How does photorespiration differ from regular respiration in plants?
-Photorespiration differs from regular respiration because it involves oxygen being bound by rubisco instead of carbon dioxide, leading to the production of carbon dioxide and ammonia, whereas regular respiration uses organic substrates to produce energy and does not involve the intake of light.
What factors influence the rate of photorespiration?
-The rate of photorespiration is influenced by the oxygen-to-carbon dioxide ratio in the leaf cells, the intensity of light, temperature, and the net photosynthesis rate of the plant.
Why is photorespiration considered wasteful for plants?
-Photorespiration is considered wasteful because it consumes energy and reduces the efficiency of photosynthesis by using up CO2 and O2 in a less productive process, leading to energy loss.
How do plants C4 and CAM reduce photorespiration?
-C4 and CAM plants reduce photorespiration by utilizing alternative mechanisms to concentrate CO2 in their cells, using enzymes like PEP carboxylase, which is more efficient than rubisco in binding CO2, especially in high-oxygen conditions.
What happens when rubisco binds with oxygen during photorespiration?
-When rubisco binds with oxygen, it leads to the formation of a molecule of phosphoglycolate, which is broken down into two molecules: 3-phosphoglycerate for the Calvin cycle and 2-phosphoglycolate, which undergoes a series of reactions involving peroxisomes and mitochondria.
What are the main steps involved in the photorespiration process?
-The main steps in photorespiration include rubisco binding with oxygen, the breakdown of rubp (ribulose bisphosphate) into 3-phosphoglycerate and 2-phosphoglycolate, the conversion of phosphoglycolate into glycolate, the transportation of glycolate to peroxisomes for further processing, and the eventual recycling of the products for use in the Calvin cycle.
What role do peroxisomes and mitochondria play in photorespiration?
-Peroxisomes help convert toxic hydrogen peroxide produced during photorespiration into water and oxygen, while mitochondria assist in converting glyoxylate into glycine, which is then used for protein synthesis.
How does temperature affect photorespiration?
-As temperature increases, both aerobic respiration and photorespiration rates also increase. This is because higher temperatures enhance the oxygenation activity of rubisco, making photorespiration more likely.
What are the functions of photorespiration in plants?
-Photorespiration helps protect plants from excessive light exposure by reducing potential damage from too much light. It also provides an alternative source of carbon dioxide and ammonia for assimilation, generates energy for plant growth, and aids in the production of amino acids like serine and glycine.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)