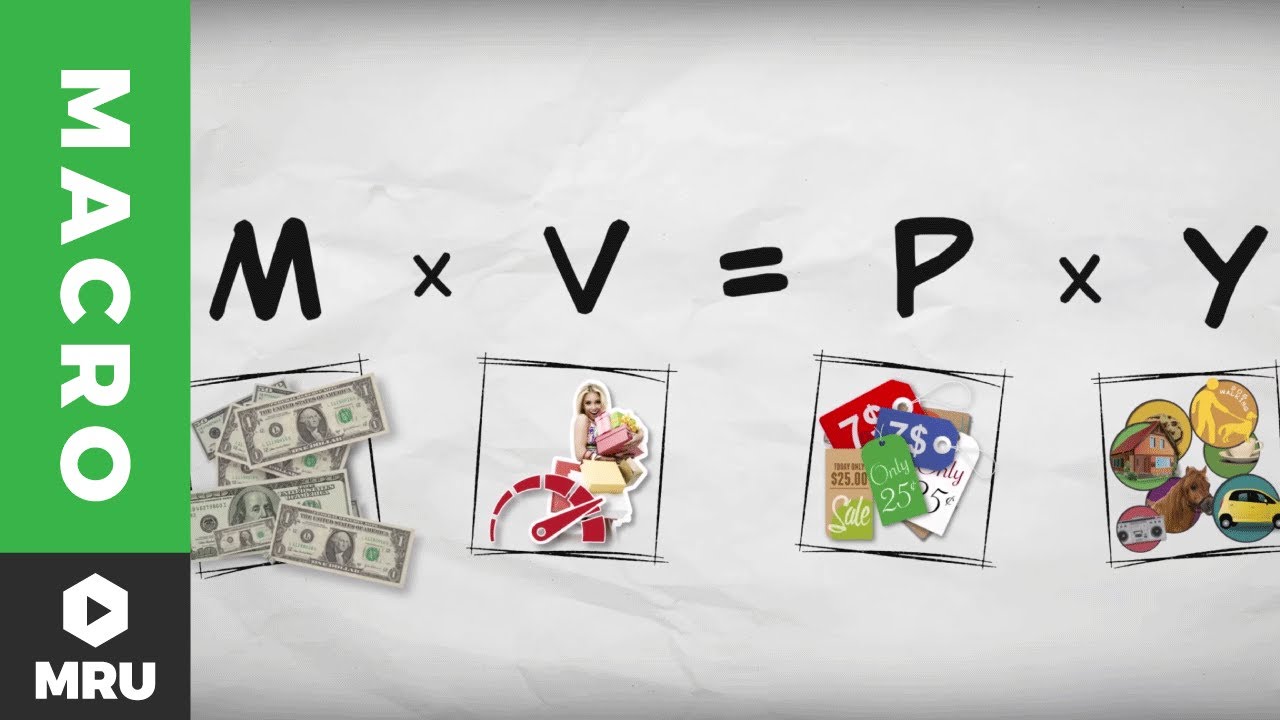Quantity Theory of Money - Fisher Equation
Summary
TLDRThe video explains the Quantity Theory of Money, highlighting how monetarists like Milton Friedman believe inflation is caused by changes in the money supply. It breaks down the Fisher Equation (MV = PQ) to show the relationship between money supply, velocity, price level, and real GDP. Monetarists argue that velocity and GDP are stable over time, leaving the money supply as the main driver of inflation. Keynesians, however, challenge this view, especially in recessions, where the velocity of money may decrease and reduce the impact of increased money supply on inflation. The debate continues to shape economic perspectives on inflation.
Takeaways
- 😀 The quantity theory of money links the growth rate of the money supply to inflation (price growth).
- 😀 This theory has been around for centuries, with significant contributions in the 20th century from economists like Irving Fisher and Milton Friedman.
- 😀 Monetarists believe inflation is caused solely by changes in the money supply and see it as a primary cause of inflation.
- 😀 The Fisher equation (MV = PQ) represents the relationship between the money supply, velocity of circulation, price level, and real GDP.
- 😀 'M' represents the money supply, 'V' is the velocity of circulation, 'P' is the price level (inflation rate), and 'Q' is real GDP (quantity of goods and services produced).
- 😀 Monetarists argue that the velocity of circulation ('V') and real GDP ('Q') remain relatively constant and do not significantly influence inflation.
- 😀 According to monetarists, the change in inflation can only be caused by changes in the money supply (M), not by 'V' or 'Q'.
- 😀 Keynesians disagree, arguing that 'V' and 'Q' are not fixed and can fluctuate significantly, especially in times of recession or boom.
- 😀 In a recession, an increase in the money supply may not lead to higher inflation if the velocity of circulation drops (e.g., due to a liquidity trap or reduced spending).
- 😀 The ongoing debate between monetarists and Keynesians highlights the complexity of understanding inflation, with each side providing differing views based on economic conditions.
Q & A
What is the Quantity Theory of Money?
-The Quantity Theory of Money is a theory that links the growth rates in the money supply to the growth rates in prices (inflation). It suggests that inflation is primarily caused by changes in the money supply.
Who were the economists that revived the Quantity Theory of Money in the 20th century?
-The theory was revitalized by economists like Irving Fisher and monetarists such as Milton Friedman.
What does the Fischer equation, MV=PQ, represent?
-The Fischer equation links the money supply (M), the velocity of circulation (V), the average price level (P), and the quantity of goods and services (Q) in the economy. It helps to explain the relationship between money supply and inflation.
What do the variables in the Fischer equation stand for?
-In the Fischer equation, M represents the money supply, V is the velocity of circulation (the number of times money changes hands), P is the average price level (inflation), and Q is the quantity of goods and services sold (real GDP).
According to monetarists, what is the primary cause of inflation?
-Monetarists argue that the primary cause of inflation is changes in the money supply, not other factors such as changes in velocity or real GDP.
How do monetarists view the impact of velocity (V) and real GDP (Q) on inflation?
-Monetarists believe that velocity (V) and real GDP (Q) are relatively fixed over time and do not fluctuate enough to significantly influence inflation. Therefore, inflation is mainly influenced by changes in the money supply (M).
What is the Keynesian criticism of the Quantity Theory of Money?
-Keynesians argue that the assumption that velocity (V) and real GDP (Q) are fixed is unrealistic. They point out that during a recession, the velocity of money can decrease, and an increase in the money supply may not lead to higher inflation.
What is a liquidity trap, and how does it relate to the Quantity Theory of Money?
-A liquidity trap occurs when an increase in the money supply does not result in more transactions, as the money is hoarded, often by banks. Keynesians argue that this can occur during recessions, preventing the money supply from influencing inflation as the Quantity Theory suggests.
What evidence do monetarists use to support their view on inflation?
-Monetarists use historical data to show that changes in the money supply correlate closely with changes in inflation. They argue that the velocity of circulation and real GDP remain relatively stable over time and do not deviate enough to influence inflation significantly.
Why is the Quantity Theory of Money still debated among economists?
-The theory remains debated because of differing views on the role of velocity and real GDP in influencing inflation, especially during recessions. Keynesians challenge the idea that these factors are fixed and argue that changes in the money supply do not always lead to higher inflation.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)