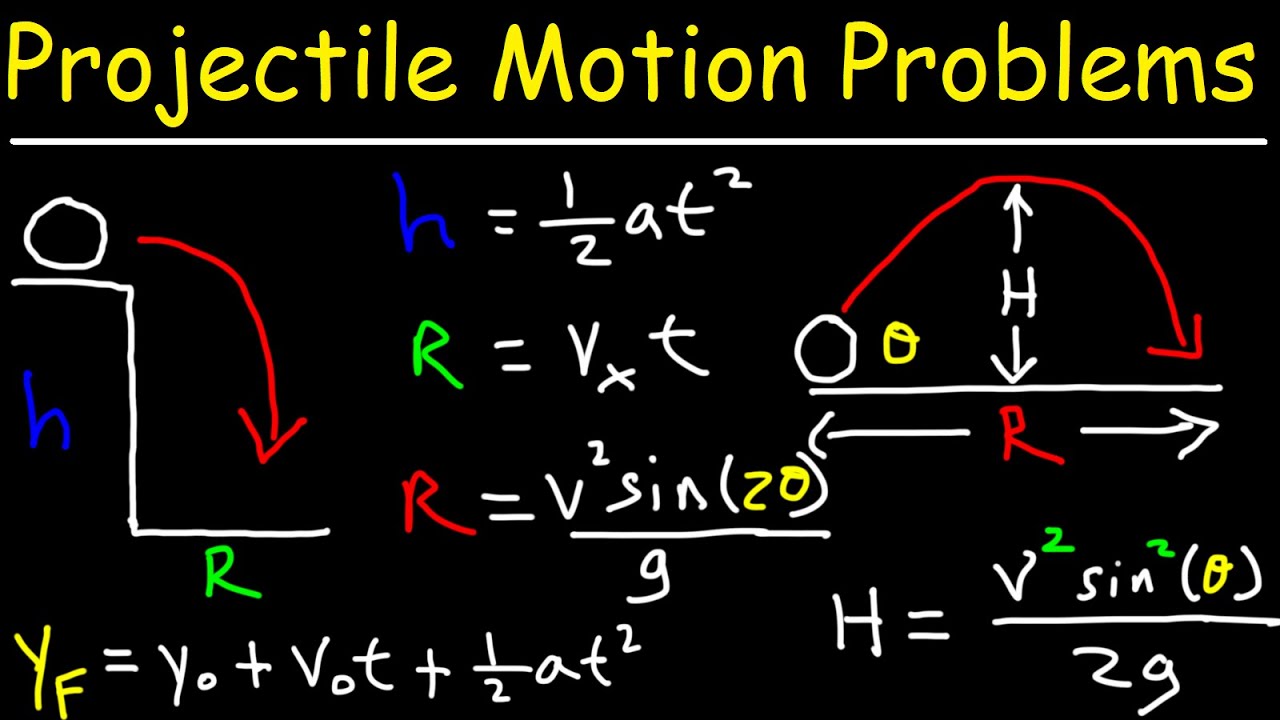
Projectile Motion: Finding the Maximum Height and the Range
Summary
TLDRThis video explains projectile motion, focusing on launching an object at an angle (Theta) with an initial velocity (V0). It breaks down the motion into independent x and y components, detailing how to calculate displacement and velocity in each direction. The constant acceleration due to gravity is highlighted, leading to the derivation of key equations for maximum height and range. The video emphasizes the symmetry of projectile motion, particularly around the peak height, and provides clear formulas to analyze the motion effectively. Overall, it serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding the dynamics of projectiles.
Please replace the link and try again.
Q & A
What is the significance of separating motion into x and y components in projectile motion?
-Separating motion into x and y components allows us to analyze each direction independently, simplifying calculations and understanding the effects of gravity only on the vertical motion.
How do we define the initial velocity components of a projectile launched at an angle?
-The initial velocity components are defined as: V₀x = V₀ cos(Theta) for the x-direction and V₀y = V₀ sin(Theta) for the y-direction.
What role does gravity play in projectile motion?
-Gravity provides a constant acceleration in the y-direction, affecting the vertical motion of the projectile, while there is no acceleration in the x-direction.
What is the equation for displacement in the x-direction?
-The displacement in the x-direction is given by Δx = V₀x * t, where V₀x is the initial velocity in the x-direction and t is the time.
How is maximum height determined in projectile motion?
-Maximum height is determined when the y-component of velocity equals zero; using the equation for y-displacement, we can find it by substituting the time to reach the peak.
What happens to the y-component of velocity as the projectile reaches its peak?
-As the projectile reaches its peak, the y-component of velocity decreases to zero, indicating a momentary halt before descending.
What is the formula for the range of a projectile?
-The range (R) of a projectile is calculated using the formula R = (V₀² sin(2Theta)) / g, where g is the acceleration due to gravity.
Why is the motion of a projectile considered symmetric?
-Projectile motion is symmetric because the time taken to ascend to the peak equals the time taken to descend back to the original launch height.
How does the angle of launch affect the maximum height and range of a projectile?
-The angle of launch affects both maximum height and range; a launch angle of 90 degrees maximizes height, while an angle of 45 degrees maximizes range.
What key factors must be considered when analyzing projectile motion?
-Key factors include initial velocity, launch angle, acceleration due to gravity, and the independence of x and y motion.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Projectile Motion Part II | Quarter 4 Grade 9 Science Week 2 Lesson

PROJECTILE MOTION | Physics Animation
How To Solve Projectile Motion Problems In Physics
Two Dimensional Motion (4 of 4) Horizontal Projection, Worked Example
Gerak Parabola • Part 2: Contoh Soal Gerak Parabola Dimulai dari Tanah
12-88 | Engineering Dynamics Hibbeler 14th Edition | Engineers Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)