Respiración celular: Crash Course Biología #27
Summary
TLDRIn this Crash Course Biology episode, the focus is on cellular respiration, the essential process that generates energy for all aerobic organisms. The video explains how mitochondria, often called the 'engines of the cell,' convert food and oxygen into ATP, the energy currency of cells. The process is broken down into three stages: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Through complex biochemical reactions, cells produce ATP to maintain homeostasis and power various bodily functions. The episode highlights the speed and efficiency of these processes and concludes by praising the mitochondria for fueling the body's activities.
Takeaways
- 😀 Mitochondria are the 'engines' of the cell, converting food and oxygen into the energy needed to perform various functions.
- 😀 Cellular respiration is the process by which cells use food and oxygen to produce energy in the form of ATP.
- 😀 ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is like a rechargeable battery, providing energy for essential cellular functions and maintaining homeostasis.
- 😀 Humans and many organisms are aerobic, meaning they need oxygen for energy production, whereas some organisms can use anaerobic processes.
- 😀 Cellular respiration can be compared to a series of connected reactions, like a Rube Goldberg machine, where each step activates the next.
- 😀 The process of cellular respiration involves three main stages: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
- 😀 Glycolysis, occurring in the cytoplasm, breaks down glucose into pyruvate, producing small amounts of ATP and NADH.
- 😀 The citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) occurs in the mitochondria and further breaks down pyruvate, releasing carbon dioxide and producing additional ATP and NADH.
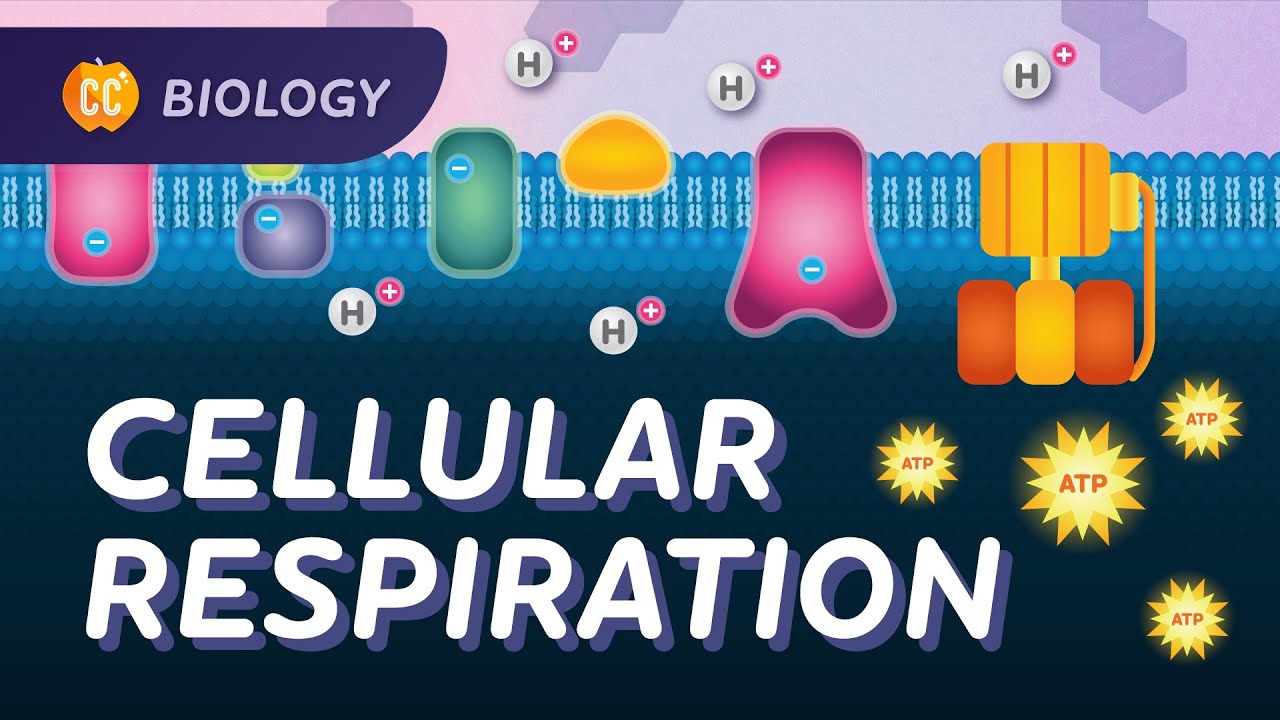
- 😀 In oxidative phosphorylation, electrons from NADH and FADH2 travel through the electron transport chain, helping create a proton gradient that drives ATP production.
- 😀 The process of generating ATP through the movement of protons is similar to how water flows through a hydroelectric dam to generate electricity.
- 😀 Cellular respiration is a highly efficient process, generating around 30 ATP molecules from one glucose molecule, powering cellular functions and keeping our bodies energized.
Q & A
What is the role of mitochondria in a cell?
-Mitochondria are the 'engines' of cells, responsible for converting the energy from food and oxygen into the energy needed for cellular functions, including processes like texting or running a marathon.
What molecule stores energy in the human body?
-ATP (adenosine triphosphate) stores energy in the human body. It acts like a rechargeable battery, powering many critical cellular processes.
How does cellular respiration relate to ATP production?
-Cellular respiration is the process by which cells break down food and oxygen to produce ATP, which is the energy currency used in numerous cellular functions. ATP is continuously recycled during this process.
What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic organisms?
-Aerobic organisms, like humans, require oxygen for survival and energy production, while anaerobic organisms, such as some bacteria, can produce energy without oxygen through processes like anaerobic respiration.
What happens during glycolysis?
-During glycolysis, glucose, a simple sugar, is broken down in the cytoplasm to produce two molecules of pyruvate, two ATP molecules, and two NADH molecules, initiating the conversion of glucose into usable energy.
What is the Krebs Cycle, and where does it occur?
-The Krebs Cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle, occurs in the mitochondria. It processes two-carbon molecules derived from pyruvate to produce ATP, NADH, FADH2, and carbon dioxide.
What role does NADH and FADH2 play in cellular respiration?
-NADH and FADH2 are electron carriers that transport electrons to the electron transport chain during oxidative phosphorylation, ultimately helping to produce a large amount of ATP.
How does the electron transport chain generate ATP?
-The electron transport chain uses energy from electrons to pump protons across the mitochondrial membrane, creating a proton gradient. The flow of protons back through ATP synthase drives the production of ATP.
Why is oxygen important in cellular respiration?
-Oxygen is essential in cellular respiration because it acts as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, allowing for the production of water and facilitating the production of ATP.
How much ATP is generated from one molecule of glucose?
-One molecule of glucose can generate around 30 molecules of ATP through cellular respiration, specifically through the processes of glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)