Graph of Linear Equations Using Slope Intercept (Part 1)
Summary
TLDRThis video tutorial explains how to graph linear equations using the slope-intercept form (y = mx + b). It details the process of rewriting equations to identify the slope (m) and y-intercept (b), followed by systematic steps to graph these equations on a Cartesian plane. The instructor provides several examples, illustrating how to plot points and draw lines based on calculated slopes and intercepts. The tutorial concludes with practice problems, reinforcing the techniques learned, making it accessible for learners to apply these concepts independently.
Takeaways
- 😀 Understanding how to convert equations into slope-intercept form (y = mx + b) is crucial for graphing linear equations.
- 😀 To rewrite an equation like 2x + y = 6 into slope-intercept form, isolate y to find the slope (m) and y-intercept (b).
- 😀 The slope-intercept form allows easy identification of slope and y-intercept, aiding in graphing.
- 😀 When graphing, first identify the slope and y-intercept from the equation.
- 😀 Plot the y-intercept on the Cartesian plane before using the slope to find additional points.
- 😀 Slope is represented as rise over run; a positive slope means moving up and to the right, while a negative slope means moving down.
- 😀 For horizontal lines (e.g., y = 3), the slope is zero, resulting in a flat line across the y-axis.
- 😀 It's important to label your graphs correctly to indicate the equation represented.
- 😀 Practice by graphing different equations using the slope-intercept method to solidify understanding.
- 😀 Questions and clarifications during the learning process are encouraged to enhance comprehension.
Q & A
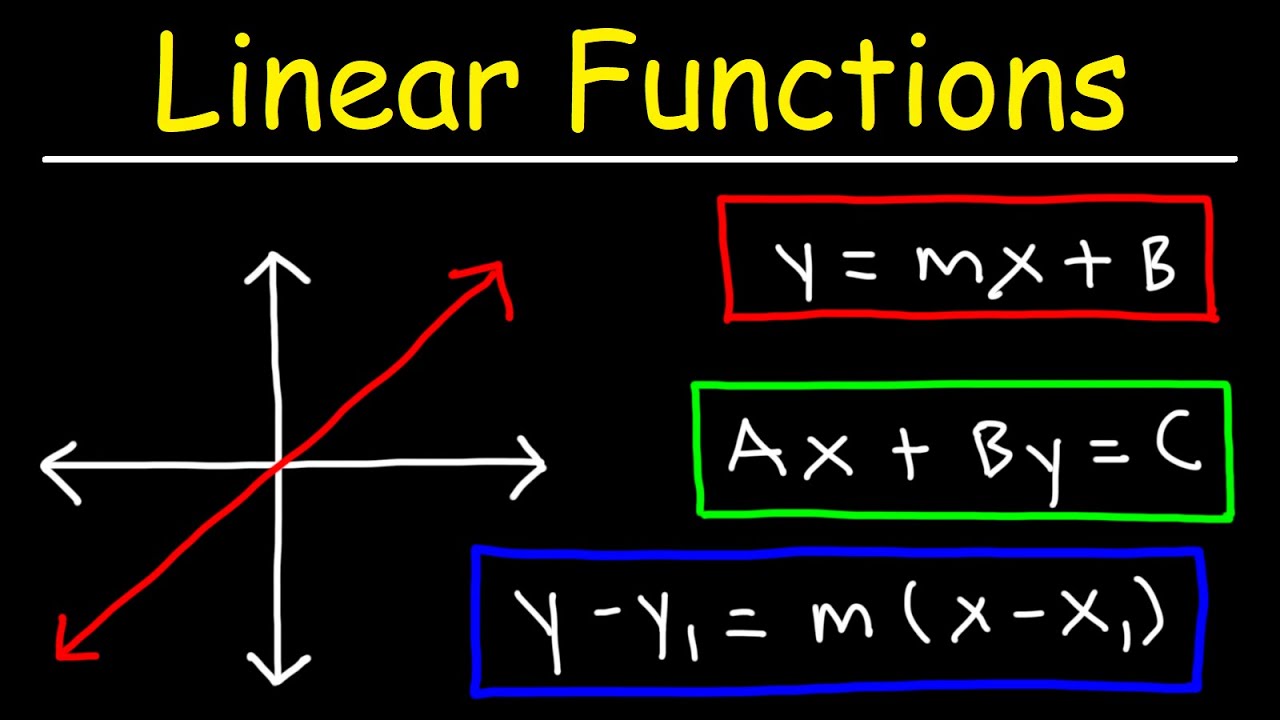
What is the slope-intercept form of a linear equation?
-The slope-intercept form is expressed as y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept.
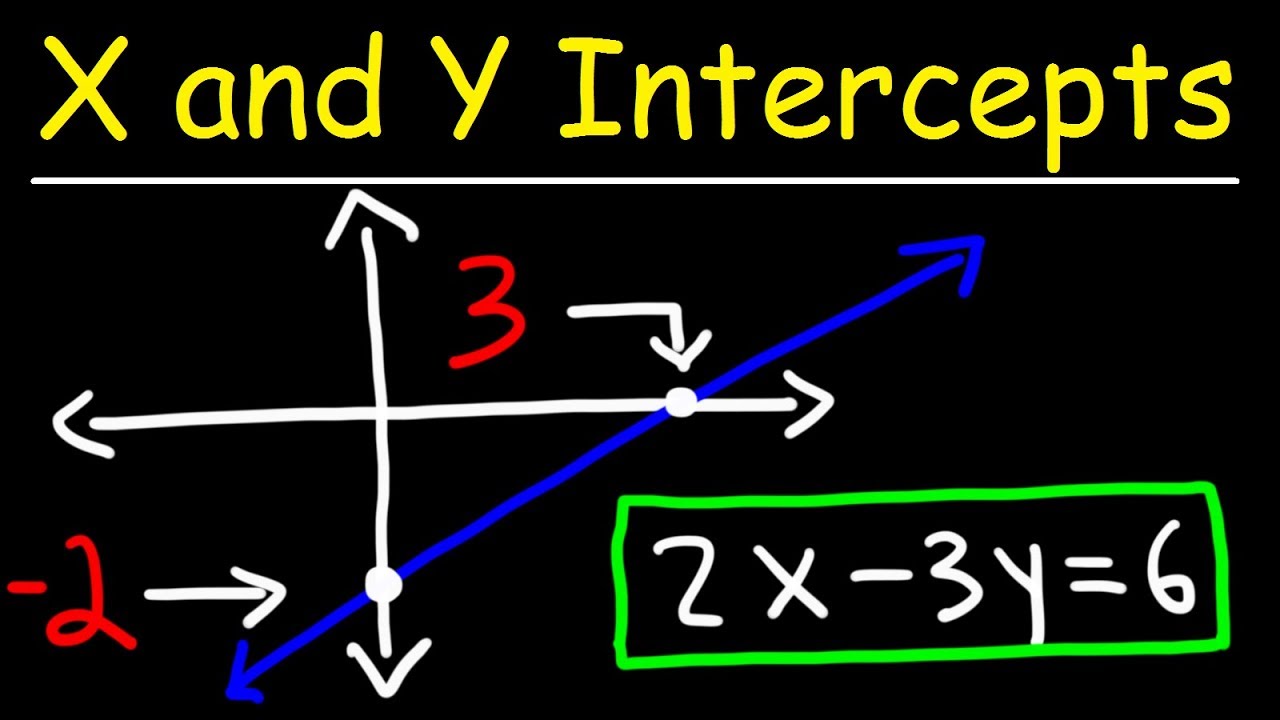
How do you convert the equation 2x + y = 6 into slope-intercept form?
-To convert 2x + y = 6 into slope-intercept form, isolate y: y = -2x + 6. Here, the slope m is -2 and the y-intercept b is 6.
What does the slope represent in a linear equation?
-The slope (m) represents the rate of change of y with respect to x, indicating how steep the line is.
How do you graph a linear equation using its slope and y-intercept?
-First, plot the y-intercept (0, b) on the Cartesian plane, then use the slope (rise/run) to find another point, and connect the points with a line.
For the equation y = 3, what is the slope and how is it graphed?
-The slope is 0 since there is no x term. It is graphed as a horizontal line at y = 3.
What is the importance of finding the y-intercept when graphing a linear equation?
-Finding the y-intercept allows you to identify a starting point on the graph, which is essential for plotting the line accurately.
How do you interpret the slope of -4/3 in the equation y = -4/3x + 5?
-A slope of -4/3 indicates that for every 4 units the line drops down, it moves 3 units to the right.
In the equation y = x + 2, what are the values of m and b?
-In this equation, m (slope) is 1 and b (y-intercept) is 2.
What are the steps to graph the equation y = -3x - 3?
-First, identify the slope m = -3 and y-intercept b = -3. Plot the point (0, -3), then use the slope to find another point by moving down 3 units and right 1 unit, then connect the points.
What should you do after plotting two points on a graph?
-After plotting the points, connect them with a straight line and add arrows on both ends to indicate that the line extends infinitely.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)